Hypothecation Meaning
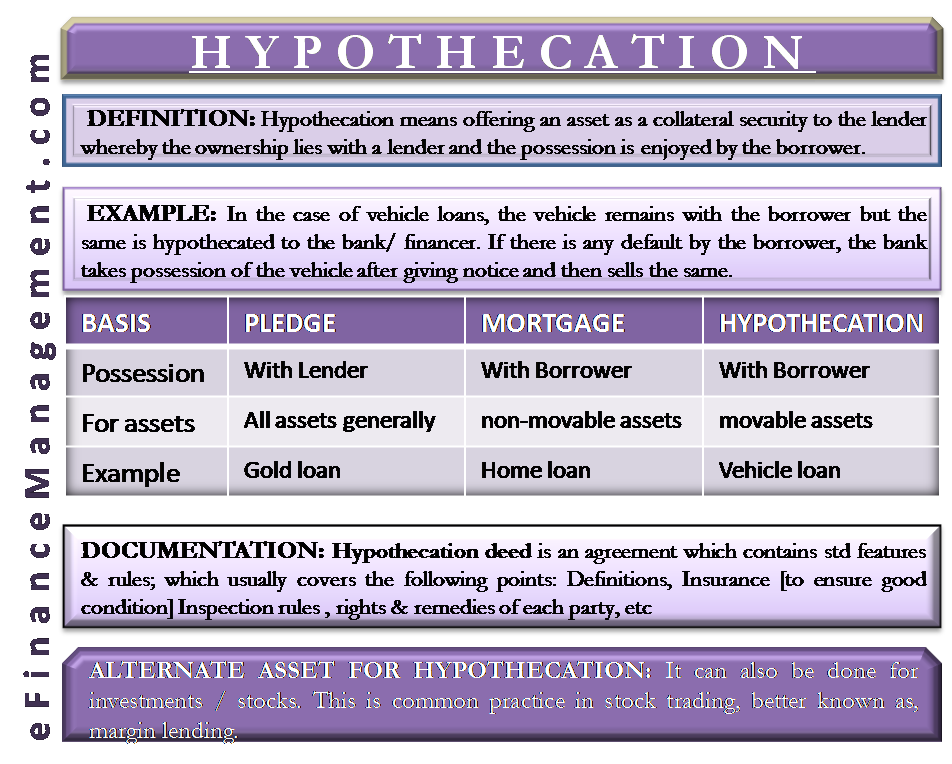
Hypothecation means offering an asset as collateral security to the lender. The ownership lies with a lender, and the borrower enjoys the possession. In the case of default by the borrower, the lender can exercise his ownership rights to seize the asset.
It is usually done in movable assets to create the charge against collateral for the loan given. Under hypothecation, the possession of the security remains with the borrower itself. Hence, if the borrower defaults on payments, the lender would have to first take possession of the security (asset under hypothecation). And then sell the asset to recover dues. Sometimes a bank or financial institution puts the already pledged asset as collateral for borrowing from another bank is called rehypothecation.
Example of Hypothecation
In the case of vehicle loans, the vehicle remains with the borrower, but the same is hypothecated to the bank/ financer. If the borrower defaults, the bank takes possession of the vehicle after giving notice and then sells the same. The loan account is credited with the sales proceeds of the asset to recover the dues towards the principal amount and interest amount. Any balance left after that shall be given back to the borrower. Apart from vehicles, It can be done for stocks and bills receivables.
Though pledge seems similar to hypothecation as both are types of charges created on movable assets. There lie some differences between pledge, hypothecation, and mortgage. Let us look at the differences to understand these terms better.
Also Read: Advantages & Disadvantages of Hypothecation
Pledge V/s Hypothecation
The possession of the asset remains with the lender in case of a pledge, while it remains with the borrower in case of hypothecation. Common examples include the gold loan in case of pledge and vehicle loan in case of hypothecation. Read a detailed article on Pledge vs Hypothecation vs Lien vs Mortgage vs Assignment.
Mortgage V/s Hypothecation
The possession remains with the borrower in both these cases; however, mortgages are usually for non-movable assets while hypothecation is for movable assets. Common examples include the home loan in case of mortgage and vehicle loan in case of hypothecation. For more about differences: Mortgage V/s Hypothecation.
Alternate Asset for Hypothecation
It can also be done for investments/stocks. This is a common practice in stock trading, better known as margin lending. In such a case, the buyer, buying shares on margin, places his existing shares as collateral with the brokerage firm. The brokerage firm can sell these shares if the buyer faces a margin call. A margin call is received when the value of securities bought decreases more than a certain limit or the account value reduces beyond a certain limit.
Documentation
This activity usually requires an agreement to be made and is known as the hypothecation deed.
The hypothecation deed is an agreement that contains standard features and rules; which usually cover the following points: Definitions, Insurance , Inspection rules , rights and remedies of each party , security details marked for hypothecation, sale realizations, insurance proceeds, the liability of each party, jurisdiction prevailing, marking of the assets, etc. This deed protects the rights of both parties to the contract.
To learn more, you can visit our Advantages & Disadvantages of Hypothecation.
Conclusion
Hypothecation is a way by which borrowers can raise funds by providing security (movable) as collateral. And still get to use it since the possession remains with the borrower. The bank/financer gives this source of a loan at a rate lower than the unsecured loan as it provides a sense of security to the lender.
The lender runs a risk as there may be instances where the borrower sells off the hypothecated asset without the lender’s knowledge. However, periodic checks and proper clauses in this deed can provide protection to a large extent to both the borrower and the lender.
Quiz on Hypothecation


What is the next course of action in case of breach of contract, say the borrower sells the hypothecated collateral to use the funds for other purposes? What are the powers with the lender in such scenarios when the borrower defaults and the property is no longer existing with borrower?
Hi Mousumi,
Thanks for writing in.
At the time of lending money or buying an asset, if the bank has taken additional security apart from the asset that is hypothecated, the bank can seize that asset.
Else, the banker can take the legal route.
Happy Reading. Keep Commenting.
I am the dealer of three wheeler vehicle. I want to sell the vehicle on part payment and the rest dues money with interest to collected in EMI. can i give my firm name in hypo.