Definition of Factoring
Factoring is a financial service in which the business entity sells its bill receivables to a third party at a discount in order to raise funds. This is a type of business loan. Factoring differs from invoice discounting. The concept of invoice discounting involves getting the invoice discounted at a certain rate to get the funds, whereas the concept of factoring is broader. Factoring involves the selling of all the accounts receivable to an outside agency. Such an agency is called a factor.
Concept of Factoring
The seller makes the sale of goods or services and generates invoices for the same. The business then sells all its invoices to a third party called the factor. If the factor is a bank or financial institution, then such factoring is called reverse factoring. The factor pays the seller after deducting some discount on the invoice value. The rate of discount in factoring ranges from 2 to 6 percent. However, the factor does not make the payment of all invoices immediately to the seller. Instead, it pays only up to 75 to 80 percent of the invoice value after deducting the discount. The remaining 20 to 25 percent of the invoice value is paid after the factor receives the payments from the seller’s customers. It is called factor reserve. Another name for factoring is receivables/invoice factoring.
Why Receivables/Invoice Factoring?
Achieving milestones and milestones in sales is not sufficient to generate cash profits; they are generated only after the sales are realized in cash. In a business, converting sales into cash is a more difficult task than making sales itself. Factoring is the ultimate solution to this difficulty.
Types of Factoring
There are various types of factoring, such as:

- Recourse and non-recourse factoring
- Advance and maturity factoring
- Full factoring
- Disclosed and undisclosed factoring
- Domestic and cross-border factoring
- International factoring
- Specialized factoring
- Reverse factoring
Functions of Factor
The factor performs the following functions:
Collection from Customer
The factor performs the duty of collecting funds from the client’s debtors. This enables the client to focus on core business areas instead of putting energy into the collection of money.
Also Read: Advantages and Disadvantages of Factoring
A Short-Term Finance
From a different perspective, accounts receivable factoring can be seen as an innovative way of Working Capital Financing. Although cost-wise, the deal may not be very attractive because the factor charges would include the interest on the amount advanced to the business and the service charge for other services. At the same time, comparing factoring costs with other financing options would not be correct because it is not direct financing. It is a bundle of more than one service.
Factoring Services apart from Financing
The other services which can be a part of factoring services apart from advancing the invoices are
- Collection from customers,
- Credit investigation,
- Sales ledger management, etc.
Subscribing to such services may be at the seller’s option or the company taking factoring services.
Maintenance of Sales Ledger
A factor is responsible for maintaining the sales ledger of the client. So the factor takes care of all the sales transactions of the client.
Factoring Fee
A commission/fee is charged as per the agreement between factor and business. It is normally charged in percentage terms.
Credit Protection
In the case of non-recourse factoring, the risk of non-payment or bad debts is on the factor.
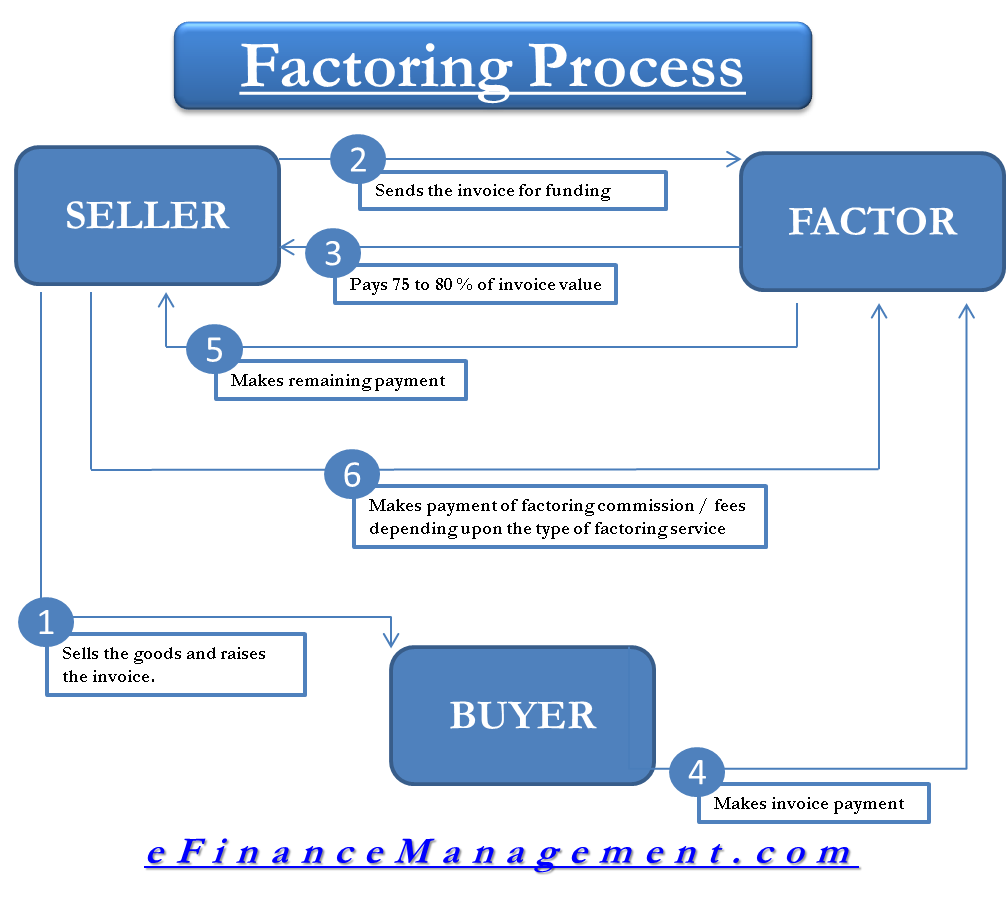
Factoring Process
The following steps are involved in the process of factoring:
- The seller sells the goods to the buyer and raises the invoice on the customer.
- The seller then submits the invoice to the factor for funding. The factor verifies the invoice and decides on the terms of factoring.
- After verification, the factor pays 75 to 80 percent to the client/seller.
- The factor then waits for the customer to make the payment to him.
- On receiving the payment from the customer, the factor pays the remaining amount to the client.
- Fees charged by factor or interest charged by a factor may be upfront, i.e., in advance, or it may be in arrears. It depends upon the type of factoring agreement.
- In the case of the non-recourse factoring services factor bears the risk of bad debt, so in that case, the factoring commission rate would be comparatively higher.
- The rate of commission, factor reserve, and the rate of interest all of them is negotiable. These are decided depending upon the financial situation of the client.
Also refer to Factoring Accounting.
Factoring Example with Calculations
Let us assume that a company has sold goods worth $2000 to a customer, the proceeds of which shall be received 3 months from now. The company now wishes to undergo invoice factoring and approaches the factoring company. This is what the process and calculations shall look like.
| Transactions / Events in Factoring | Amount |
|---|---|
| Invoice Amount (for goods sold) | $2000 |
| Cash advanced by factoring company (assuming 80%)(The balance of 20% is kept as reserve, $ 400 in this case) | $1600 |
| Amount paid by the customer to the factoring company on the due date | $2000 |
| Amount charges by factoring company as interest and processing charge (Assumed processing charge and interest cost together as 12% p.a. = 2000*0.12*3/12) | $60 |
| Balance payment from factoring company ($ 400 balance less $ 60 charges) | $340 |
| Total Amount received by the company ($ 1600 + $ 340) | $1940 |
| Total Amount earned by the factoring company (the interest and charges) | $60 |
Learn more about Factoring Companies and How do Factoring Companies Work?
Advantages of Factoring
The following are the advantages:
- It reduces the credit risk of the seller.
- The working capital cycle runs smoothly as the factor immediately provides funds on the invoice.
- Sales ledger maintenance by the factor leads to a reduction in cost.
- Improves liquidity and cash flow in the organization.
- It leads to the improvement of cash in hand. This helps the business to pay its creditors on time which helps in negotiating better discount terms.
- It reduces the need for the introduction of new capital into the business.
- There is a saving on administration or collection costs.
Disadvantages of Factoring
The following are the disadvantages:
- Factor collecting the money on behalf of the company can lead to stress in the company and the client relationships.
- The cost of factoring is very high.
- Bad behavior of factor with the debtors can hamper the company’s goodwill.
- Factors often avoid taking responsibility for risky debtors. So the burden of managing such a debtor is always on the company.
- The company needs to show all the details about company customers and sales to factors.
Conclusion
Thus, factoring forms an important part of a business, especially those businesses which are big in size. However, if used wisely and to the benefit of the company, it can help the business to grow significantly.
To learn more about the advantages and disadvantages, visit our article: Advantages and Disadvantages of Factoring.
Quiz on Factoring
This quiz will help you to take a quick test of what you have read here.


I love it when people come together and share opinions, great blog, keep it up.
A lot of my business friends is using and recommending me invoice factoring. This article is very helpful for me. I want to try this as well for my business financing. Thanks for sharing the factoring process. Thanks for sharing this article.
thanks man
learning day by day