IPO Underwriters: Meaning
IPO Underwriters are the ones helping the companies in the public issuance of equity/common stock or preferred stock. They not only help in the public issue but also take responsibility for the distribution of the company’s stock. Sometimes, IPO Underwriters take a risk of buying a company’s stock and later selling it to the public. Thus they bear the whole risk by charging nominal commission or fees. Moreover, at the time of under-subscription, sometimes the IPO Underwriter also buys the company’s remaining stocks so as to avoid the failure of the IPO process.
Roles of IPO Underwriters
There are many roles of IPO Underwriters, but their main role is conducting the whole process of Initial Public Offerings (IPO). In the IPO process, there could be either a single underwriter or a group of underwriters. When the size of issuance is large, there exists a lead investor followed by a group of underwriters working under him and together with him. Thus the number of underwriters in the IPO process would depend on the size of the public issue. The other name of IPO Underwriters is Securities Underwriters or Equities Underwriters.
Mostly IPO Underwriters are Investment Banks and commercial banks, who charge commission/fees for rendering all these services. They are acting as a mediator between the issuing company and the subscribing public or institutions. These Investments Banks work with the issuing company from the start of the issuance process and remain with them till the end when the listing takes place. They perform all the procedures with due diligence. Registration of these Investment Banks takes place as securities brokers or dealers under the Securities Exchange Commission (SEC).
The term Underwriting is useful in different industries with different meanings. Underwriting of loans would be different from underwriting of insurance or underwriting of an IPO, and so on. Thus using this term with the correct context and meaning is important.
Also Read: Types of Underwriters – All You Need To Know
Responsibilities of IPO Underwriters
Let us understand the responsibilities of the IPO Underwriters with the help of step by step IPO process.
Valuation and Expert Advice
The first responsibility of the Underwriter is to provide proposals/options regarding the valuation and type of securities to consider for the purpose of public issuance. The company asks various Investments Banks to provide such proposals stating the valuation and best suitable advice for raising funds.
Underwriter Agreement
The second responsibility is coming up with the best agreement between the Underwriter and the Issuing Company. The Investment Banks bear the responsibility of the Initial Public Offering process according to the type of contract they have signed. The rate of commission is also dependent on the type of agreement. Thus the Investment Banks determine the type of Agreement according to the size of issuance, risk factor, capacity of the underwriter, and so on.
The following are four major types of agreements with different kinds of financial commitments.
Firm Commitment Agreement
Under this arrangement, the Underwriter promises to raise a certain sum of amount. The agreement claims that the Underwriter will buy a whole lot of securities and later sell them to the public. Thus this is the riskiest agreement, where the Underwriter bears the whole risk.
Best-Effort Agreement
As the name suggests, under this agreement, the Underwriter makes its best effort to sell the securities. The Underwriter is not under obligation to sell a certain amount of securities but tries their level best to sell as much security as they can. The amount to be raised is also not fixed here. All unsold shares will go back to the issuing company. The underwriter is not under any obligation to buy the same, as they are only selling on the behalf of the issuing company.
Also Read: Underwriting Syndicate
All or None Agreement
As the name of the agreement says, ‘All or None Agreements,’ which means either the issuance takes place fully, or it completely gets canceled. Under this type of agreement, the issuing company expects the full selling of shares, and if it does not happen, then the cancellation of the public issue takes place. Till the time the issue is not fully-subscribed, all the funds of the public are held in the Escrow Account.
The underwriter makes full efforts to get the issue fully subscribed but does not guarantee anything and does not buy the leftover or unsubscribed stocks.
Syndicate Agreement
The fourth agreement takes place when there is more than one Underwriter. When the size of the public issue is large Syndicate Agreement comes into effect. Under this agreement, the lead Investment Banker forms a strategic alliance with other underwriters. The division of IPO for selling purposes takes place amongst all Investment Banks. In this agreement, it is necessary to submit an S-1 form to the US SEC.
Thus the second responsibility of the Equities Underwriter is to determine the type of agreement for public issues by giving a formal written commitment to the company.
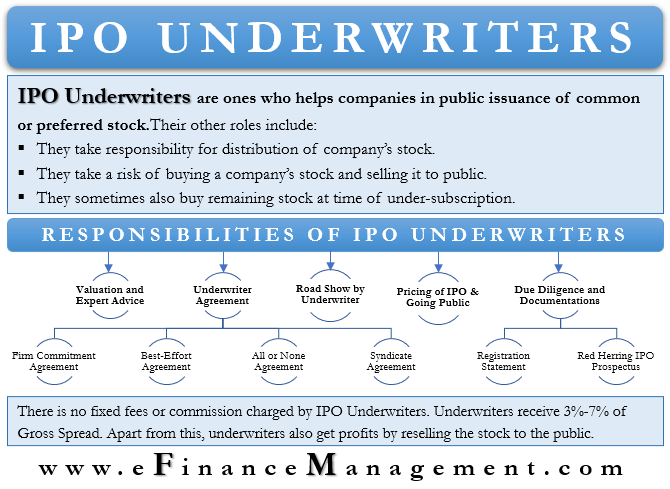
Due Diligence and Documentations
The third responsibility is the preparation of a lot of documents with utmost details for the IPO process. The preparation of all the documents should be with due diligence to comply with the regulations of the Securities Exchange Commission (SEC).
Registration Statement
This is the first formal statement submitted to the SEC. The Underwriter should ensure it is prepared with the utmost due diligence. It is a detailed document stating the history of the company, valuation details, and type of public issuance (common stock or preference stock), deployment of the funds, business plans, financial statements of the company, insider holdings, etc.
If the SEC is not satisfied with the statement, then the Underwriter has to modify and again submit the same. The main purpose of this statement is to prove the stability of the company in the eyes of the SEC. Thus the Underwriter should be very particular while preparing this document.
Red Herring IPO Prospectus
Once the SEC gives the approval of the registration statement, the next responsibility of the Underwriter is to create a Red Herring Prospectus. As the name suggests, this is not the final prospectus. Only the price estimation along with basic details of IPO is given in this.
Road Shows by IPO Underwriters
This is the most important responsibility of an Investment Banker. Just before the listing of IPO, the Investor Bankers moves across the country to market their IPO. These roadshows attract a lot of Institutional Investors. The main target of the Investment Banker is to create as many positive sentiments as they can. The projection of a lot of financial data and figures takes place to attract investors. In Road Shows creation of a lot of marketing materials and corporate presentations takes place.
Pricing of IPO
This is one of the major decisions of the Underwriter, whether to enroll for Fixed Pricing IPO or Book Building IPO. In the case of the former, the issuing price remains the one or the fixed one. However, in the latter, there exists a price band. After Stocks are open to the public, the selection of the best price between the bands takes place. Thus this is the biggest responsibility of the Underwriter.
Going Public
The last responsibility of the Investment Banker is to draft a final prospectus and put stocks open for the public. According to the subscription by the public, the price and allocation of shares occur.
Thus above are a few responsibilities of an IPO Underwriter, which are non-exhaustive in nature.
Fees/Commission of Underwriters
There is no fixed remuneration component here. Generally, the Underwriters receive 3%-7% of Gross Spread (Sale price of the public issue by the Investment Bank – Purchase price of the public issue by the Investment Bank). Apart from the basic commission, Underwriters also profit by reselling the stock to the public. Thus that additional remuneration is for taking risks.
And in the case of the Syndicate Agreement, again, there is no fixed or any hard and fast principle about the distribution of the gross spread. However, usually, the Lead Underwriter gets 20-25% of the Gross Spread, other underwriters in the group stand to get about 50-60%, and the rest 15-20% remains for the expenses.
Conclusion
IPO Underwriting is a bit different as compared to other types of Underwriting. The success or failure of the IPO heavily depends on the scrutiny and due diligence of the IPO Underwriter. The cost of going public is very high, and thus the Securities Underwriter has to take care of all its responsibilities with full accuracy. Any error in estimation with regard to valuation, type of securities, and quantum thereof can practically fail the IPO process. Moreover, it increases the overall costs, stress, and risk of the company or the underwriter.
Read more about other Types of Underwriters.
RELATED POSTS
- Insurance Underwriters: Meaning, Roles, Common factors, Types and More
- IPO Process
- Types of Investment Banking Services
- Loan Underwriters: Meaning, Factors useful for the process, licensing and More
- Mortgage Underwriters: Meaning, Useful Factors, Outcomes and More
- IPO Underpricing – Meaning, Formula, Reasons And More

