Budgeting
Budgeting for business plays a vital role in the management control system. It gives a brief understanding of what budgets are, what are budgeting, and its different methods, i.e., zero-based, incremental, traditional, and activity-based.
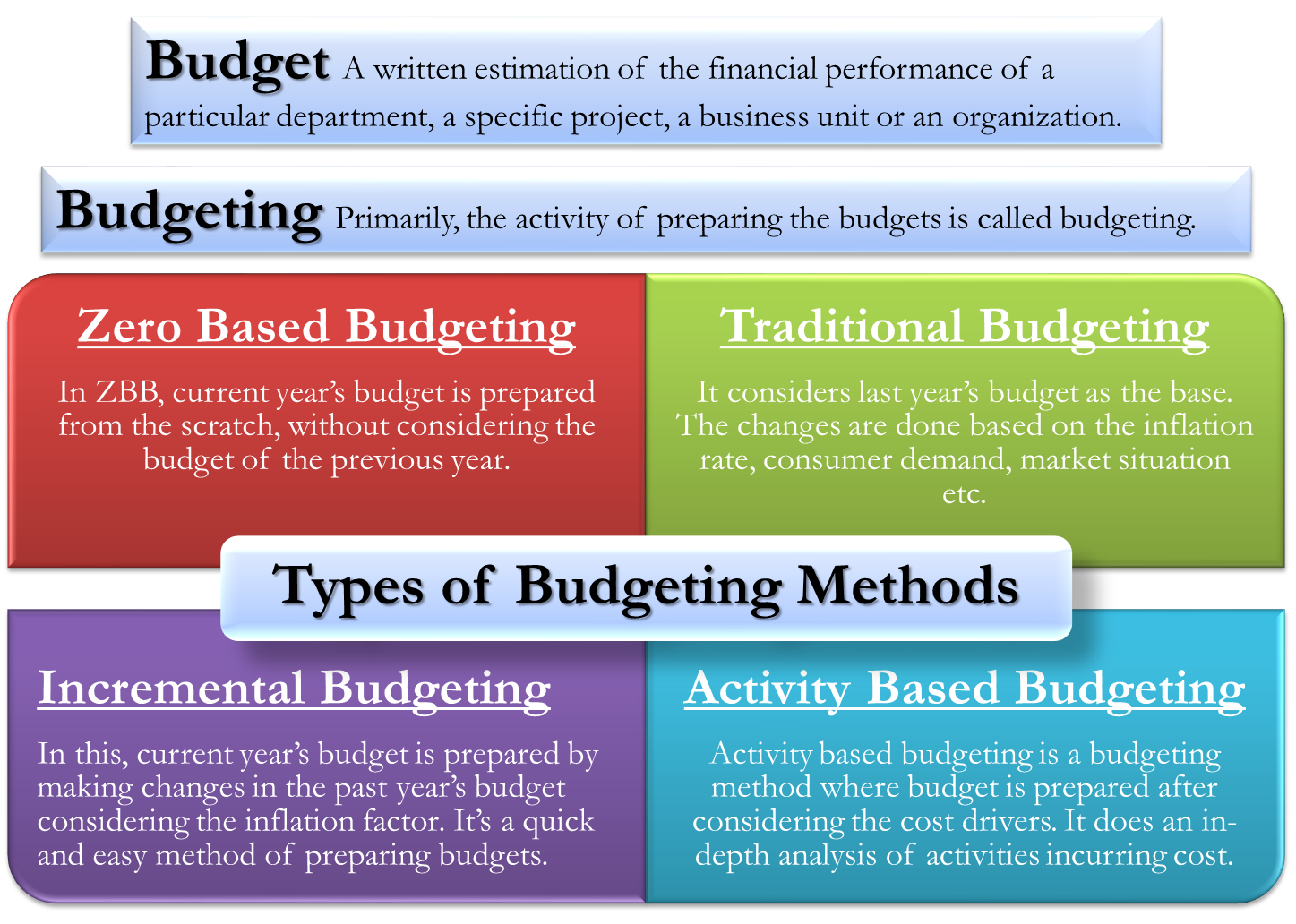
Before we understand the different types of budgeting methods, let us know the meaning of the budget.
- What is a Budget?
- What is Budgeting?
- Importance of Budgeting
- Budget Monitoring and Course Correction
- Types of Budgeting Methods / Techniques
- What is the Traditional Budgeting Method?
- What is the Incremental Budgeting Method?
- What is the Zero-Based Budgeting Method?
- What is Activity-Based Budgeting Method?
- Choosing a Method of Budgeting
What is a Budget?
A budget is a written projection of a particular department’s financial performance, a specific project, a business unit, or an organization for the period under consideration. Usually, budgets for businesses or departments are created for an accounting period, i.e., for one year. However, the period could be less or more than a year. Complete flexibility is there as the method remains the same, and the business can make or plan a budget for the period they want.
Also read – Budget Example
There are different types of budgets and, thus, budgeting methodologies.
What is Budgeting?
Primarily, the activity of preparing a budget is called budgeting. In many organizations, it is a separate department taking care of only the preparation and implementation of budgets.
Importance of Budgeting
In the business world, we can not afford to overstate the importance of a budget. At every stage of decision making, planning, and coordination, budgets or plans are the essential tools for Management Control.
It gives a direction to the entire organization internally where it needs to run and reach on the one hand and will help management in communication and guiding the team with full clarity. On the other hand, this document is also useful to the outside world. It shows what the business is trying to achieve and whether the path and direction are right or have a flaw. Whether the objective and targets or aligned with the market realities. Whether the budget is only a dream on paper or it has a clear-cut and well-defined plan of action to achieve those dreams.
Also, read Why is Budgeting important? & Limitations of Budgeting
Budget Monitoring and Course Correction
Making well-defined budgets is not enough. The progress of the business also needs continuous monitoring and comparison with the budgets. The comparison of budgeted performance with actual performance throws light and indicates:
- Whether the company is performing as planned,
- Whether the organization is on the right track, and what are the chances of achieving the budget.
- What areas are not seeing traction as desired, and what is needed to get the traction.
- Whether something somewhere is going wrong that requires immediate attention or there is a need for a different strategy to contain that wrong,
- It will help the organization to do midway course correction so that deviations are minimized. The expectation or performance could be re-allocated amongst the departments. It may help the organization to achieve the budgeted targets still, making internal adjustments.
This article also aims to highlight different budgeting methods and procedures.
Types of Budgeting Methods / Techniques
Types of Budgets
As per the requirements of the business, there are various types of budgets made and planned. Let’s first talk about the most popular types of budgets, which are:
- Annual Operating Budget
- Cash Budget
- Rolling Budgets
- Performance Budget
- Master Budget
- Operating Budget
- Program Budget
- Financial Budget
Budgeting Methods / Techniques
Mostly, budget preparation follows one of these methods. Listed below are the most popular types of business budgeting methods.
- Traditional
- Incremental
- Zero-Based
- Activity-Based
- Participative
- Top-Down
What is the Traditional Budgeting Method?
Traditional budgeting is a budget preparation method that considers last year’s budget as the base. The current year’s budget is prepared by making changes to the previous year’s budget by adjusting the expenses on the basis of the inflation rate, consumer demand, market situation, etc. The basis of the preparation of the current year’s budget is last year’s revenues and costs. Only those items in traditional budgets need to be justified, which are over and above the last year’s budget. This technique is easy to prepare and implement, barring some amount of rigidity as budgets, once prepared, cannot change.
To have a detailed understanding of the method and its advantages and disadvantages, visit – Traditional Budgeting.
What is the Incremental Budgeting Method?
Incremental budgeting is a method where the executives prepare the current year’s budget by making changes to the past year’s budget. The changes are in the form of the addition or reduction of expenses to last year’s budget. In Incremental budgeting, the starting point for preparing a budget is the prior period’s budget. The budgeting technique gives no priority to the vital activities of a business. We simply adjust last year’s budget, considering the inflation factor. This is a quick and easy method of preparing budgets.
For a detailed understanding of the advantages and disadvantages, visit – Incremental Budgeting,
What is the Zero-Based Budgeting Method?
The zero-based budgeting method is commonly in use by many organizations. In ZBB, the current year’s budget preparation begins from scratch without considering the budget of the previous year. For every financial period, a new budget is prepared to take the base as zero, and resources allocated to each department are justified according to the expenses of that particular period. The ranking for allocation of resources is on the basis of the priority of all the activities of the business. Though this method is time-consuming, it gives accurate results.
To have a detailed understanding of the method and its pros and cons, visit – Zero Based Budgeting.
What is Activity-Based Budgeting Method?
Activity-based budgeting is a method where the output or the budget targets or activity is decided first. In other words, here, the management adopts a top-down approach. After defining and determining the activities, the analysis of all cost drivers required to complete that activity, target, or output is analyzed. And then, a budget is prepared after considering all those cost drivers.
It does not take into account last year’s budget or expenses. This method does an in-depth analysis of all the activities that incur the cost. The outcome of the research determines the allocation of resources to an activity. This method aligns business activities with business goals. It helps in increasing the efficiency and profitability of a business.
To have a detailed understanding of the method and its advantages and disadvantages visit – Activity-Based Budgeting.
Choosing a Method of Budgeting
All the above-stated budgeting methodologies or techniques are relevant and suitable for all kinds of businesses and can be used by all. However, to get the maximum advantage of the entire budgeting process, a company needs to compare and meticulously choose which budgeting technique will be most suitable or fits right into the organization.
Factors Responsible
The decision to select a particular method depends on various factors like
- size of the business,
- area of operations of a company,
- the focus of the business,
- competition in the industry,
- market situation,
- complexity and
- availability of data for projections, etc.
For example, businesses with stiff competition tend to go for zero-based and activity-based budgeting. ZBB justifies and explains each item of cost. Similarly, in an activity-based method, all the business functions align with the business goals. It leads to eliminating all wasteful activities, resulting in cost savings. So, ZBB and activity-based budgeting are the best choices to cut the cost of production and survive the competition.
On the other hand, incremental and traditional budgeting methods can be used where there is limited fluctuation in the market price, consumer demand, etc. Since these budgeting methods consider the previous year’s budget as a base and do only incremental changes like an adjustment for the inflation rate, consumer demand, market situation, etc., This method could be most suitable for the organization not much affected by the change in environment. No significant internal or external changes are anticipated or can influence the business.
In the same way, large-scale organizations generally do not opt for zero-based or activity-based budgeting because these methods are costly and consume many resources. Also, the manager’s primary focus is to prepare an easily achievable budget, and that in turn ignores the business’s core activities.
To conclude, there are different methods of preparing budgets, and there is no best method that fits all. The choice of method depends upon the type of business requirements. However, choosing the right budgeting technique goes a long way toward better business performance.
References