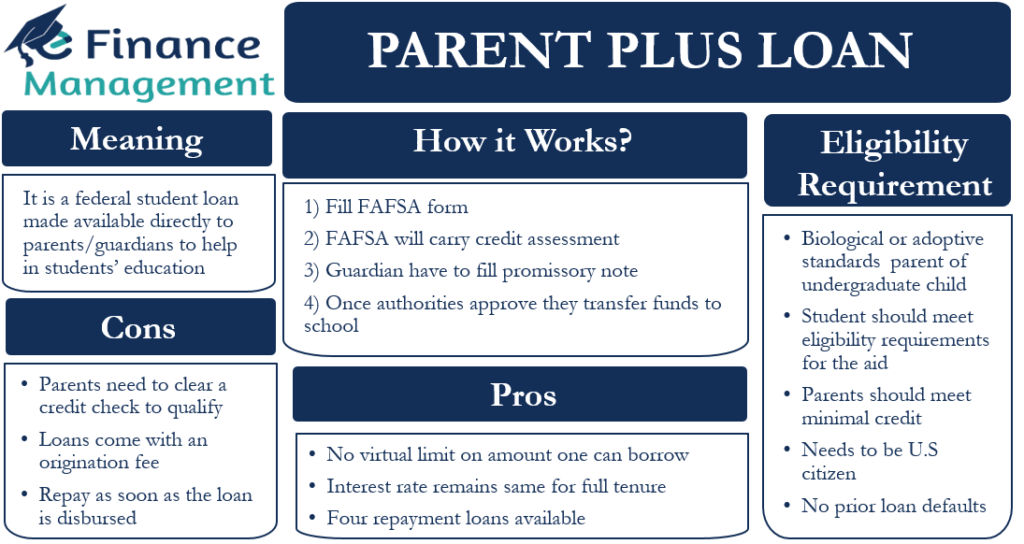
Parent PLUS Loan is a type of federal student loan that is made available directly to the parents or guardians to help in covering the cost of students’ education. This loan is part of the Direct PLUS loan, which is a federal student loan program.
Such a loan program allows the parent to get funding up to the cost of attendance of their child’s school, less financial aid that the child already got. The biggest plus of this type of loan is that it offers parents flexible repayment options.
A point to note is that such a credit is the financial obligation of the parents or guardians and not of the students. This means the parents can not transfer the financial burden of the loan to students after the completion of school.
Also, such a loan has no grace period. This means parents need to start repaying the loan as soon as the authorities disburse it. There is, however, an option for the parents to request some delay in making the payments. Parents need to contact their loan servicer to get more details on this front. Even if their request to delay is approved, parents are still responsible for the interest obligation during the deferment period.
Interest Rate on Parent PLUS Loan
The interest rate for the Parent PLUS loan is typically more in comparison to a private student loan. Also, the interest on this loan could be more than the rate of other possible sources of finance. This means that if you own a home, you could be able to take a mortgage loan at a lower rate than this federal loan.
These loans also attract an origination fee along with a higher interest rate. The parent must pay the origination fee for each loan when applying for a loan. Authorities deduct this fee before disbursing the loan. But, they calculate the interest on the gross amount of loan sanctioned, i.e., before deducting this fee.
How Parent PLUS Loans Works?
The first step in getting this loan is to fill out the FAFSA. Once the parent fills out the FAFSA, the authorities would carry out a credit assessment to find out any recent defaults or late payments. Once this primary evaluation is over, the parents or guardians are required to fill and submit the promissory note. This note covers the various terms and conditions of the loan, amount sanctioned, rate of interest, and the repayment plan. The form of this promissory note is available on the school’s financial aid office web page. The same can be downloaded for further completion.
Once authorities approve the loan application, they would send the funds to the school directly. The school will use the funds first for payment of the student’s tuition and school fee, room and boarding charges, and any other school expenses. Moreover, if any surplus fund is available after applying for the school charges, then it is transferred to the parent or guardian. It can also be transferred to the student after getting permission from the parents.
A point to note here is that parents can choose to borrow part of the funds available under the Parent PLUS Loan. In case they borrow a part amount, the remaining they can fund from other sources, such as their own income, private loan, student income, or more.
Eligibility Requirements
Parent PLUS loan has easy and clear-cut eligibility requirements. These are:
- The applicant parent should be a biological or adoptive parent of an undergraduate child. Moreover, the applicant’s parent income tax return should have claimed the child as a dependent one.
- The student needs to meet the usual eligibility requirements for the aid.
- Parents should meet minimal credit standards. If parents fail to pass the credit check, they can still qualify for the loan. But for that, they need to get an endorser or win approval from the Department of Education by explaining to them the circumstances resulting in their bad credit history. However, there are no minimum credit score requirements as such.
- The student must not have any prior student loan defaults.
- If the loan is for a male student aged 18 to 25, then he needs to register for Selective Services.
- And the last but the most important requirement is that both the applicant parents and the students should be US Citizens. Or they both should be eligible non-citizens.
What Credit Score You Need?
A Parent PLUS loan is very different from private loans that put more emphasis on parents’ creditworthiness to determine their eligibility for the loan and the loan terms.
However, the parents should be able to meet the standard credit requirements for being eligible for grants of such loans. Of course, there is nothing like minimum credit score requirements. Though there is no requirement for a credit score, parents still need to pass a credit check. What all this means is that the credit history of the parents plays an important part in the sanction of such loans. And any adverse status may make it difficult.
Thus, it is crucial that the parents evaluate their credit history themselves before going for this loan. One easy way to do this is to get a credit report from a credit reporting bureau (Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion). One can ask for this credit report free of charge from these agencies once a year.
Do they Qualify for Public Service Loan Forgiveness?
Yes, these types of loans do qualify for Public Service Loan Forgiveness or PSLF. However, for availing of such a facility, there are a few qualifying criteria that one needs to fulfill. These are:
- In the past, one must have made 120 on-time payments.
- The applicant’s parent should be an employee of a qualified company.
- Moreover, one should fall under an eligible repayment plan. One such option is to be under the income-driven repayment plan. And for this eligibility, one must first add the loan into a direct consolidation loan.
Parent PLUS Loan: Pros and Cons
Following are the benefits of this type of loan:
- This loan has no virtual limit on the amount one can borrow. Specifically, one can borrow up to the cost of attendance less any other available grant, scholarship, etc.
- During the entire tenure of the loan, the rate of interest remains the same/constant. That means there is no change or fluctuations in the rate of interest during the entire tenure. And thus, one will have to pay the same interest rate even if the national interest rate goes up.
- The parent gets to choose from four repayment plans. This unique facility (option) is not available with other loans. These repayment plans are 1. Standard Repayment Plan (pay a fix installment over the tenure of 10 years); 1. Graduated Repayment Plan (small payment initially and payment increases gradually over 10 years); 3. Extended Repayment Plan (pay fix or increasing payment over 25 years); and 4. Income-Contingent Repayment (pay lower of the two: 20% of your discretionary income or an amount equaling in a 12-year plan).
Following are the drawbacks of this type of loan:
- Parents need to clear a credit check to qualify for the loan.
- These loans come with an origination fee. This fee was 4.228% as of Oct. 1, 2020.
- Even though it is a student loan, one needs to start repayment as soon as the loan is disbursed.
- One also needs to pay interest as soon as the loan is disbursed and even if there is a deferment period available.
Parent PLUS Loan or a Private Loan: Which is Better?
Both these types of loans have their share of advantages and disadvantages. So, if one is going for a student loan, then one must evaluate the pros and cons of the Parent PLUS Loan and Private Loan to arrive at a suitable final decision. These pros and cons, as well as the difference between the two loans, are detailed below:
- The biggest plus of a Parent PLUS Loan is that parents can benefit from income-driven repayment plans. And this repayment option is not available to private student loan borrowers.
- Another crucial distinction between the two is regarding the collection options. For instance, the government can take your wages, tax refund, or Social Security to collect a federal loan from you. Moreover, parents may not be able to get rid of it at the time of bankruptcy. On the other hand, private student loan lenders do not have the same authority to collect the loan money.
- Another distinction is regarding forgiveness. The forgiveness is applicable in the case of federal loans, where the government forgives the loan when the student or the borrower’s parent dies. On the other hand, private loans may not have such policies.
- Another critical and most important distinction is that the parent loan is sanctioned to the applicant parent for the student. Hence, the responsibility for the payment of such loans remains that of the parents and not that of the students. This could risk the parents’ retirement; thus, many financial experts do not recommend such loans. Whereas in the case of a private student loan, it remains the liability and responsibility of the student for whose benefit the loan was taken.
The biggest advantage of a private student loan is that they come at a lower interest rate. The difference in the interest rate between these two types of loans could be 2% or more, depending on the credit score of the borrower. Such a difference in interest rate could result in noteworthy savings in the longer term.
Final Words
The Parent PLUS Loan could prove great support for parents seeking funds to finance their child’s education. But it has its own comparative advantages and disadvantages. For instance, the Parent PLUS Loan comes with more repayment plans and qualifies for forgiveness. But, the interest rate is relatively more. So, one must evaluate these pros and cons against their own needs to decide whether or not to go for the Parent PLUS Loan.

