Equity Market: Meaning
An equity market is a marketplace where shares of public companies are bought and sold. It is commonplace where the issuers of the shares (Companies) and the subscribers of the shares (Investors) to come together. The trading takes place on a stock exchange or on the over-the-counter (OTC) markets, depending on the type of issue. After the listing of stocks takes place, there is a substantial number of buyers and sellers.
Equity Markets are a win-win situation for the company and the investors. It gives a platform to the companies for raising equity share capital, and investors get a platform for making investments with expectations of getting good returns in the future. Equity Market helps the companies to transform from private to public. The equity market boosts the Equity Financing process. It is also termed as Stock Market or Stock Exchange.
How does Equity Market Work?
The functioning of an Equity Market is a bit similar to that of an Auction Market. In Primary Markets, lots of buyers bid for the stock according to their estimation of the market value within the price bands. The company, after analyzing all bids, allocates the shares according to the timing of the bid and the price band. In the case of the Secondary Market, the companies list their shares on the Stock Exchange or Over-the-Counter Exchange, and the buyer’s bid for the same. Prices of the security fluctuate according to the demand-supply factor. In the case of the Primary Market, the issuance takes place directly from the companies end through an IPO (Initial Public Offering) and FPO (Follow-on-Public Offering). In the case of the Secondary Market, the buying and selling of shares occur from one shareholder to another through the broker on the stock exchange.
Stock Exchange or Over-the-Counter
In the investment world, the purchase or sale of shares and securities can be from publicly listed and traded securities, or it could be privately traded shares and securities. The buying and selling of the shares can be in the form of publicly-traded securities or privately-traded securities. Trading of public stocks takes place on Stock Exchanges, and that of private stock takes place on Over-the-Counter Markets. The Company has an option of listing its shares on a Stock Exchange or on the OTC Market.
Also Read: Stock Exchange
Stock Exchange functions on a centralized system in a systematic manner. Here there is no involvement of any third party like dealers in the trade. The trading takes place through a designated exchange and in a completely transparent manner. The exchange could be a physical place or a virtual place. The prices offered for particular security remain the same for all investors, as all trades are undertaken from the same place. The exchanges are continuously monitored by the Authority, like the Securities Exchange Commission (SEC) of the USA, Securities Exchange Board of India (SEBI) of India, etc. Trading through Stock Exchange eliminates counterparty risk.
Over-the-Counter (OTC) Markets work on a decentralized system. Third-parties like brokers and dealers play a very vital role in making this whole system work. They are the ones who mostly quote the prices of stock. There exists a high counterparty risk in OTC Markets. It is less transparent and less regulated.
Types of Equity Market
The division of Equity Markets takes place in two major types, i.e., Primary Market and Secondary Market.
Primary Market
The type of Equity Market, where the shares are sold directly by the company to the public, is known as the Primary Market. The issuance is through Initial Public Offering (IPO) or Follow-on-Public Offering (FPO). In this market, the company dilutes its ownership in the company by offering it to the public. Primary Market gives a platform to the private company to metamorphose into a public company. Mostly in this market, the issuance of shares takes place for the first time.
Secondary Market
The type of Equity Market where trading of already listed shares takes place is known as the Secondary Market. Here, the buying and selling of shares take place from one investor to another. There is no direct trading between the company and a shareholder. In this Market, there is no dilution of ownership by the company; existing listed shares are only traded in this market.
Secondary Market gives an opportunity to all those investors who could not subscribe or could not get an allotment of shares in the Initial Public Offer of the company in the Primary Market.
Participants of Equity Market
Let’s look at a few Equity Market participants which play a different set of rules.
Companies
There are many companies from different sectors, segments, countries, sizes, etc. issue their shares in the Equity Market for the general public.
Retail Investors and Institutional Investors
Both types of investors play a very important role in Equity Markets. Retail Investors are individual investors, investing a smaller chunk. Institutional Investors make investments in a larger chunk.
Financial Intermediaries
There are many Financial Intermediaries in the Equity Market, which makes this market function well.
Depository and Depository Participants are the authorized body who are responsible for keeping the share certificate safe with them. The certificate can be in electronic form or physical form.
Clearing Houses are the second most important participants in the Equity Market. Their main job is to settle all the trades within 2-3 days of the trade.
Stock Brokers are licensed financial intermediaries, linking investors and the stock exchange, thereby facilitating the trade.
Stock Exchanges act as a platform for trading in an Equity Market.
Banks are an important participant which transfers funds for facilitating trade.
These were important financial intermediaries in the Equity Market.
Regulatory Authority
The Regulatory Authority acts as a watchdog in the Market. Their main role and objective are to ensure and see that no fraud takes place and investors’ interest is taken care of in all the regulatory, controlling, and operational matters. If any participant works unethically, they have full authority to take any stringent action. The Securities Exchange Commission (SEC) is the regulatory body of the USA, and the Securities Exchange Board of India (SEBI) is the regulatory body for India.
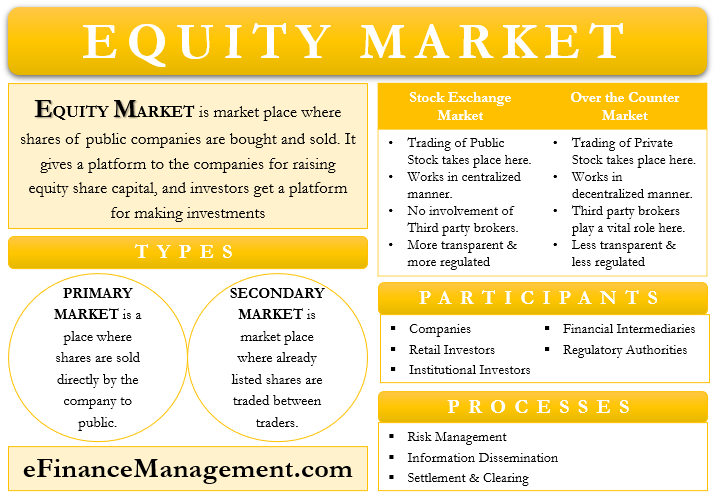
Procedures of Equity Market
Equity Market performs many procedures, apart from trading. Other procedures are as follows:-
Risk Management
The Equity Markets, with the help of the Securities Exchange Commission (SEC), tries to work in the best interest of the investors. It tries to reduce the risk for the retail investors by curbing frauds initiated by the Company. The Equity Market adopts many practices like margin requirements, liquid assets management, and voluntary closeout for Risk Management.
Information Dissemination
The Stock Exchanges also insist the company to regularly file information about the company and any change in its management, developments in the board meetings, a decision with regard to the declaration of dividend, rights or bonus issues, etc., for timely dissemination of information to the investors. So, they can make an informed decision with regard to investments.
Settlement and Clearing
The Stock Exchange of the country acts as a settlement and clearinghouse for the trade settlement. After the trade takes place, it takes 2-3 days for the stock exchange to clear and settle the trade.
Apart from Trading, the above-mentioned were some important procedures conducted by the Equity Markets.
Advantages of Equity Market
- Equity Markets help in the creation of wealth for the investors by getting ownership in the company. It is a tool useful for investors to make high profits.
- It is a platform that gives access to a cheaper source of finance for the issuing company.
- This Market boosts the Company’s expansion and research and development targets.
- Equity Market gives Companies a platform for making them visible to the world.
- A presence in Equity Market claims stability and attracts investors, including Foreign Direct Investments (FDIs) and Foreign Portfolio Investments (FPIs).
- It provides liquidity for investors. They can easily enter and exit the markets.
- The investors get a dividend return and capital gain return, which is, however, not fix in nature.
- The investors have limited liability in the company. The risk is borne only to the extent of ownership.
- By having part ownership, the shareholders enjoy voting rights in the company and are able to vote on the important decisions of the company.
- The Equity Market frees the company from any interest rate burden as there is no commitment about dividend on equity by the company.
Disadvantages of Equity Market
- Equity Market’s volatility is the biggest risk for the issuing company and the subscriber.
- This market does not give a guaranteed return to the investor.
- As Equity shareholders have ownership in the company, at the time of liquidation, they get money on the basis of the residual claim.
- One of the biggest disadvantages of the Equity Market is that disclosure of a lot of information takes place for the general public at large.
The advantages and disadvantages are non-exhaustive in nature.
Conclusion
The equity market is an important financial market that keeps the economy running. Irrespective of all of its limitations, it is helpful for the investor, company, and the country at large. A country with a stable equity market is considered a good country. In conclusion, the Equity Market, along with all other participants, acts as a backbone of the economy.
Quiz on Equity Market
Let’s take a quick test on the topic you have read here.

