We put ‘shareholders vs. stakeholders’ as ‘owners vs. any parties interested in the company.’ Note that shareholder is a subset of stakeholders. A shareholder is someone who owns a financial share (equity stock) in the company and thus has an ownership share in the company. A stakeholder is someone who has an interest in the company’s performance for reasons other than just capital appreciation due to an increase in the stock price.
Stakeholders’ welfare is a superior corporate goal over shareholders’ wealth maximization. Stakeholder’s welfare looks after all the factors responsible for its success, whereas the wealth maximization as an objective overemphasizes the importance of money provider, i.e., shareholders.
Shareholders vs Stakeholders: Differences
There has been a lot of debate on the shareholders vs stakeholders and on who of the two sets of people are of more importance. Let us first have a look at the major differentiating factors between shareholders and stakeholders.
Nature
Shareholders are common people who become part owners of the company by buying equity stock either from the company, i.e., through an initial public offering , or from the secondary market. The shareholders make profits in terms of dividends and capital appreciation if the companies make profits and the price of their share of the index increases. On the other hand, companies make a loss that negatively affects their share price and their return.
Stakeholders are people who have an interest in the company either directly or indirectly. Employees, customers, creditors, suppliers, etc., who will suffer from what happens in the company, are all company stakeholders. The general public is also considered stakeholders under CSR (Corporate Social Responsibility) governance. One can say that all shareholders are stakeholders, but not all stakeholders may be the company’s shareholders.
Impact
Shareholders are affected directly by the company’s monetary performance, like profits or losses, as it quickly reflects the price of the stock.
Stakeholders may be directly or indirectly affected by what happens in the company. The stakeholders have an impact/influence on what will happen to the company’s performance. Whereas shareholders are only affected by the outcome.
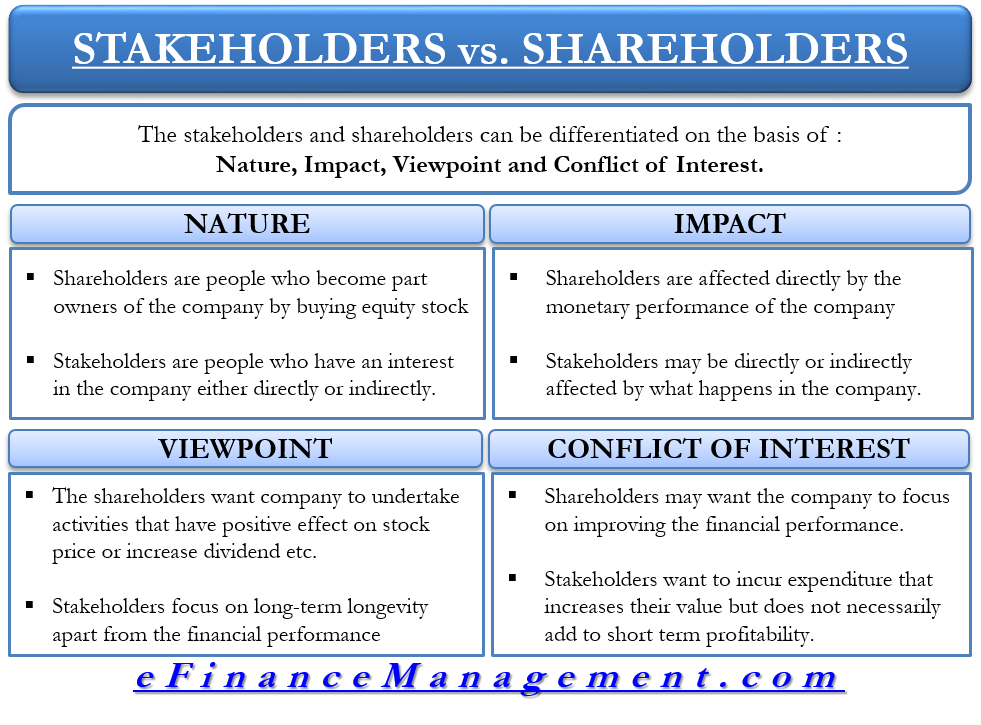
Shareholders Vs Stakeholders Viewpoint
The shareholders want the company to undertake activities that ensure having a positive effect on the stock price. Increase dividends or actions that improve the company’s financial condition in the immediate future.
On the other hand, stakeholders focus on the long-term longevity of the organization, apart from the company’s financial performance. The stakeholders (employees and staff) may seek a better quality of services from the company rather than higher profitability. In other words, shareholders focus on quantity, and stakeholders focus on quality.
Conflict of Interest
The company is always in a dilemma as to whom to give higher priority, viz., shareholder’s wealth maximization vs stakeholder welfare as a corporate objective. The shareholders being the key controllers, may want the company to focus on improving its financial performance. On the other hand, stakeholders want to incur expenditure that increases their value but does not necessarily add to profitability, especially in the short term. With changing economic dynamics, companies have now started treating increasing stakeholder value as a part of corporate social responsibilities.
However, given the number of frauds that corporations have seen under the disguise of stakeholder value creation. There are clouds of doubts created on which aspect to be given higher priority. Many companies now try to balance the two by focusing on increasing the shareholder value without compromising or violating any stakeholder rights and also doing business activities in a legally correct manner. The objective is to maximize profit and keep the long-term stability and sustenance of the firm intact.
Shareholder’s Wealth Maximization Vs. Stakeholder Welfare
Shareholder wealth maximization is a well-accepted corporate objective in almost the whole world, barring a few exceptions. Indisputably, it is a superior and healthier goal than profit maximization, which lacks a long-term perspective. Apart from shareholders, various parties suffer from a business conducted by an organization, viz. employees, customers, suppliers, communities, etc. Wealth maximization as a corporate goal does not mention concerns of any of these parties except shareholders. Hence, a stakeholder’s welfare evolves as a further improved and wider corporate objective.
Management Decision

Should a manager take the decision only for shareholders and neglect the interest of all the other stakeholders? Let us think the other way round. How is a manager able to maximize the wealth and welfare of shareholders? It is only with the support of all the other stakeholders. If the supplier does not supply good raw materials, can managers produce good quality products? If the employee does not work efficiently, can the managers alone do everything? And if the customers are provided with low-quality goods, will they continue buying them? The answer to all these questions is a clear “No.”
If we see, there is simple math. The management is able to serve the shareholder’s objective with the help of other stakeholders of the business, and stakeholders are also not doing it for charity. Naturally, they would also look for their well-being. If their objective is not fulfilled, sooner or later, their interest in working with the organization will be lost, and they may mend their way. Without the welfare of the stakeholders, shareholder wealth creation is not possible.
Different countries support different cultures. In the US, UK, etc., wealth maximization of shareholders is the main corporate objective whereas, in countries like Germany, the interest of the workers is the first priority. In Japanese companies, employees and customers are at par with shareholders.
Growth Requirement
Do you know a tree that grows only one branch and the rest remains the same?
When a tree grows, all its branches grow. Wealth maximization as a sole objective resembles the first situation, which is not practical and possible. At the same time, the stakeholders, including shareholders’ welfare, resemble the second situation, which is natural and healthier.
The growth and development of a business have a number of requirements and not only the money. Shareholders only provide money, and the rest is provided by the other stakeholders of the business. When all the stakeholders share the input required for growth, the outcome in the form of wealth and welfare should also be shared among all the stakeholders.
Also read – Difference Between Shareholders and Equity Holders and Activist Shareholder.
RELATED POSTS
- Activist Shareholder – Who They Are And What They Do
- Friedman Doctrine – Meaning, Importance, Criticism and More
- Agency Theory in Corporate Governance
- Statement of Stockholders Equity – Format, Example and More
- Equity Share and its Types
- Bonus Issue vs Stock Split – Meaning, Differences, Benefits, and Impacts

