Michael Porter is a well-known management expert who developed three generic competitive strategies in 1985. The motive behind this was to help businesses deal with the five forces affecting their industry. These forces include:
- Bargaining power of buyers,
- Suppliers,
- Existing competitors,
- Potential new entrants, and
- The threat of substitutes.
Porter’s three generic competitive strategies are:
- Cost leadership,
- Focus, and
- Differentiation.
The differentiation strategy is one of these three strategies and involves creating a unique product or service that sets a business apart from its competitors. In this article, we will explore the differentiation strategy and its benefits and drawbacks.
What is the Differentiation Strategy?
The differentiation strategy is a way for businesses to stand out from their competitors by creating a product or service that is unique and desirable to customers. This can be achieved through a variety of means, such as innovative product design, the use of advanced technology, special features or high-quality materials. The aim is to create a product or service that is perceived as superior to those offered by competitors and which customers are willing to pay a premium price for. By doing so, businesses can establish a competitive advantage and defend their position against rivals. Moreover, this strategy can enable businesses to earn more profit as customers are less sensitive to price. This is because the product or service offers superior value.
Advantages: Differentiation Strategy
For Company
Reduced Price Sensitivity
By differentiating products or services, companies can create a unique value proposition that sets them apart from their competitors. This can result in customers being less price-sensitive and more willing to pay a premium for the unique features or benefits that the company offers.
A great example of this is Apple. It differentiates its products through design, functionality, and user experience. This allows the company to charge premium prices for its products compared to its competitors.
Build Brand Loyalty
Differentiation can also help build brand loyalty by creating a strong emotional connection with customers.
Nike’s branding strategy focuses on differentiation by creating a unique image that is associated with its products. The company’s “Just Do It” slogan and the iconic “swoosh” logo have helped to differentiate the brand from its competitors, creating a loyal customer base that is willing to pay a premium for Nike’s products.
Reduce Competition
By creating a unique product or service, companies can reduce competition and increase their market share.
For example, Tesla uses a differentiation strategy by producing electric cars with advanced technology and unique features, such as self-driving capabilities. This has helped to reduce competition in the electric car market and has allowed Tesla to dominate the industry with a large market share.
Increased Profit Margins
By offering a differentiated product or service, companies can often charge premium prices, leading to higher profit margins. Additionally, by reducing price sensitivity, companies can maintain these higher prices over the long term, leading to sustained profitability.
An example of this is Starbucks, which has differentiated itself through high-quality coffee, comfortable stores, and personalized customer service. This allows the company to charge premium prices for its products and maintain high-profit margins despite the presence of competitors.
For Customer
Improved Product Quality and Performance
Differentiation strategy often involves investing in research and development to create high-quality and innovative products that meet or exceed customer expectations.
For example, Apple’s iPhone differentiates itself from other smartphones on the market by offering unique features like the Face ID facial recognition system and the Apple A-series chips that provide exceptional performance and energy efficiency.
Enhanced Customer Experience
Companies that differentiate themselves often prioritize delivering exceptional customer service and support.
For example, the Ritz-Carlton Hotel Company differentiates itself by providing personalized service. This includes anticipating guests’ needs and preferences and tailoring their experience accordingly.
Time and Energy Savings
While increased brand loyalty is primarily a benefit to the company, it can also provide benefits to customers, such as time and energy savings. A customer who is loyal to a particular brand is likely to trust the quality and consistency of the products or services offered by that brand. And they may be less inclined to spend time and effort researching and comparing alternatives. This can save the customer time and effort in decision-making and may result in a more satisfying overall experience
Greater Choice and Variety
Differentiation strategy can also lead to increased product variety and customization options that cater to individual customer preferences.
For example, Starbucks offers a wide range of coffee beverages and customization options that allow customers to personalize their drinks.
Status Symbol
When a company creates a unique and desirable product or service that stands out from competitors, customers who use or own that product or service may feel a sense of status or prestige. This can be particularly true for luxury goods and services, such as high-end fashion brands like Louis Vuitton or luxury car brands like Rolls-Royce, where the price and exclusivity of the product can be seen as a symbol of wealth and social status.
In addition to luxury brands, status symbol benefits can also be seen in other industries. For example, owning an iPhone may be perceived as a status symbol due to its high price point and association with Apple’s reputation for quality and innovation. Similarly, driving a hybrid or electric car like a Tesla may be seen as a symbol of environmental consciousness and progressive values.
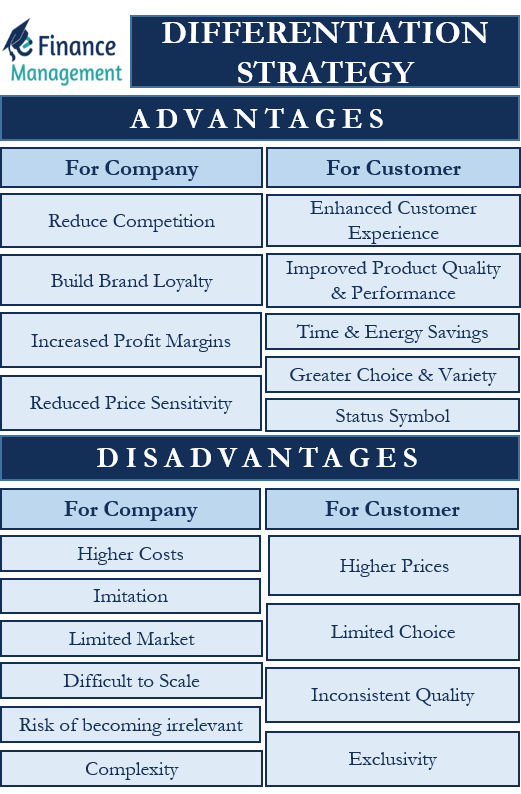
Disadvantages: Differentiation Strategy
For Company
Higher Costs
Differentiating products or services can require significant investments in research and development, marketing, and other areas. Companies may need to spend more on high-quality materials, skilled labor, and specialized equipment in order to create products or services that stand out from the competition. These higher costs can reduce profitability and may also make it difficult for companies to compete on price.
For example, Rolex is a luxury watch brand that differentiates itself by producing high-quality, prestigious timepieces. However, this differentiation strategy comes at a cost – Rolex watches are often priced much higher than those of its competitors, making them less accessible to a broader market.
Imitation
Companies that successfully differentiate their products or services may also be at risk of imitation from competitors. Competitors may attempt to replicate the differentiated features of a product or service. This can result in reducing the unique value proposition of the original company. This can lead to a decrease in market share and profitability.
For example, Nike is a global sportswear brand that has faced imitation of its differentiated products, such as its iconic sneakers, from competitors such as Adidas. Nike has also faced lawsuits related to intellectual property infringement and imitation of its products.
Limited Market
Differentiated products or services may be less accessible to customers who are not willing to pay a premium for unique features or attributes. This can limit the potential market for a company’s products or services. And also make it difficult to expand into new markets where customers may have different preferences or price points.
For example, Ferrari is a luxury sports car manufacturer that differentiates itself by producing high-performance vehicles with iconic designs. However, this differentiation strategy comes at a cost – Ferrari’s cars are often priced higher than those of its competitors. This makes them less accessible to a broader market.
Difficult to Scale
Companies that differentiate themselves through high-quality, personalized, or artisanal products or services may find it difficult to scale production and distribution as they expand into new markets. This can lead to longer lead times, higher costs, and reduced consistency or quality, which can negatively impact customer satisfaction and loyalty.
For example, Hermes is known for its high-quality, handmade products that command premium prices. However, the difficulty of scaling up production to meet demand means that Hermes is not able to fully capitalize on the demand for its products. While this strategy maintains the exclusivity of the brand, it also limits the company’s potential for growth. And this can lead to a secondary market for counterfeit goods.
Risk of Becoming Irrelevant
Companies that differentiate themselves through unique products or services may also be at risk of becoming irrelevant if customer preferences change or if new competitors emerge with even more innovative or differentiated offerings. This can result in a decline in market share, profitability, and brand equity.
For example, Nokia was once a leading player in the mobile phone market. But it failed to keep up with changing customer preferences and the shift towards smartphones. As a result, Nokia’s once-differentiated products became less relevant, and the company lost market share.
Complexity
Differentiating products or services can increase the complexity of a company’s operations. This can be particularly in areas such as supply chain management, production, and quality control. Companies may need to invest in additional resources and expertise to manage this complexity. This can result in increased costs and reduced efficiency.
For example, Nestle is a global food and beverage company. It produces a wide range of differentiated products, such as premium chocolates and gourmet coffee. Managing the supply chain for these products can be complex, as Nestle sources ingredients from all over the world and must ensure the quality and consistency of its products across different markets.
For Customer
Higher Prices
Companies that use differentiation strategies often charge a premium for their products, which can make them more expensive for customers. This can limit the accessibility of the product and exclude some customers who cannot afford it.
Apple’s iPhones are known for their high-quality design and advanced features. But they also come with a premium price tag that may make them inaccessible to some customers. This can be seen in emerging markets where low-cost smartphones from competitors such as Xiaomi and Huawei are gaining popularity.
Limited Choice
Differentiation strategies often focus on offering a limited range of products that have specific features or benefits. This can limit the choices available to customers and make it difficult for them to find a product that meets their specific needs.
Tesla is known for producing electric vehicles with advanced technology and long driving ranges. While these features appeal to a specific customer base, they may not meet the needs of all customers who are looking for different features or options in their vehicles.
Inconsistent Quality
Differentiation strategies can involve producing products with unique features or processes that are difficult to replicate consistently. This can lead to variations in the quality of the product, which can be frustrating for customers who expect a consistent level of quality.
Starbucks is known for its high-quality coffee and customer service. But there have been instances where customers have reported inconsistencies in the quality of their drinks or service at different locations. This is very obvious because preparation still involves human intervention, and that may vary. This can lead to a loss of trust and loyalty among customers who expect a consistent experience from the brand.
Exclusivity
Differentiation strategies can create a sense of exclusivity around a product or brand, which can make it difficult for some customers to access or afford the product. This can lead to a sense of exclusion or frustration among customers who feel that they are being left out of the brand experience.
Luxury fashion brands such as Louis Vuitton and Chanel are known for their high-quality products and exclusive brand image. While this appeals to a specific customer base, it can also create a sense of exclusion among customers who cannot afford or access these products. This leads to negative perceptions of the brand.
RELATED POSTS
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Focus Strategy
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Cost Leadership Strategy
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Multidomestic Strategy
- Ansoff Matrix – Meaning, Strategies, Steps and Examples
- Canvas Strategy or Blue Ocean Strategy – Meaning, Benefits, and Steps
- Strategic Options

