What is a Gross Lease?
Gross Lease is the simplest type of lease. In this format, the lessee agrees to pay the lessor a fixed amount of rent to the landlord, which includes all operating expenses for the property. This means that the tenant does not have to worry about paying for additional costs like property taxes, insurance, maintenance, or utilities. Instead, the fixed rent amount includes these expenses. It is a rent agreement in which the lessor bears the cost of keeping up the rented asset, including its protection and charges.
Gross lease rental is usually higher than the net lease rental as the lessor would have factored in different types of expenses in the rentals that are being charged.
Types of Gross Leases
On the basis of requirements, gross leases can be carried out in different variations. It can be entered as an absolute gross lease agreement or can be modified to have the best of both gross as well as net lease features. In some cases, it may be agreed upon as a full-service lease.
Modified Gross Lease
The modified gross lease is a mix of a gross and a net lease. You can also address them as a modified net lease. As the name suggests, in this type of lease agreement, the tenant pays a fixed rent amount that includes some, but not all, operating expenses for the property. This allows for negotiation between the landlord and tenant regarding which expenses are the responsibility of each party.
Also Read: Modified Gross Lease
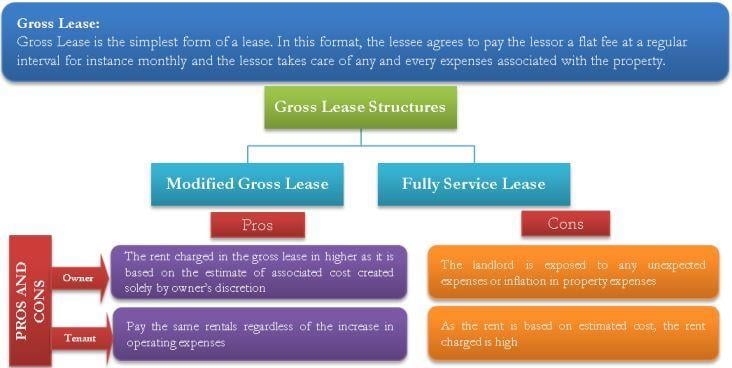
Fully Service Lease
A full-service lease is similar to an absolute or flat gross lease but also contains provisions to pass on some or total inflation in cost to the tenant. Unlike an absolute gross lease, the terms of a full-service lease usually require the tenant to be responsible for any increase in operating expenses beyond the base year of the lease.
Advantages of Gross Lease
The advantage of a gross lease is that it simplifies the rental process for both the landlord and the tenant. Let us look at the advantages to both landlord and tenant.
Advantages to the Tenant
A gross lease can offer several advantages to a tenant, including:
Simplicity
With this type of lease, the tenant pays a fixed amount of rent that includes all operating expenses. This can simplify the rental process and make it easier for the tenant to budget for monthly expenses.
Predictability
Because the tenant’s rent amount is fixed, they don’t have to worry about unexpected increases in operating expenses that could result in higher rent payments.
Also Read: Triple Net Lease (NNN)
Lower Risk
With a gross lease, the landlord assumes the risk of increases in operating expenses. This means that the tenant is protected from unexpected costs that could impact their business or personal finances.
Fewer Expenses to Manage
Since the tenant is not responsible for paying for individual operating expenses, they do not have to spend time managing and paying these expenses.
Reduced Administrative Burden
The tenant does not have to worry about tracking expenses, submitting receipts, or negotiating with the landlord over operating expenses.
Advantages to the Landlord
There are several benefits of a gross lease for a landlord, including:
Predictable Income
With this type of lease, the landlord receives a fixed amount of rent each month, which can help with financial planning and budgeting.
Easier to Lease
A gross lease is simpler to lease than a net lease because there are fewer expenses to negotiate and track.
Reduced Risk
While the landlord assumes the risk of any increases in operating expenses, a gross lease can provide a more stable income stream compared to a net lease, where fluctuations in expenses could impact the landlord’s bottom line.
Lower Vacancy
This type of lease can be attractive to tenants because it provides a predictable rental amount that includes all operating expenses. This can make the property more appealing to potential tenants, leading to lower vacancy rates and higher occupancy levels.
Disadvantages of Gross Lease
While a gross lease can offer advantages to both tenants and landlords, there are also some potential disadvantages to consider:
Disadvantages to the Tenant
The following are the disadvantages to a tenant:
Higher Rent
In this type of lease, the landlord assumes the risk of any increases in operating expenses. As a result, the landlord may charge a higher rent amount to cover these expenses, which could make it more expensive for the tenant.
Limited Negotiation
Since the tenant pays a fixed amount of rent that includes operating expenses, there may be limited opportunities for negotiation on individual expenses.
No Control over Expenses
The tenant has no control over which operating expenses are included in the fixed rent amount, which could result in paying for expenses that they don’t necessarily benefit from.
Disadvantages to the Landlord
The following are the disadvantages to a landlord:
Increased Risk
Since the landlord assumes the risk of any increases in operating expenses, they may be at a disadvantage if operating expenses rise significantly.
Administrative Burden
The landlord is responsible for paying all operating expenses, which can create additional administrative tasks and record-keeping.
Potential for Lower Profit Margins
Since the landlord is responsible for paying all operating expenses, their profit margin may be lower compared to a net lease, where the tenant pays for some or all operating expenses separately.
Gross Lease vs Net Lease
In a gross lease, the tenant agrees to pay a flat rent, and the landlord assumes the responsibility of paying for all the expenses, including maintenance, insurance, and taxes. The cost of these is usually factored in increased lease fees. In a net lease, the tenant, along with the rental fee, assumes some or all the cost of other expenses associated with the property. Thus the rental fee in comparison to the gross lease is less. Net lease is usually long-term in tenure, whereas gross lease is usually short-term.

