Preference shares are one of the special types of share capital having a fixed dividend rate. They carry preferential rights over ordinary equity shares in sharing of profits and claims over the firm’s assets. It is ranked between equity and debt as far as the priority of capital repayment is concerned.
Definition of Preference Share
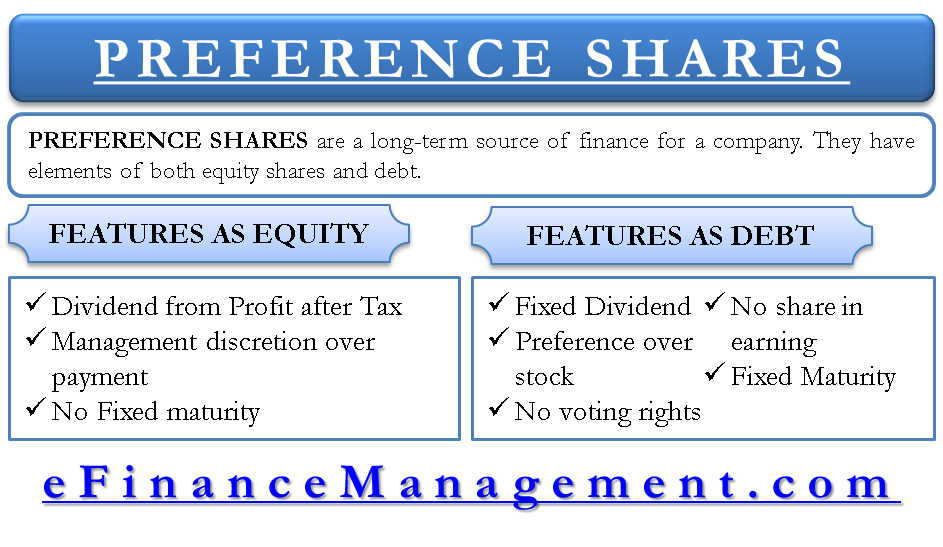
Preference shares are a long-term source of finance for a company. They are neither entirely similar to equity nor equivalent to debt. The law treats them as shares, but they have elements of both equity shares and debt. For this reason, they are also called ‘hybrid financing instruments.’ These are also known as preferred stock, preferred shares, or only preferred in a different part of the world. There are various types of preference shares used as a source of finance.
Let us understand the preference share in detail with its specific features. Some of the features are of debt, and others are of equity. It makes sense to discuss the features similar to debt and equity separately.
Features of Preference Shares Similar to Debt
Fixed Dividends
Like debt carries a fixed interest rate, these shares have fixed dividends.
But the obligation of paying a dividend is not as rigid as debt. Non-payment of a dividend would not amount to bankruptcy in the case of preference share.
Also Read: Types of Preference Shares

Preference over Equity
As the word preference suggests, these types of shares get preference over equity shares in sharing the income and claims on assets. Alternatively, this share dividend has to be paid before any dividend payment to ordinary equity shares. Similarly, at the time of liquidation, these shares would also be paid before equity shares.
No Voting Rights
Preference share capital is not allotted any voting rights usually. They are similar to debenture holders and do not have any say in the management of the company.
No Share in Earnings
Preference shareholders can only claim two things—one agreed-on percentage of dividend and second the amount of capital invested. Equity shares are entitled to share the residual earnings and residual assets in case of liquidation, which preference shares are not entitled to.
Fixed Maturity
Just like debt, these shares also have a fixed maturity date. The preference capital will have to be repaid to the preference shareholders on the date of maturity. A special type of shares, i.e., irredeemable preference shares, is an exception to this. They do not have any fixed maturity.
Also Read: Cost of Preference Share Capital
Features of Preference Shares similar to Equity Shares
Dividend from PAT
Equity share dividend is paid out of the profits left after all expenses and even taxes, and the same is the case with preference share. The preference dividend is paid out of the divisible profits of the company. Out of the divisible profits, the preference dividend would be paid first, and the remaining profits can be utilized for paying any dividend to equity shareholders.
Management Discretion over Dividend Payment
The payment of preference dividend is not compulsory and is a management decision. Equity shareholders also do not have any right to ask for dividends, and the dividends are paid at the discretion of the management of the company. Unlike debt, the non-payment of a preference share dividend does not amount to bankruptcy.
No Fixed Maturity
The maturity of a special variant of preference share is not fixed, just like equity shares. This variant is popularly known as irredeemable preference shares.
There are some advantages and disadvantages of preference shares like no legal obligation for dividend payment, improved borrowing capacity, no dilution on control, costly source of finance, etc.
Also read – Preferred Stock Vs Bond.


very good work sir..
thanks it was very helpful in my studies.
thank sir helped in my course work
Appreciated
The content is very nice. Each and every topic has been explained in a very lucid manner.
Sir your content is of great help… regards and GOD Bless you