What is Management Accounting?
Management accounting is a very important branch of accounting. It is an important decision-making tool used internally by the management. Tools like budgeting, variance analysis, cost-volume-profit analysis, and BEP are prominent tools used in management accounting.
In simple terms, management accounting is the accounting of an organization’s resources to ensure optimum utilization. It provides top management with the proper insight into their business operations to optimize the utilization of resources and streamline operations.
Definitions of Management Accounting
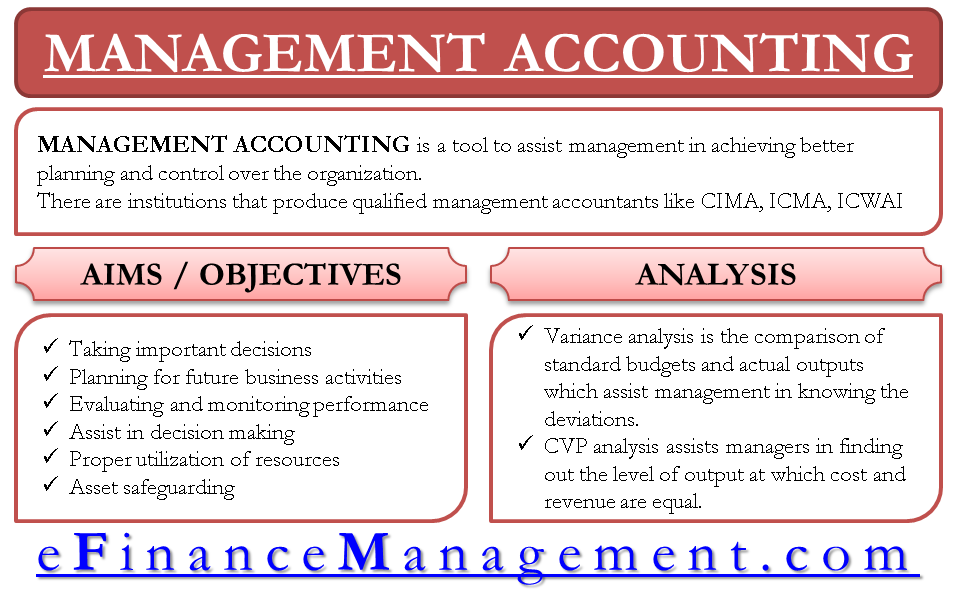
Management accounting is a tool to assist management in achieving better planning and control over the organization. It is relevant for all kinds of organizations, including not-for-profit organizations, government, or sole proprietorships. It has a significant place in businesses and is widely used by management to achieve better control and quality decision-making.
Definition: American Accounting Association
“It includes methods and concepts necessary for effective planning for choosing among the alternative business actions and for control through the evaluation and interpretation of performances.”

Management accounting is not a layman’s job, but educated professionals can do this kind of accounting. There are institutions that produce qualified management accountants. The most prestigious ones include the Chartered Institute of Management Accountants (CIMA), United Kingdom (UK), the Institute of Certified Management Accountants (ICMA), Australia, Institute of Cost and Works Accountants of India (ICWAI), India. Let us look at how CIMA defines management accounting.
Definition: CIMA
“Management accounting is the practical science of value creation within organizations in both the private and public sectors. It combines accounting, finance, and management with the leading edge techniques needed to drive successful businesses.”
Financial Accounting Vs. Management Accounting
Financial accounting and management accounting are significantly different from each other. Like financial accounting, the purpose of management accounting is not ‘Disclosure’ to the stakeholders. Financial accounting is helpful for the stakeholders for their information about the company, whereas management accounting is helpful for the management to make informed decisions about the business. Reports of management accounting are a secret of the company, and hence management does not disclose it to anyone except the core management team responsible for making decisions.
Aim of Management Accounting
The aims behind such accounting are as follows:
Strategic Decision
The management can decide about continuing a product or modifying the sale strategy taking essential strategies based on the information presented in management accounting. Since any law does not regulate management accounting, the management can decide the areas that require more analysis, and investigation and accordingly draw up strategies.
Also Read: Cost Accounting and Management Accounting
Planning Business Activities
Managers can do analysis and plan the activities of the organization. For example, if the recent data shows a dip in sales for a specific region, the sales manager can advise his team and plan some action to rectify the situation.
Evaluation and Monitoring Performance
Monitoring and Evaluation (M&E) is a process that helps improve performance and achieve results. Its goal is to improve current and future management of outputs, outcomes, and impact.
Assisting in Decision-Making
It supplies the necessary information to the management, which may be helpful in its decisions. The historical data is studied to see its possible impact on future decisions. The implications of various decisions are also taken into account.
Proper Utilization of Resources
Management utilizes all the physical & human resources productively, leading to efficacy in management. It provides maximum utilization of scarce resources by selecting its best possible alternate use in industry from various uses.
The basis for Financial Reports
Management accounting provides various periodical reports, which are the basis for the financial reports to achieve the organization’s goal.
Asset Safeguarding
It provides reasonable assurance regarding the prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Scope of Management Accounting
Strategic Management
It involves formulating and implementing the primary goals and initiatives, which the top management of an organization takes on behalf of owners.
Performance Management
It focuses on the performance of an organization, a department, an employee, or the processes in place to manage particular tasks.
Risk Management
It contributes to frameworks and practices of identifying, measuring, and reporting risks to the organization.
Cause and Effect Analysis
It discusses the cause-and-effect relationship, the reason for the loss is probed, and factors directly influencing profitability are studied. And it compares the profits to sales, different expenditures, current assets, interest payable, share capital, etc.
Forecasting
It helps the organization plan and forecast the future course of action based on historical information.
Tools of Management Accounting
There are many tools. Some important ones are discussed below:
Budgeting and Variance Analysis
Organizations prepare budgets for every year, and they are based on the long-term organization planning and hence assist in achieving the long-term goals of an organization. Variance analysis compares standard budgets and actual outputs, which enables managers to know about the deviations from the plans. The deviations can be good or bad, positive deviations are called favorable variance, and negative deviations are called unfavorable variance.
Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis
CVP analysis assists managers in finding out the level of output at which cost and revenue are equal. It is a ‘no profit – no loss’ situation known as the breakeven point.
Other Accounting Tools
Most of the cost accounting techniques are used by management accountants. Other important techniques are incremental analysis, cost behavior analysis, economic order quantity (EOQ), economic production quantity (EPQ) and economic batch quantity (EBQ), return on investment analysis, safety stock, lead time, segment reporting, etc.
Limitations
Data Based on Financial Accounting
Decisions taken by the management team are based on the data provided by financial accounting, cost accounting, and other records. The limitation of these records can become a limitation.
Less knowledge
Management might have insufficient knowledge of economics, statistics, etc., which becomes a limitation.
Expensive
Setting up a management accounting team organization requires a lot of investment.
Outdated data
Management receives historical data. But, when there is a change in the situation, data might not be helpful for decision-making.
Broad-Based Scope
The scope of management accounting is broad. This creates difficulties in the implementation process, leading to in-exactness and subjectivity in conclusions obtained through it.
Provides Only Data
It only provides data and not decisions, and it only informs, not prescribes. One should also keep the limitation in mind while using its techniques.
Continue reading – Cost Accounting and Management Accounting
Quiz on Management Accounting


Very interesting