Exchangeable Bonds are a way to ease the interest rate burden on the company for a short while. A company’s financial structure is based on different types of financial instruments, with bonds being one. Bonds are a debt instrument that companies issue for acquiring funds for their business and pay interest on the same. A high-interest rate is not payable on every debt instrument in this volatile business environment. So, they issue exchangeable bonds on which the rate of interest or the coupon rate is low. The company offers purchase options of shares of other companies, especially in the subsidiaries, to compensate for the lower coupon rate.
What are Exchangeable Bonds?
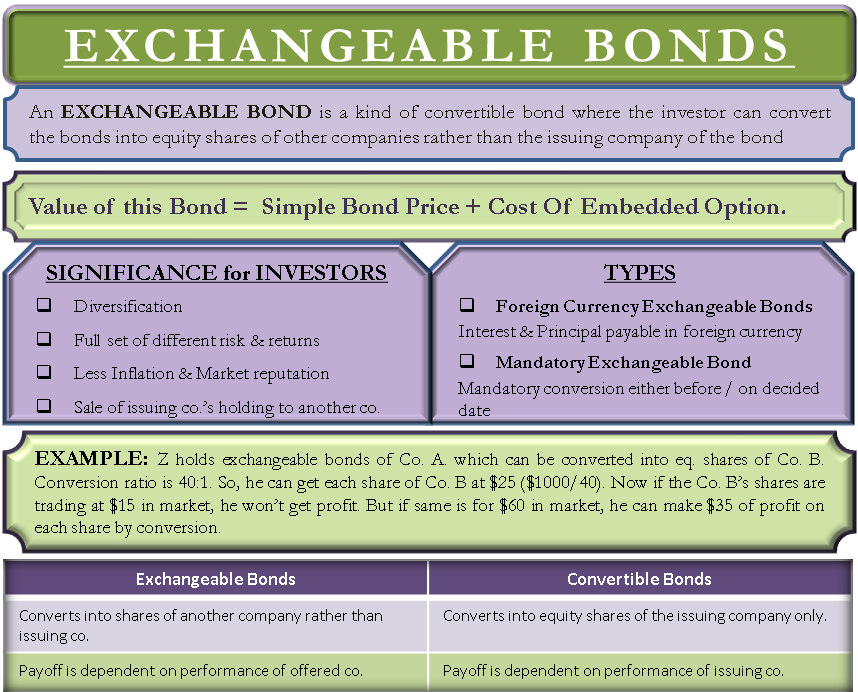
An exchangeable bond is a diversified debt instrument. The rights of the bondholder are exercised to purchase shares of other companies with this bond. It is a kind of convertible bond where the investor can convert the bonds into equity shares of other companies rather than the issuing company of the bond. In most cases, the option is exercised to purchase shares of subsidiaries of the issuing company. There are certain conditions which are needed to be satisfied to convert this bond. There is a specific time limit for the conversion of the bonds. Bond indenture specifies the time limit or debt maturity, conversion price, conversion ratio, and other terms and conditions.
The coupon rate on these bonds is lower than normal or straight bonds as the former has the provision for exchange. Exchangeable bondholders have the right to take part in the company’s share price appreciation which straight bondholders don’t have.
Types of Exchangeable Bonds
There are two other kinds of Exchangeable bonds apart from normal exchangeable convertible bonds, which are –
Foreign Currency Exchangeable Bonds
In this type of bond, the interest amount and the principal is payable in foreign currency. The offered company, which is the company whose equity shares can be purchased by the bondholder to exercise the right to conversion, must receive foreign investments.
Also Read: Foreign Currency Convertible Bond (FCCB)
Mandatory Exchangeable Bonds
These bonds have to be converted to equity shares before or on the predetermined date for conversion. The bondholder is bound to exercise his right for the conversion of bonds into equity shares.
What is the Value of an Exchangeable Bond?
Exchangeable bonds are higher in value than simple bonds. This is because of the added option of conversion. The price of these bonds is the summation of the simple bond price and the cost of the embedded option. It is at the discretion of the bondholder (except for mandatory exchangeable bonds) whether he wants to convert the bonds into equity shares or not. He can convert if the underlying shares would give more return/profit. Otherwise, he can redeem the bond at par on maturity earning the interest gained.
Example of Exchangeable Bonds
Suppose you hold exchangeable bonds of Company A, and you can convert them to the equity shares of Company B. Given the conversion ratio is 40:1, which means for every $1000 you have in Company A’s bond at par value and can purchase 40 shares of Company B. So, effectively you can get each share of Company B at $25 ($1000/40). Now, if Company B’s shares are trading at $15 in the market, you won’t get any profit by converting your bonds into it. But if the same is trading for $60 in the market, you can make $35 of profit on each share. In such a situation, you can use your call option on exchangeable bonds of Company A to convert the same into Equity shares of Company B.
How is it Different from Convertible Bonds?
The main difference between exchangeable and convertible bonds lies in conversion. The former converts into shares of another company rather than the company issuing the bond. Similarly, the latter converts into equity shares of the issuing company only. The payoff of the exchangeable bonds is dependent on the performance of the offered company, and for the convertible bond, the issuing company’s performance matters.
Significance of Exchangeable Bonds
Exchangeable bonds are a good candidate for creating diversification in the portfolio. It provides a complete set of different risks and returns from the issuing company to the investors. Another attractive fact about these bonds is they provide some kind of inflation protection. When the share price of the underlying asset is below the exchange price, these bonds yield like a bond, but when the share price is above the exchange price, they act like stocks.
From the company’s point of view, issuing these bonds is done to sell a large portion of their holdings to another company. The issuer dilutes its shareholders by selling its shares directly to the other company. It also affects the market reputation. Doing this using exchangeable bonds will save these issues from arising.
Conclusion
Exchangeable bonds are profitable from both company’s and investor’s aspects. Investors have the right to take part in the share price appreciation of the offered company. It can increase their return on investment without diluting the issuing company’s shareholding.
Also, read Bonds and their Types to know about various other types of bonds.

