An intangible asset is a useful resource without any physical presence. Patents, copyrights, trademarks, goodwill, etc., are intangible assets. Such assets produce economic benefits, but you can’t touch them like other physical assets like Property Plants and Equipment (PPE).
Assets can be classified into different types based on
- Meaning of Intangible Assets
- Types of Intangible Assets (List)
- Goodwill
- Franchise Agreements
- Patents
- Copyrights
- Trademarks
- Licenses
- Broadcast Rights
- Government Grants
- Non-competition Agreement
- Internet Domain Names
- Customer Lists and Relationships
- Backlog of Orders
- Works of Artistic Importance
- Service Contracts and Lease Agreements
- Trade Secrets and Know-how
- Research and Development
- Conclusion
- Convertibility – Current Assets and Fixed Assets
- Physical Existence – Tangible Assets and Intangible Assets
- Usage – Operating Assets and Non-operating Assets
To learn more about the types of assets, refer to the article – Meaning and Different Types of Assets.
This article will focus on understanding the meaning and types of Intangible Assets.
Meaning of Intangible Assets
An intangible asset is an asset that does not have any physical existence. Like tangible assets, you cannot touch or feel them, but they have a current and future value. They are long-term assets of a company having a useful life greater than one year. A business can either develop these assets internally or acquire them in a business combination.
Types of Intangible Assets (List)
Following are the common types of Intangible assets:
Goodwill
It is a type of intangible asset that is recognized when one business acquires another business. Goodwill equals the cost of purchase of the business by the purchasing company minus the value of net assets of the purchased company. It represents the business reputation of a company.
Let’s say; A Ltd. acquires B Ltd. for $ 10 million. At the time of purchase, the fair value of the net assets (assets-liabilities) of B Ltd is $ 7 million. Here the difference between the cost of purchase of $ 10 million paid by A Ltd. And the $ 7 million net fair value of the assets of B Ltd. is the value of goodwill, which amounts to $ 3 million.
Also Read: Intangible Assets
Franchise Agreements
Franchise agreements are another type of intangible asset that grants the legal right to a business to operate using the name of another company or sell a product or service developed by another company. These are classified as assets because the business owners reap monetary gains with the help of these intangible assets.
For example, many fast-food restaurants like KFC, McDonald’s, Subway, Dominos, etc., operate using a franchise system. Here, the franchisor grants the franchisees a varying amount of autonomy to use the brand name. And benefit from the franchisor’s extensive marketing.
Patents
A patent is a type of intangible asset that grants a business the exclusive right to manufacture, sell or use a specific invention. A company can purchase a patent from another company, or it can invent a new product and receive a patent for it.
Copyrights
Copyright grants an extensive right to the business to reproduce and sell software, book, journal, magazine, etc. It is an intangible asset used to secure legal protection by preventing others from reproducing or publishing a work of authorship.
Also Read: Real vs Financial Assets
Trademarks
A trademark is an intangible asset that legally prevents others from using a business’s name, logo, or other branding items. It is a design, symbol, or logo used in connection with a particular product or a business.
Licenses
A licensor can permit a licensee to use a trademark, patent, or copyright through a license in exchange for a fee or a charge. Such licenses usually have fixed time validity and may even set geographical validity or restrictions. Intellectual property licensing, such as technology transfer, franchising, and publication rights, is very important in present-day business. Violation of the license terms by the licensee or a third party is also a punishable offense under the law.
Broadcast Rights
Broadcast rights enable a broadcasting organization to display or relay products or activities of a trade body on media such as television or the internet. The broadcaster pays a fixed fee for these rights over a fixed period. Such agreements are subject to renewal after expiry.
Broadcasts of football or tennis matches on television or broadcast of movies or shows on the internet are typical examples of the use of such rights today.
Government Grants
Government grants are an essential form of intangible asset. To promote particular business activity or to promote business activity in a specific region, the government provides various grants and financial assistance to companies to encourage them to engage in that activity or region.
One point to be noted with such grants is that these should be recognized and valued only if the company receives these benefits. Also, it should not have violated any of the terms and conditions for such grants, and these should still be valid at the time of sale.
Non-competition Agreement
A non-competition agreement is an agreement between two parties that prohibits one party to work or become a competitor in a certain field. Such agreements are usually for a fixed interval of time. Such agreements may be entered to protect one’s market or a product and are legally binding.
A non-competition agreement is very worthy in cases where only two or three players are present in the market. Hence, these agreements are considered an important intangible asset for any company.
Internet Domain Names
Internet domain names help to identify different resources like a computer, network, or service. They convert complex numbers of resources into easily identifiable names that are easy to memorize. They indicate ownership or control of a useful resource and are treated as an intangible asset for a company.
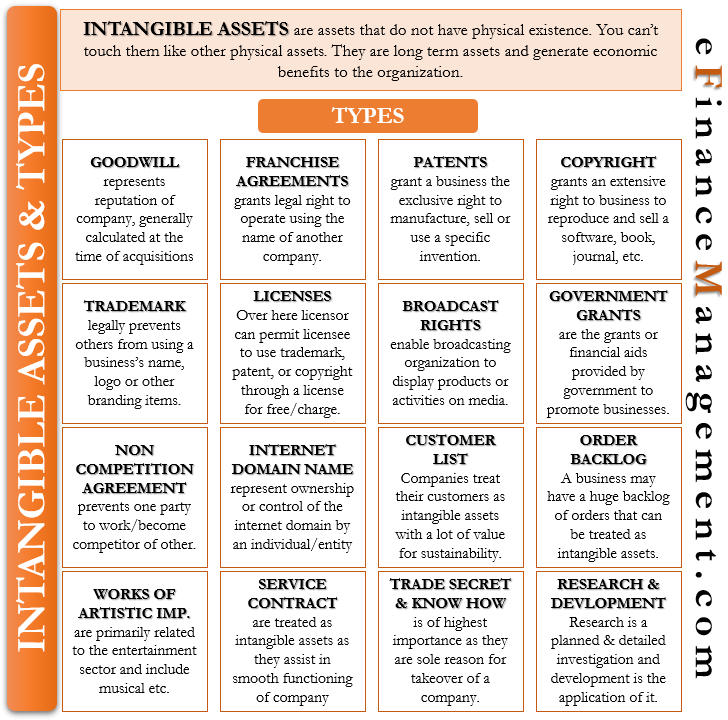
Customer Lists and Relationships
A business takes a long time to identify, build and create a customer base loyal to it and its products. Also, it usually spends a lot to maintain customer relationships to avoid deflecting customers to rival brands and products.
Therefore, companies treat their customer lists and relationships as intangible assets with a lot of value for sustaining and growing their business.
Backlog of Orders
The main goal of any business is to generate orders for its products and services, which in turn will generate revenue for it. A business may have a huge backlog of orders that can be treated as intangible assets. This becomes a boon, especially at the time of sale or takeover of the business.
Works of Artistic Importance
There are many intangibles of artistic importance that are very valuable from an owner’s point of view. Such intangibles are primarily related to the entertainment sector. They include musical or dramatic stage works, audio-visual works, graphic novels and comics, and works of pictorial art and photographic works.
Such assets may also include geographical and other maps, plans and sketches, etc., useful in sectors other than the entertainment industry.
Service Contracts and Lease Agreements
We treat service contracts and lease agreements as intangible assets for a company. It is so because they have a lot of value as they assist in the smooth functioning of an organization. For example, at the time of sale of a company, its service contracts with its existing employees can prove to be a valuable asset. The buyer need not worry about finding new personnel immediately and save a lot of money. Also, subscription contracts of a cable company, magazines, etc., also have a monetary value.
Lease agreements at rates lower than the current market rates can benefit the buying company as it will help in saving a lot of money.
Trade Secrets and Know-how
Trade secrets and know-how are intangible assets of high importance. In fact, they can be the sole reason for the takeover of a company, too, even if it is a very small company.
Some examples of trade secrets and know-how are Coca-cola’s recipe for its highest-selling beverage worldwide. Or the search algorithm of Google or the recipe of burgers of McDonald’s. As we can see, these trade secrets can make or break a company and hence, are of very high value.
Research and Development
Research is a planned and detailed investigation into a product or service for gaining scientific or technical know-how. Development is the application of such research to develop new and better products and services than the current portfolio a company has.
R&D is a part of the internally generated intangible assets of a company. Companies spend millions of dollars on R&D., And hence, it is a valuable intangible asset capable of taking a company to new heights.
Conclusion
Intangible assets lack physical substance, but they have value because of the long-term benefits, exclusive privileges, and rights they provide to a company. Like other assets, companies account for intangible assets in the balance sheet. However, the cost of intangible assets is periodically allocated to the expense during the asset’s useful life or its legal life, whichever is less.
Quiz on Intangible Assets and its Types
This quiz will help you to take a quick test of what you have read here.

