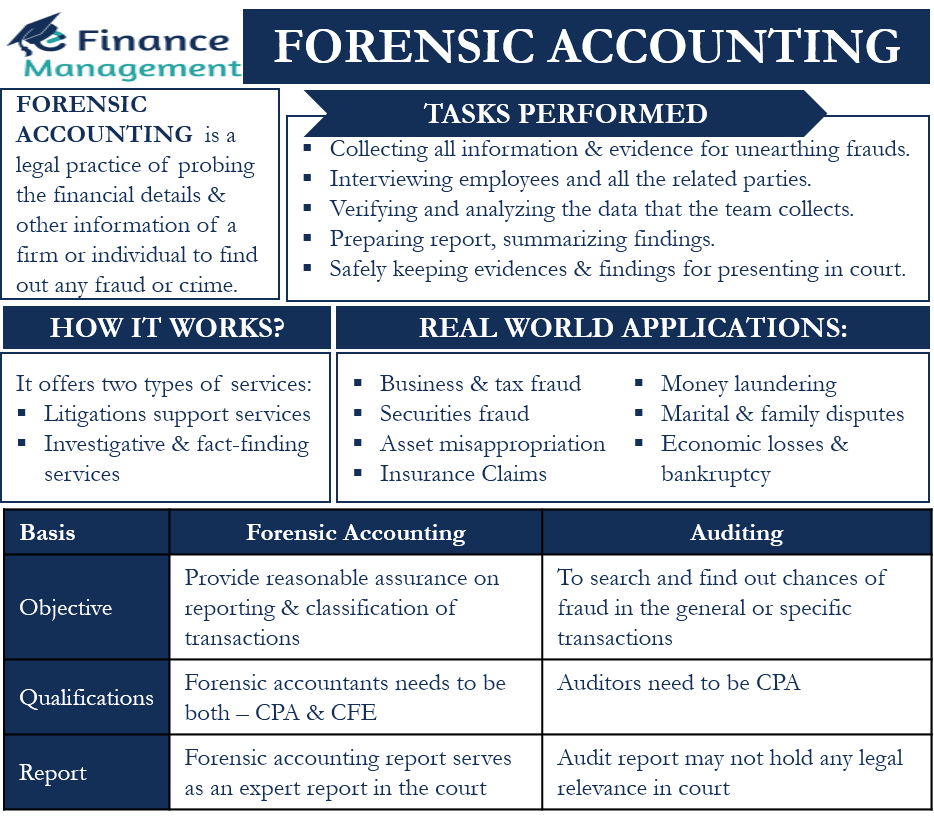
Forensic Accounting is the use of accounting and financial skills to find out whether or not there is any accounting fraud. Every company needs to prepare and report accounting statements. However, there have been instances and chances that those annual reports and statements do not reflect or suppress any financial fraud. Hence, the company and other stakeholders try to find out if there is any financial misreporting or financial crime through forensic accounting. We can also say it is a legal practice of probing the financial details and other information of a firm or individual to find out any fraud or crime.
It will not be wrong to say that it is the use of accounting to unearth scandals involving bankruptcy, insurance claims, money laundering, tax evasion, asset misappropriation, and more. A certified forensic accountant is the one that does such type of accounting.
Every major accounting firm has a department for such accounting. Some of the top forensic accounting firms in the U.S. are Deloitte, PwC, Ernst & Young, KPMG, and Grant Thornton.
Forensic Accounting – How it Works?
A forensic accountant makes use of accounting principles, as well as other financial skills and investigative techniques, to attain the objective. The objective could be to find fraud involving money laundering, tax evasion, etc.
Such an accounting basically offers two types of services:
Litigation support services – in case of a legal dispute, a forensic accountant can help settle the dispute by accurately quantifying the losses. They can either help without court settlement, and if the case reaches the courtroom, they can provide evidence to support their clients’ claims.
Investigative and fact-finding services – here, the forensic accountant needs to find evidence of any employee felony, misappropriation of funds, securities fraud, or more.
Generally, it is a team of forensic accountants that are responsible for carrying out the work. Also, the team could include CPA (Certified Public Accountants) and forensic accountants. The team usually performs the following tasks:
- Collecting all information and evidence that could help in unearthing the fraud.
- Interviewing employees and all the related parties.
- Verifying and analyzing the data that the team collects.
- Preparing reports, summarizing findings, and making recommendations.
- Safely keeping the evidence and findings for presenting in the court.
- Forensic personnel, if there is a need, may also have to testify before the court.
Real-World Application of Forensic Accounting
Forensic Accounting is a niche accounting, but it has many applications in the real world. These are:
Business Fraud
In such a case, a forensic accountant has to deal with asset identification, asset recovery, tracking misappropriation, and more. The primary objective is to identify the offender, and the investigation involves a thorough review of the financial documents and related transactions.
Tax Fraud
Here the accountant needs to find whether or not there is tax evasion. Many people and businesses hide their income and other financial details to lower their tax liabilities.
Also Read: Accountant
Securities Fraud
With globalization and the interdependence of markets, there is a rise in cases involving misrepresenting stocks and other similar investments. Also, the forensic accountant has to deal with scams involving Ponzi schemes, insider trading, and more.
Asset Misappropriation or Hidden Assets
To save on taxes, people and firms try to hide assets or hide the real ownership of assets from the tax authorities. Thus, a forensic accountant has to dive deep into the asset ownership documents to find if there is any misappropriation of assets or hidden assets.
Partnership and Shareholding Dispute
This involves disputes regarding the compensation that shareholders get. In such a case, the forensic accountant analyzes the accounting and financial records to determine the right compensation.
Insurance Claims
In case of vehicle accidents and medical negligence, such an accounting helps calculate the economic damages. The accountants analyze the insurance documents and look into the coverages and settlements to come up with the damages. A point to note is that both policyholders and insurance companies can use the services of such accountants.
Economic Losses and Bankruptcy
Forensic accountants can look into several types of business losses, such as patent infringements, product liability claims, etc. In these cases, the accountant mainly looks into the circumstances resulting in the dispute and uses it to quantify the losses. Also, they work out recovery procedures in bankruptcy cases.
Money Laundering
In such cases, forensic accountants try to find out unlawful sources of money, including un-registered bank accounts.
Marital and Family Disputes
In personal cases also, such as divorces and property disputes, these accountants can help to quantify the compensation.
How Forensic Accounting is Different from Audit?
To many, forensic accounting and audit may look similar. This is because auditors also help to verify the accuracy of the financial statements, as well as point out issues, if any.
- The first and foremost difference is that the auditor gives a reasonable assurance about the reporting and classification of transactions. They will not deep dive if there is no prima facie trigger or clue available to think otherwise. And also if they are satisfied with the explanations offered by the management. But, forensic accountants usually probe the financial statements and quantify the losses that may occur. And they start their work with a clear objective to search and find out if there is any chance of fraud, non-reporting, or financial crime involved in the general or specific transactions. So, auditors do not usually go for investigation unless otherwise, evidence is available. But the, forensic accountants attempt to get those evidence through detailed investigations that go beyond accounting.
- Another difference is that auditors need to be CPA to put their sign on the audit report. Forensic accountants, on the other hand, generally need both the qualifications – CPA and CFE.
- An audit report may not hold any legal relevance in court. But a forensic accounting report serves as an expert report in the court.
Issues with Forensic Accounting
There is a massive demand for forensic accounting nowadays. However, this area has its own challenges. These challenges are:
- First of all, this being an investigative affair, it requires a lot of technical and other skills together with a thorough understanding of financial accounting.
- There are instances when such investigations result in leaking confidential details. This impacts the reputation of the suspect.
- Generally, news of such an investigation attracts negative publicity for the company.
- The kind of skill, exercise, and details needed in this investigation also needs a lot of time, effort, and expense. So forensic accounting is, in a way, quite a costly affair.
Examples of Forensic Accounting
There are many high-profile financial scandals and cases that have highlighted the importance and need of such a type of accounting. These examples are:
Almost everyone is aware of the Enron scandal. It was one of the biggest audit scandals, where the Texas company made false representations by hiding massive debts. After the company’s shares dropped to below $1, the U.S. SEC initiated an investigation.
Lehman Brothers’ bankruptcy is another big example of such an accounting. During the subprime mortgage crisis in 2008, the company’s assets fell apart and went into bankruptcy. After this, the government started investigating the event and found various evidence of account manipulation.
The AIG (American International Group) bailout of $180 billion during the 2008 financial crisis is also an example of such an accounting. Following objectionable financial decisions, the company was also found to be involved in a questionable life insurance scheme. Forensic accountants played a crucial role in uncovering such malpractices.
The case of Jorge Alberto Garcia is the most recent example of this type of accounting. A forensic investigation found Garcia guilty of tax evasion and fraud in November 2021. It was found that Garcia illegally acquired property and money from the public using a home repair scheme by making false representations.
Final Words
With the advent of new financial instruments and cryptocurrencies, there is no doubt that the forensic accounting segment will only grow in the future. Also, such accounting is very important for protecting the financial interest of the general investors.

