Dividend Decisions
What are Dividend Decisions?
Dividend decisions, as the very name suggests, refer to the decision-making mechanism of the management to declare dividends. It is crucial for the top management to determine the portion of earnings available for the distribution as the dividend at the end of every reporting period. A company’s ultimate objective is the maximization of shareholders’ wealth. It must, therefore, be very vigilant about its profit-sharing policies to retain the faith of the shareholders. Dividend payout policies derive enormous importance by virtue of being a bridge between the company and shareholders for profit-sharing. Without an organized dividend policy, it would be difficult for the investors to judge the intentions of the management.
Impact of Dividend Decisions on Price
The dividend policies of an organization have a significant bearing on the market value of stocks. Companies must distribute dividends in line with the industry standards and previously distributed dividends by the company. The shareholders will otherwise perceive this variability negatively. It casts suspicion on the financial health and motives of the management (signaling effect). In aggregate, an inefficient dividend decision mechanism would adversely impact the valuation of the company.
Factors affecting Dividend Decisions
Cash Requirement
The financial manager must take into account the capital fund requirements while framing a dividend policy. Generous distribution of dividends in capital-intensive periods may put the company in financial distress.
Evaluation of Price Sensitivity
Companies chosen by investors for their regularity of dividends must have a more stringent dividend policy than others. It becomes essential for such companies to take effective dividend decisions for maintaining stock prices.
Stage of Growth
Dividend decisions must be in line with the stage of the company- infancy, growth, maturity & decline. Each stage undergoes different conditions and therefore calls for different dividend decisions.
Good Dividend Policy
What Constitutes a Good Dividend Policy?
There does not exist a single dividend decision process that works for every organization. A decision suitable for one company may prove fatal for another company. For example, businesses with a consistent order book such as telecom and banking are expected to pay regular dividends. It may impact the stock prices if they do not pay dividends regularly. On the contrary, sectors of pharmaceutical and technology are highly research-oriented. These require huge cash expenses to further their operations. Therefore they cannot afford to pay a regular dividend. Investors of such stocks earn income mainly through capital appreciation. In essence, there are a lot of factors affecting dividend policy or decisions.
We can refer to the following renowned theories on Dividend Policy:
- Modigliani- Miller Theory on Dividend Policy
- Gordon’s Theory on Dividend Policy
- Walter’s Theory on Dividend Policy
A good financial manager must, therefore, answer the following questions before taking crucial dividend decisions
Importance of Dividend Decisions
While deciding the distribution of dividends, management has to answer various questions such as:
Q. How much Dividend should a Company Distribute to its Shareholders?
- The ideal dividend decision should be commensurate with the profitable investment opportunity available to the company. If it can invest a dollar and reap two, it is insensible to lose out on that dollar by paying dividends.
- Industry standards are another input to be factored in. A company paying fewer dividends than its peers can face problems while raising capital.
- It also depends on the kind of investors which the company wants to attract. For example, companies such as American Express and Coke can be relied upon for their stable dividend policies. They attract investors with a longer horizon and larger disposable funds since they are compensated by steady cash flows.
Q. What will be the Impact of Dividend Decisions on the Share Prices of the Company?
To answer this question, it is important to know the dividend history of the company. If the company is known for regularly paying dividends, pressure for maintaining the payout hovers over it. A one-off year, where it may not want to pay dividends and divert the funds for reinvestment plan or retention may be hazardous. Conversely, an interesting phenomenon occurs in cases of companies depicting no stability in dividend policies. When it does declare a dividend, the share prices see a huge spike before the ex-dividend date. More and more people seek to make a quick buck by buying its shares on dividend declaration. These shares are then sold as soon as the dividends are declared. This is followed by a fall in the share prices (dividend stripping). Thus the shares of a sparsely dividend-paying company undergo great volatility between the date of dividend declaration and payment.
Q. What is the Consequential Impact of Inability to Maintain Dividend Year after Year?
Only a company with sustainable profitability and cash flows can expect to reasonably pay dividends year after year. If any other company claims the same, it is a hoax. If the stock of the company in question is a growth stock such as Qualcomm (NYSE), the shareholders may pardon a stingy dividend policy. Such shareholders expect to earn via a fat capital appreciation and hardly through the dividend.
On the other hand, if the shareholders are sensitive to the dividend decisions of the company, it is not a good idea to have an irregular policy. For example, Avista Corp and CMS Energy Corporation (NYSE) have been consistently paying dividends for a while. Investors which buy into these companies are conditioned to expect the same. Having established the expectation of regular dividends, the companies must ensure regular payouts. The failure of same could drive down the prices.
Types of Dividend Decision
There are various types of dividends and dividend decisions.
Stable Dividends
- The same amounts of dividends are paid out every year irrespective of the profitability.
- Shareholders remain immune to fluctuations and volatility faced by the company.
- Only long-standing and well-established companies with steady cash flows can afford to follow this policy
- Investors that buy into stock dividend investing companies have a low-risk appetite. They also do not get to participate in the profits of the company
Constant Dividends
- Dividends are paid at a fixed percentage of the profits.
- The brunt of recession is as much borne by them as much they reap benefits of the boom.
- This policy is suitable for companies in their infancy stage as well as those prone to volatility.
- Investors of these companies are risk-taking. They prefer to swing with the company in its earnings
Alternate Dividend Decisions
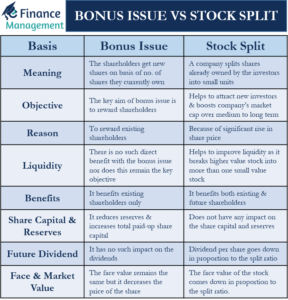
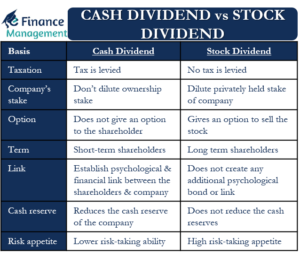
A company may not always issue dividends in cash. A stock dividend is a significant option with the management for recourse to non-cash options. It is a handy tool to which management may resort when it wants to balance both, shortage of cash and shareholder expectations. Such decisions are only helpful in exceptional circumstances.
References: Dividend Decisions, Strategic Financial Management, CA Final.
CFA Curriculum L I&II