There are three basic types of financial statements. We categorize another two important parts of an annual report as financial statements. Let’s begin our discussion with a small definition of what financial statements are?
What are Financial Statements?
Financial statements are a mirror that shows a true and fair view of the financial performance of the last financial year and overall financial position at the end of the financial year. These are prepared by all those organizations that have financial transactions, whether for-profit or not-for-profit organizations. The forms could be different. These statements are a crucial part of any annual report of a company.
Financial Statement Analysis
Financial statements analysis takes place after financial statements and reports are published. The main users of these financial statements are shareholders, debenture holders, bankers, financial intermediaries, financial analysts, and all other stakeholders of the business. This helps in overcoming the drawbacks of financial statements.
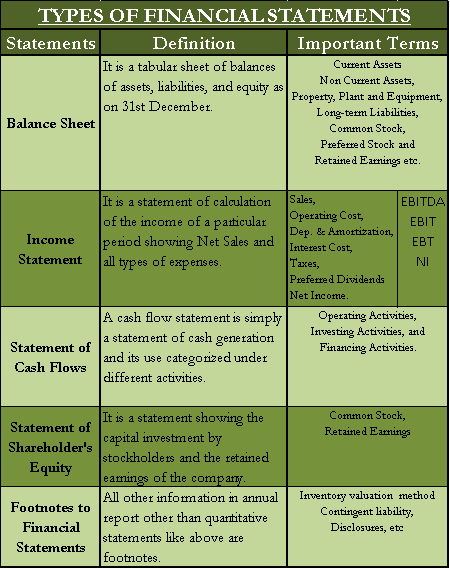
Types of Financial Statement
There are broadly three types of financial statements viz.
- Balance Sheet
- Income Statement
- Cash Flow Statement
Part of the world considers the statement of stockholders equity as another financial statement. In the true sense, explanatory notes in the annual reports should also be called financial statements. These footnotes or explanatory notes to financial statements speak about inventory method contingent liabilities and explain all the important line items of quantitative financial statements. Let’s try to understand each type of financial statement in little depth.
| TYPES OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS | ||
| Statements | Definition | Important Terms |
| Balance Sheet | It is a tabular sheet of balances of assets, liabilities, and equity. | Current Assets Non-Current Assets, Property, Plant, and Equipment, Long-term Liabilities, Common Stock, Preferred Stock and Retained Earnings etc. |
| Income Statement | It is a statement of calculation of the income of a particular period showing Net Sales and all types of expenses. | Sales, Operating Cost, Depreciation and Amortization, Interest Cost, Taxes, Preferred Dividends and Net Income. |
| Statement of Cash Flows | A cash flow statement is simply a statement of cash generation and its use categorized under different activities. | Operating Activities, Investing Activities, and Financing Activities. |
| Statement of Shareholder’s Equity | It is a statement showing the capital investment by stockholders and the company’s retained earnings. | Common Stock, Retained Earnings |
| Footnotes to Financial Statements | All other information in the annual report other than quantitative statements like above is footnotes. | Inventory valuation method Contingent liability, Disclosures, etc |
Balance Sheet
As the term balance sheet suggests, it is a tabular sheet of balances of assets, liabilities, and equity. Assets are normally classified as current assets and property plant and equipment. Liabilities are generally further classified into current and long-term liabilities. Equities are common stock, preferred stock, and retained earnings, all shown separately. There is a great significance in each line item on a balance sheet.
As we just noted that the balance sheet is nothing but a set of balances. Balances can change every day. Therefore, a balance sheet is presented at the end of a particular date. The date for presenting a balance sheet for the annual report is the last date of the financial year. In the US, it is 31st December every year.
Companies show balances of last year and the balances of last to last year for the sake of visible comparison. For example, if the balance of equity at the end of 2018 is 1,000 million and 900 million at the end of 2017, the change in the balance of equity by 100 million is clearly visible. The analysts will understand and interpret this change through their skills in financial analysis.
Income Statement
Unlike the balance sheet, income statements are presented for a period and not as on a date. Here also, as the income statement suggests, it is a statement that shows the calculation of the income of a particular period. The main components of an income statement are net sales, operating cost, depreciation and amortization, interest cost, taxes, preferred dividends, and net income. All the components are deducted from net sales to arrive at net income. After deduction of every type of cost, you arrive at a different interpretation of income which is expressed as below:
Also Read: Presentation of Financial Statements
- Earnings before Interest Tax Depreciation and Amortization (EBITDA)
- Earnings before Interest and Taxes (EBIT)
- Net Income before Preferred Dividends
- Net Income (NI)
It is also known as Profit and Loss Statement.
Statement of Cash flows
All the while, we have heard the importance of net cash flows in calculating the fundamental or intrinsic value of businesses. Cash generation, therefore, has got more value than income reported in the financial statements. It is simply because the real source of value creation is cash and not Income reported on the income statement.
A cash flow statement is simply a statement of cash generation and its use by different activities categorized under three different broad activities i.e.
- Operating Activities,
- Investing Activities, and
- Financing Activities.
There are many factors that make net income totally different from cash balance, and they are
- Noncash adjustment to net income
- Changes in working capital
- Investment
- Capital Inflow and Outflow
- Dividend Payment
The income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement together known as the three statement model
Statement of Stockholders Equity
It is a statement showing the capital investment by stockholders and the retained earnings of the company. Like the balance sheet, a statement of stockholders’ equity is also a statement presented as on a particular date. This date is commonly 31st December in the US. The two main parts of this statement are common stock and retained earnings, and the total of both makes it to total equity.
Footnotes to Financial Statements
You may consider financial statement notes as one of the types of financial statements or additional information to supplement financial statements. It will be misleading for investors if they do not understand the financial statements in their true sense. Footnotes help in clarifying how financial statements are prepared. They provide information about inventory valuation methods, contingent liability, etc. They also offer the disclosures with respect to compliance with Standardized Accounting Principles. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) are followed in the US, and IFRS is the International Standard for Reporting.
Also, read ‘Limitations of Financial Statements.’
Quiz on Types of Financial Statements


Excellent presentations; easy to understand by any level of readers. Congratulations for carrying this wonderful work.
Thanks Mr. Natarajan….
Thanks to do a very important work about financial statement
Thanks for positive words. Keep visiting the site you may get more such important topics.
It’s a very wonderful statement Thanks a lot !!!
Thanking you for giving such value-added information.
very nice I need more information about financial statement thank you
thanks you find our content nice and helpful. You may visit our site. We have more posts on financial statements where you can gain more in depth knowledge and analysis. Thanks
Very helpful!