Sources of Finance
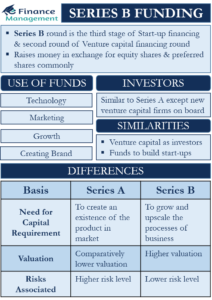
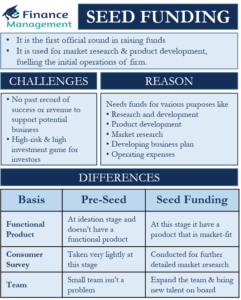
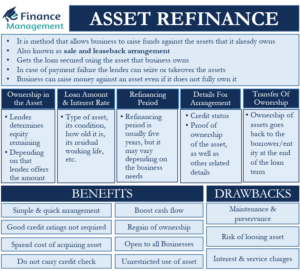
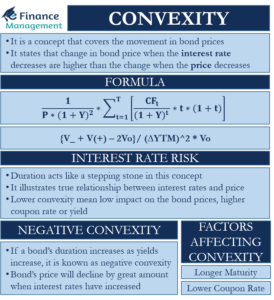
Sources of finance for business are equity, debt, debentures, retained earnings, term loans, working capital loans, letter of credit, euro issue, venture funding, etc. These sources of funds are used in different situations. They are classified based on time period, ownership and control, and their source of generation. It is ideal to evaluate each source of capital before opting for it.
Sources of capital are the most explorable area, especially for the entrepreneurs who are about to start a new business. It is perhaps the most challenging part of all the efforts. There are various capital sources we can classify on the basis of different parameters.
Knowing that there are many alternatives to finance or capital a company can choose from. Choosing the right source and the right mix of finance is a crucial challenge for every finance manager. Selecting the right source of finance involves an in-depth analysis of each source of fund. For analyzing and comparing the sources, it needs an understanding of all the characteristics of the financing sources. There are many characteristics on the basis of which sources of finance are classified.
On the basis of a time period, sources are classified as long-term, medium-term, and short-term. Ownership and control classify sources of finance into owned and borrowed capital. Internal sources and external sources are the two sources of generation of capital. All the sources have different characteristics to suit different types of requirements. Let’s understand them in a bit of depth.
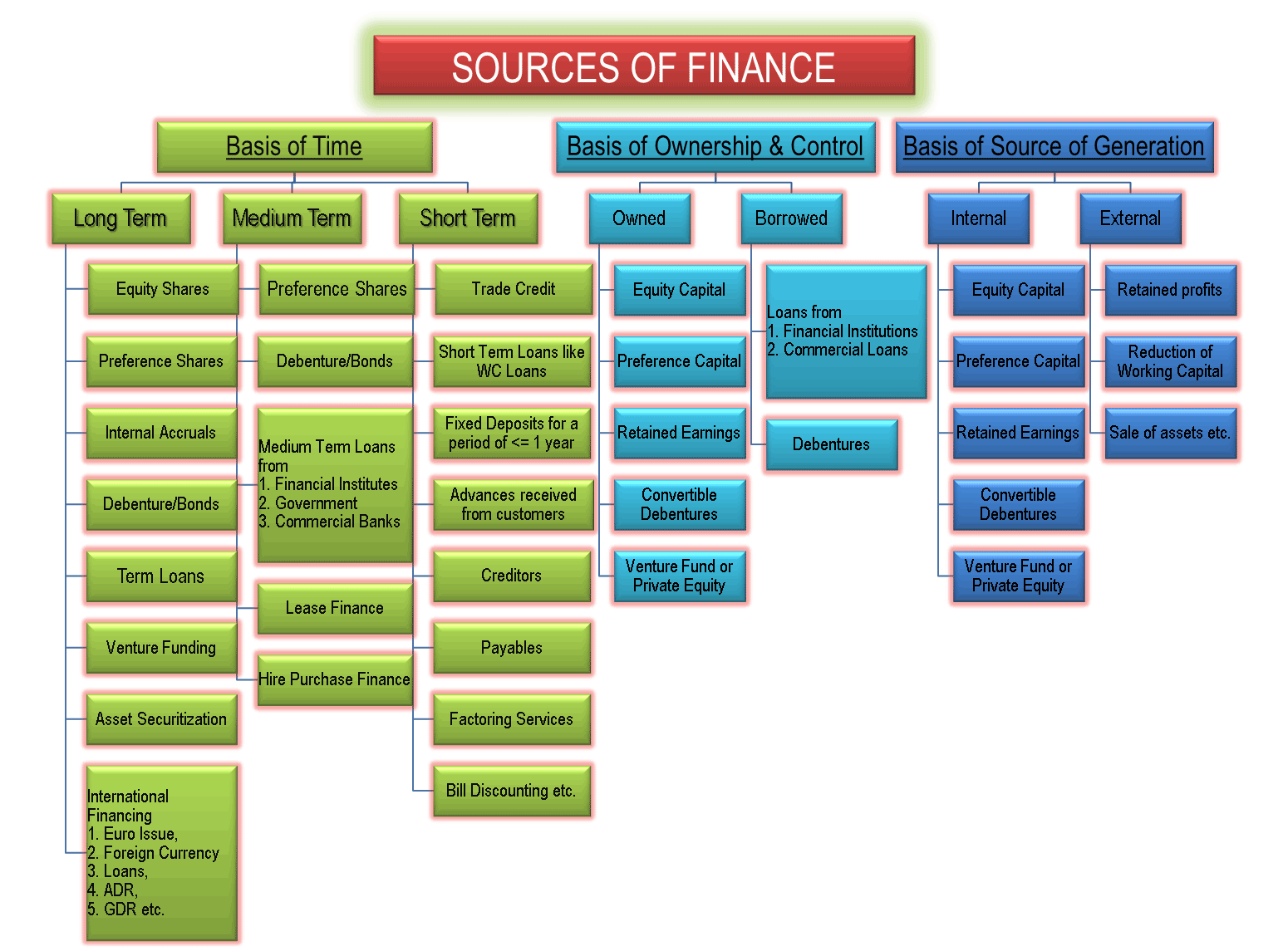
According to Time Period
Sources of financing a business are classified based on the time period for which the money is required. The time period is commonly classified into the following three:
| LONG TERM SOURCES OF FINANCE / FUNDS | MEDIUM TERM SOURCES OF FINANCE / FUNDS | SHORT TERM SOURCES OF FINANCE / FUNDS |
| Share Capital or Equity Shares | Preference Capital or Preference Shares | Trade Credit |
| Preference Capital or Preference Shares | Debenture / Bonds | Factoring Services |
| Retained Earnings or Internal Accruals | Lease Finance | Bill Discounting etc. |
| Debenture / Bonds | Hire Purchase Finance | Advances received from customers |
| Term Loans from Financial Institutes, Government, and Commercial Banks | Medium Term Loans from Financial Institutes, Government, and Commercial Banks | Short Term Loans like Working Capital Loans from Commercial Banks |
| Venture Funding | Fixed Deposits (<1 Year) | |
| Asset Securitization | Receivables and Payables | |
| International Financing by way of Euro Issues, Euro Equity, Foreign Currency Loans, ADR, GDR etc. |
Long-Term Sources of Finance
Long-term financing means capital requirements for a period of more than 5 years to 10, 15, 20 years or maybe more depending on other factors. Capital expenditures in fixed assets like plant and machinery, land and building, etc of business are funded using long-term sources of finance. Part of working capital which permanently stays with the business is also financed with long-term sources of funds. Long-term financing sources can be in the form of any of them:
- Share Capital or Equity Shares
- Preference Capital or Preference Shares
- Retained Earnings or Internal Accruals
- Debenture / Bonds
- Term Loans from Financial Institutes, Government, and Commercial Banks
- Venture Funding
- Asset Securitization
- International Financing by way of Euro Issue, Foreign Currency Loans, ADR, GDR, etc.
Medium Term Sources of Finance
Medium term financing means financing for a period of 3 to 5 years and is used generally for two reasons. One, when long-term capital is not available for the time being and second when deferred revenue expenditures like advertisements are made which are to be written off over a period of 3 to 5 years. Medium term financing sources can in the form of one of them:
- Preference Capital or Preference Shares
- Debenture / Bonds
- Medium Term Loans from
- Financial Institutes
- Government, and
- Commercial Banks
- Medium Term Note
- Lease Finance
- Hire Purchase Finance
Short Term Sources of Finance
Short term financing means financing for a period of less than 1 year. The need for short-term finance arises to finance the current assets of a business like an inventory of raw material and finished goods, debtors, minimum cash and bank balance etc. Short-term financing is also named as working capital financing. Short term finances are available in the form of:
- Trade Credit
- Short Term Loans like Working Capital Loans from Commercial Banks
- Fixed Deposits for a period of 1 year or less
- Advances received from customers
- Creditors
- Payables
- Factoring Services
- Bill Discounting etc.
According to Ownership and Control:
Sources of finances are classified based on ownership and control over the business. These two parameters are an important consideration while selecting a source of funds for the business. Whenever we bring in capital, there are two types of costs – one is the interest and another is sharing ownership and control. Some entrepreneurs may not like to dilute their ownership rights in the business and others may believe in sharing the risk.
| OWNED CAPITAL | BORROWED CAPITAL |
| Equity | Financial institutions, |
| Preference | Commercial banks or |
| Retained Earnings | The general public in case of debentures. |
| Convertible Debentures | |
| Venture Fund or Private Equity |
Owned Capital
Owned capital also refers to equity. It is sourced from promoters of the company or from the general public by issuing new equity shares. Promoters start the business by bringing in the required money for a startup. Following are the sources of Owned Capital:
- Equity
- Preference
- Retained Earnings
- Convertible Debentures
- Venture Fund or Private Equity
Further, when the business grows and internal accruals like profits of the company are not enough to satisfy financing requirements, the promoters have a choice of selecting ownership capital or non-ownership capital. This decision is up to the promoters. Still, to discuss, certain advantages of equity capital are as follows:
- It is a long-term capital which means it stays permanently with the business.
- There is no burden of paying interest or installments like borrowed capital. So, the risk of bankruptcy also reduces. Businesses in infancy stages prefer equity for this reason.
Borrowed Capital
Borrowed or debt capital is the finance arranged from outside sources. These sources of debt financing include the following:
- Financial institutions,
- Commercial banks or
- The general public in case of debentures
In this type of capital, the borrower has a charge on the assets of the business which means the company will pay the borrower by selling the assets in case of liquidation. Another feature of the borrowed fund is a regular payment of fixed interest and repayment of capital. Certain advantages of borrowing are as follows:
- There is no dilution in ownership and control of the business.
- The cost of borrowed funds is low since it is a deductible expense for taxation purpose which ends up saving on taxes for the company.
- It gives the business the benefit of leverage.
ACCORDING TO SOURCE OF GENERATION:
Based on the source of generation, the following are the internal and external sources of finance:
| INTERNAL SOURCES | EXTERNAL SOURCES |
| Retained profits | Equity |
| Reduction or controlling of working capital | Debt or Debt from Banks |
| Sale of assets etc. | All others except mentioned in Internal Sources |
Internal Sources
The internal source of capital is the one which is generated internally by the business. These are as follows:
- Retained profits
- Reduction or controlling of working capital
- Sale of assets etc.
The internal source of funds has the same characteristics of owned capital. The best part of the internal sourcing of capital is that the business grows by itself and does not depend on outside parties. Disadvantages of both equity and debt are not present in this form of financing. Neither ownership dilutes nor fixed obligation/bankruptcy risk arises.
External Sources
An external source of finance is the capital generated from outside the business. Apart from the internal sources of funds, all the sources are external sources.
Deciding the right source of funds is a crucial business decision taken by top-level finance managers. The usage of the wrong source increases the cost of funds which in turn would have a direct impact on the feasibility of the project under concern. Improper match of the type of capital with business requirements may go against the smooth functioning of the business. For instance, if fixed assets, which derive benefits after 2 years, are financed through short-term finances will create cash flow mismatch after one year and the manager will again have to look for finances and pay the fee for raising capital again.