The differences between two basic forms of the lease, viz. operating versus finance lease, are mainly of ‘who owns the asset under the lease, what will be the accounting and tax treatment, who bears the expenses and running costs.’ Please note that a finance lease and a capital lease are the same. We will be using these terms interchangeably.
Not only these, but operating versus finance leases also differ in whether a purchase option is present and the length of the lease term.
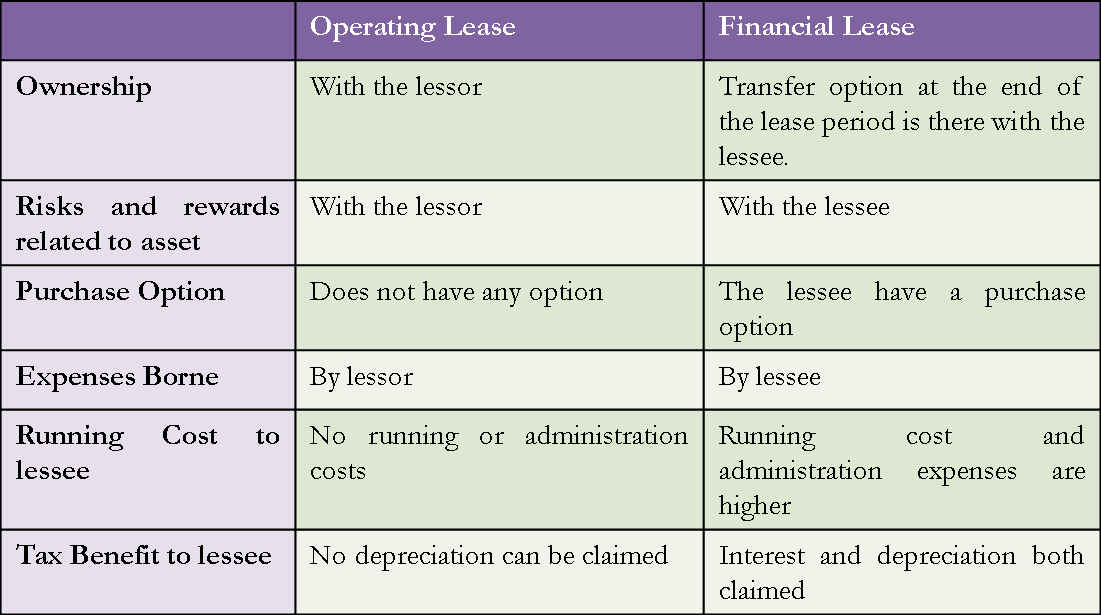
Differences Between Financial (Capital) Vs. Operating Lease
The differences between financial and operating leases are as follows. The explanation of these with the help of the following table against various aspects of operating and financial leases are below.
| Aspects of Difference | Operating Lease | Financial (Capital) Lease |
|---|---|---|
Definition |
An operating lease is a lease in which all risks and rewards related to asset ownership remain with the lessor for the leased asset. In this type of lease, the lessee returns the asset after using it for the agreed-upon lease term. Read more about Operating Lease for in-depth coverage. | In a financial lease (also known as a capital lease), the risks and rewards related to ownership of the asset being leased are transferred to the lessee. Read this article on Finance Lease for more in-depth coverage. |
Ownership |
The ownership of the asset remains with the lessor for the entire lease period. | At the end of the lease period, the ownership transfer option is available to the lessee. The title may or may not be transferred eventually. |
Accounting Effect |
An operating lease is generally treated like renting. That means the lease payments are treated as operating expenses, and the asset does not show on the balance sheet. | A financial lease is generally treated as a loan. The lessee considers asset ownership here, so the asset appears on the balance sheet. |
Aspects of Difference |
Operating Lease | Financial (Capital) Lease |
Purchase Option |
In an operating lease, the lessee does not have an option to buy the asset during the lease period. | A financial lease allows the lessee to have a purchase option at less than the fair market value of the asset. |
Lease Term |
The lease term extends to less than 75% of the projected useful life of the leased asset. | The lease term is generally the substantial economic life of the asset leased. |
Expenses Borne |
The lessee pays only the monthly lease payment in an operating lease. | In a financial lease, the lessee bears the cost of insurance, maintenance, and taxes. |
Tax Benefits |
Since an operating lease is as good as renting, the lease payment is considered an expense. No depreciation can be claimed. | The lessee can claim interest and depreciation, as a financial lease is treated as a loan. |
Running Cost |
In an operating lease, no running or administration costs are borne by the lessee, including registration, repairs, etc., since this lease gives only the right to use the asset. | In a financial lease, running costs and administration expenses are higher and are born by the lessee. |
Example |
Projectors, Computers, Laptops, Coffee Dispensers, etc. | Plant and Machinery, Land, Office Building, etc. |
Quiz on Difference between Operating and Financial Lease
This quiz will help you to take a quick test of what you have read here.


Thank you for a clear explanation!
Good And easily understandable.
can u please provide the same for Deffered tax asset and Deffered tax liability
can u please provide the same for Deffered tax asset and Deffered tax liability
Very well explained and easy to understand.
thanks was clearly explained
Still don’t get it straight…. a little bit of confusion…
Does it mean that if I buy a car to lease to someone who needs my services for two years and the year ends I can still own the car and that is operation lease?
Hi Nana,
Thanks for asking the question and sorry for a delayed revert.
You can lease out a car for 2 years to somebody. If, technically, the risks and rewards associated with the asset lie with you, yes you can call it an operating lease. In operating lease, the ownership is not transferred to the car user but you remain the owner of the car. In your case, the lease term is also less than 75% of the asset life, here also it qualifies to be called as an operating lease. I assume the life of a car is much more than 2 years.
Thanks.
Very good explanations.
But I have a problem with the accounting effect of operating lease. The “substance over form” concept of accounting requires that we treat transactions according to their economic impact but not their legal form and hence asset leased to a lessee should be recorded in the lessee’s balance sheet as he derives economic benefit from it.
PLEASE I NEED CLARIFICATION ON THIS.
Hi.
Thanks a lot for this information. However I would like to ask something.
I am not sure, but I have the feeling that after the ASC 842, even for Operatin Leases the lessee has the obligation to show the asset in the Sheet Balance. As I understood, either for Finance and Operating leases, the balance sheet must record a right-of-use asset and a lease liability. Is this correct or am I wrong?
I would really appreciate if you could clarify this question.
Thanks.
You are correct. They are recorded as right to use asset.
This was explained well and very easy to understand. Can you please describe what the substance of changes which will be brought about by IFRS 16 in 2019
I have read this publish and if I may just I desire to suggest you few fascinating issues or tips. Maybe you can write next articles referring to this article. I want to learn more things approximately it!
I love reading through and I believe this website got some genuinely utilitarian stuff on it!
Please provide me the legal link about the topics.
crystal clear.