Bonds are debt securities issued by companies, governments, or other organizations to raise capital. They typically have a fixed interest rate and maturity date, and pay interest to bondholders in the form of cash. The only factor that differentiates PIK bonds from other bonds is the payment of interest. In PIK bonds, in lieu of interest payment, additional bonds are issued. That is the interest is not paid in cash.
Difference between PIK Bonds & Traditional Bonds
PIK bonds are a unique type of debt instrument that offer issuers and investors certain benefits and drawbacks relative to traditional bonds. It is important for investors to carefully consider the risks and rewards of investing in PIK bonds before making an investment decision. Let’s understand in detail, how a PIK bond is different from a traditional bond as below:
Interest Payments
With traditional bonds, interest payments are made in cash, usually on a semi-annual or annual basis. With PIK bonds, however, interest payments can be made in the form of additional bonds, rather than cash.
Coupon Rate
PIK bonds often have a higher coupon rate than traditional bonds because of their higher risk profile.
Risk Profile
PIK bonds are generally considered to be riskier than traditional bonds. The following are the key reasons for this:
Cash Flow Uncertainty
Investor locks in the capital till the maturity of any bond but in the case of PIK bonds, the investor will not even receive interest payments in cash till maturity. This makes the investor take a call for too long for a future that is uncertain. The capital remains locked for 10 years if the maturity of the PIK Bond is 10 years.
Complicated Structure
It’s not everybody’s cup of tea to understand the structure of PIK Bonds. The issuer may at its discretion decide to pay interest or defer it. That makes it all the more difficult to gain clarity on future cash flows.
Yield
Because of the higher risk profile and higher coupon rates of PIK bonds, they typically offer a higher yield than traditional bonds.
Tax Treatment
The tax treatment of PIK bonds may differ from that of traditional bonds. The treatment depends on the law of the land and that may differ from country to country. In traditional bonds, interest received during the year will be considered as income but in PIK bonds, the part of the interest that is paid in kind is subject to different tax treatments depending on the income tax laws.
Liquidity
Naturally, PIK bonds are less liquid than traditional bonds as they are not as popular as traditional bonds. Also, it is difficult to understand the terms of PIK bonds and their short and long-run impact.
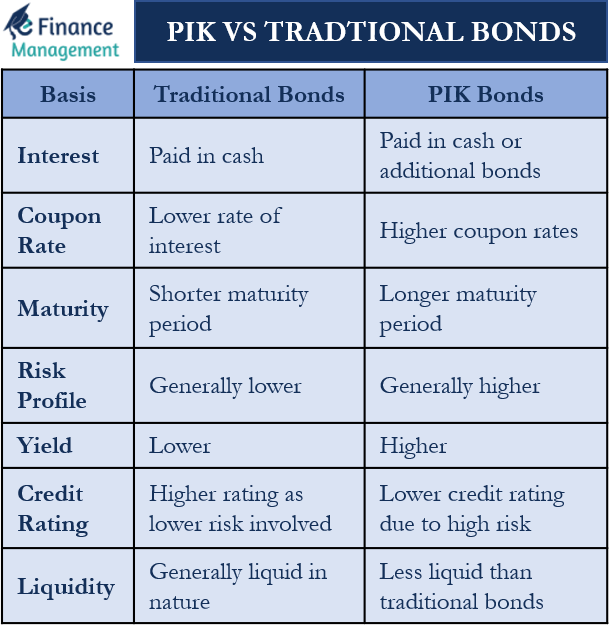
Table of Comparison
Here is a short table of comparison:
| Basis | Traditional Bonds | PIK Bonds |
|---|---|---|
| Interest | Paid in cash | Paid in cash or additional bonds |
| Coupon Rate | Lower rate of interest | Higher coupon rates |
| Maturity | Comparatively shorter maturity period | Longer maturity period |
| Risk Profile | Generally lower | Generally higher |
| Yield | Lower | Higher |
| Credit Rating | Higher credit rating because of lower risk | Lower credit rating due to high risk |
| Liquidity | Generally liquid in nature | Less liquid than traditional bonds |
It’s important to note that these are generalizations, and specific characteristics of individual bonds may vary.
Which bonds should you Invest in?
For investors who are primarily concerned with the safety of principal and steady income, traditional bonds may be more beneficial. Traditional bonds offer a reliable stream of cash interest payments, and the risk of default is generally lower than with PIK bonds. Additionally, traditional bonds may be more liquid and easier to buy and sell than PIK bonds.
Also Read: Bonds and their Types
On the other hand, for investors who are willing to take on more risk in exchange for potentially higher returns, PIK bonds may be more beneficial. However, PIK bonds also carry higher credit risk and liquidity risk, which may not be suitable for all investors.

