There are various types of debentures like redeemable, irredeemable/perpetual, convertible, non-convertible, fully secured, partly secured, mortgage, unsecured, naked, first mortgaged, second mortgaged, the bearer, fixed, floating rate, coupon rate, zero-coupon, secured premium notes, callable, puttable, etc.
The debenture classification is based on tenure, redemption, mode of redemption, convertibility, security, transferability, type of interest rate, coupon rate, etc. Ultimately, a debenture is not like a standard product configured strictly. It is an agreement between the corporation and the debenture holders that decides the characteristics of a debenture. Following are some examples of agreement templates for ready reference and quick drafting.
Types of Debentures
Following are the various types of debentures vis-a-vis their basis of classification.
Redemption / Tenure
Redeemable Debentures

Redeemable debentures carry a specific date of redemption on the certificate. The company is legally bound to repay the principal amount to the debenture holders on that date. There are various ways to redeem a debenture.
Irredeemable (Perpetual) Debentures
Irredeemable debentures, also known as perpetual debentures, do not carry any redemption date. This means that there is no specific time of redemption of these debentures. They are redeemed either on the company’s liquidation or as per the terms of the issue when the company chooses to pay them off to reduce their liability by issuing due notice to the debenture holders beforehand.
Also Read: Characteristics of Debenture
Convertibility
Convertible and Non-Convertible Debentures
Convertible debenture holders have the option of converting their holdings into equity shares. The rate of conversion and the period after which the conversion will take effect are declared in the terms and conditions of the agreement of debentures at the time of issue. On the contrary, non-convertible debentures are simple debentures with no such option of conversion into equity. Their state will always remain of debt and will not become equity at any time.
It is essential to prepare an agreement that clearly expresses all the terms and conditions.
Fully and Partly Convertible Debentures
Convertible Debentures are further classified into two – Fully and Partly Convertible. Fully convertible debentures are completely converted into equity, whereas partly convertible debentures have two parts. The convertible part is converted into equity as per the agreed rate of exchange based on an agreement. The non-convertible part becomes as good as a redeemable debenture, whose repayment takes place after the expiry of the agreed period.
Security
Secured (Mortgage) and Unsecured (Naked) Debentures
Debentures can be secured, and they may be unsecured in nature. A secured debenture is secured by the charge on some asset or set of assets known as a secured orMortgaged Debentures mortgage debenture. Another, when it is issued solely on the issuer’s credibility, is known as the naked or unsecured debenture. A trustee is appointed to hold the secured asset, which is obvious as the title cannot be assigned to each debenture holder.
First Mortgaged and Second Mortgaged Debentures
Secured / Mortgaged debentures are further classified into the first and second mortgaged debentures. There is no restriction on issuing different types of debentures, provided there is clarity on claims of those debenture holders on the company’s assets at the time of liquidation. First mortgaged debentures have the first charge over the company’s assets. In contrast, the second mortgage has the secondary charge, which means the realization of the assets will first fulfill the obligation of the first mortgage debentures and then will do for the second one.
Transferability / Registration
Registered Unregistered Debentures (Bearer) Debenture
In the case of registered debentures, the name, address, and other holding details are registered with the issuing company. Whenever the holder transfers such debenture, it has to be informed to the issuing company for updating in its records. Otherwise, the interest and principal will go to the previous holder because the company will pay the registered one. Whereas the unregistered is commonly known as bearer debenture and can be transferred by mere delivery to the new holder. They are as good as currency notes due to their easy transferability. The interest and principal are paid to the person who produces the coupons attached to the debenture certificate and the certificate.
Type of Interest Rates
Fixed and Floating Rate Debentures
Fixed-rate debentures have a fixed interest rate over their life of the debentures. Contrarily, the floating rate debentures have the floating interest rate, dependent on some benchmark rate, say LIBOR (London Inter-Bank Offer Rate), PLR (Prime Lending Rate), etc.
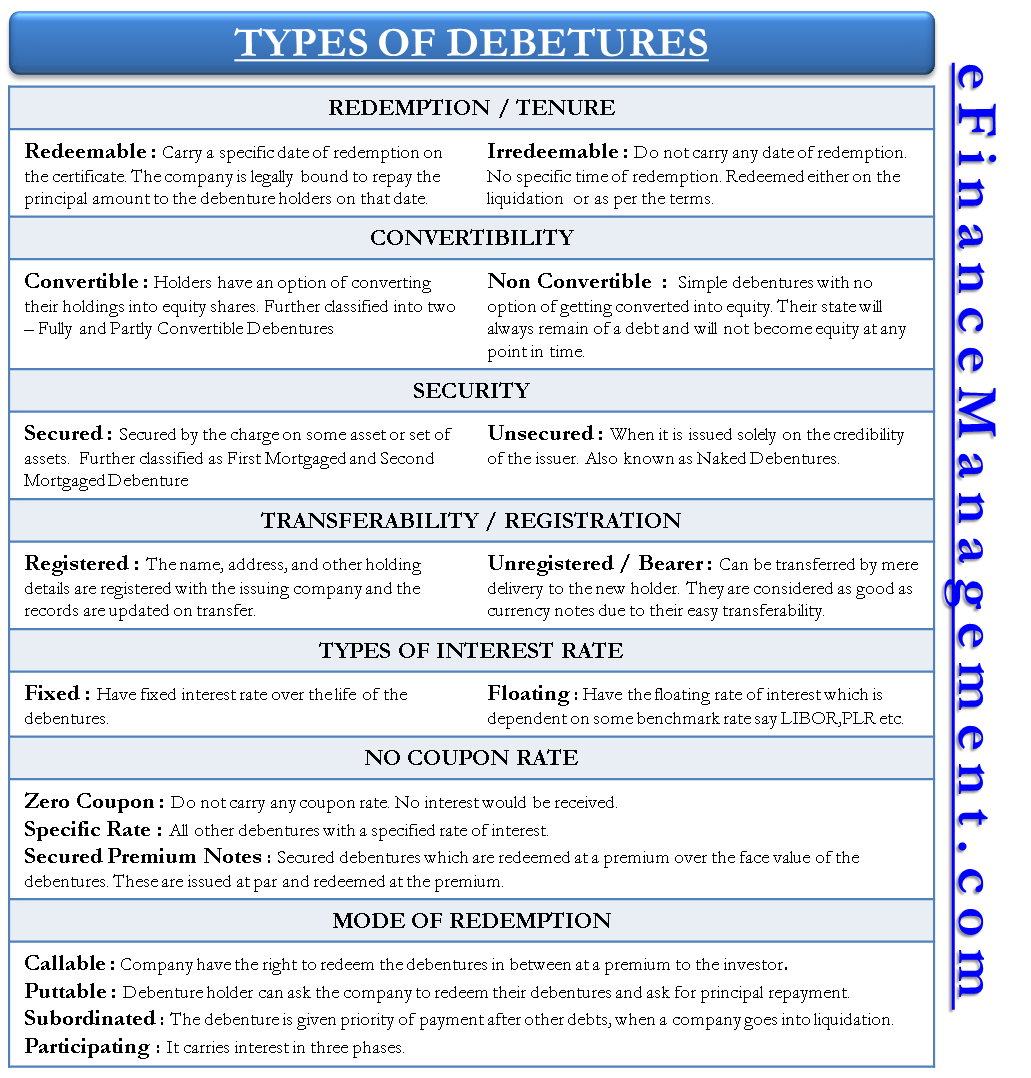
No Coupon Rate
Zero Coupon and Specific Rate Debentures
Zero-coupon debentures do not carry any coupon rate, or we can say that there is a zero-coupon rate. The debenture holder will not get any interest in these types of debentures. Need not get surprised; for compensating against no interest, companies issue them at a discounted price that is less than their face value. The implicit interest or benefit is the difference between the issue price and the face value of that debenture. These debentures are to be redeemed at face value. The other term for these is ‘Deep Discount Bonds.’ All other debentures with a specified interest rate are specific rate debentures that are just like a normal debenture.
Secured Premium Notes / Debentures
These are secured debentures that are redeemed at a premium over the face value of the debentures. They are similar to zero-coupon bonds. The only difference is the discount and premium. Zero-coupon bonds are issued at a discount and redeemed at par, whereas the secured premium notes are issued at par and redeemed at the premium.
Mode of Redemption
Callable and Puttable Debentures / Bonds
Whenever a corporation is borrowing for the long term by issuing fixed rate debentures, it risks a decrease in the rate of interest in the market. Suppose a company is issuing 20 years debentures offering a rate of interest of 7%. After 5 years, similar debentures can be issued at a market offering rate of interest of 4%; then, for a corporation, there will be a comparatively higher cost than the existing debenture. So, the corporation may issue long-term debenture with a callable feature in which it will have a right to redeem the debenture in between. However, in this case, usually, the company will offer a premium to an investor in case of early redemption.
In the case of puttable debentures, the option lies with the investors for early redemption. Generally, a company in bad need of money will issue a puttable debenture. In this case, debenture holders can ask the company to redeem their debenture and ask for principal repayment. The company can issue this type of security to avoid a hostile takeover.
Subordinated Debenture
In these types of debentures, the debentures prioritize payment after other debts when a company goes into liquidation. They are also known as subordinated loans, subordinated bonds, subordinated debt, or junior debt. Usually, they will be offered a higher return as they undertake more risk.
Participating Debenture
It is a method of financing in the case of venture capital financing. It carries interest in three phases. During the initial phase, there are no interest charges. During the subsequent stage, interest is charged at a lower interest rate, up to a particular level of operation; after that high rate of interest is charged.
Quiz on Types of Debentures


pls clarify – bank debenture classified into financial or operating activity, if the money used for operation of bank.
In which context, you are asking this question whether finance related or cash flow related??
What is the difference between the expenses on interest on debentures and discount on debentures and its relevance in accounting procedure.
Interest on debenture is a fixed cost to be paid after the issue of the debenture to the debenture holder according to the agreed terms. Discount on debentures is one-time capital expense/loss for issuing a debenture.
Accounting treatment:
For Interest in debenture: P&L A/c Dr To Interest on debenture Cr.
For Discount on debenture: P&L A/c Dr To Discount on issue of debenture Cr.
Hi , i am bit confused with zero coupon & secured premium notes – confusion in terms of issued at discount & redeemed at premium & vice a versa.
please elaborate.
so are the companies legally bound to redeem the invested amount back to the investor. ? Like in the case of DHFL, I have invested in NCD for the amount of 20000 for 10 years.
A short and quick guide on Debentures. I liked it. Thank you 🙂
Thanks, sir it’s very much helpful for me
Good afternoon
My client is looking for someone who can help with Bonds issue his company
Could you help me with this matter
Is it fair to say that an Irredeemable NCD will have the option of either Callable or Puttable option since there is no fixed redemption date? Same won’t be available for a Redeemable NCDs. Thanks in advance.