Generally Accepted Accounting Principles or GAAP are basically the set of ten accounting standards set by the United States Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB). First established by FASB in 1973, the GAAP principles are now accepted by the Securities Exchange Commission (SEC) and the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants as the official standards for financial accounting. This article will talk about GAAP financial statements, which every company following GAAP should prepare.
Reporting Requirements Under GAAP
As per the GAAP, organizations should provide reports on their cash flows, profit-making operations, and overall financial conditions. To report these things, the most important GAAP financial statements are – Balance Sheet, Income Statement, Shareholder’s Equity, and Cash Flow Statement.
The balance sheet talks about the assets and liabilities of the company, while the Shareholder’s Equity detail the available equity in the company. The income statement details the revenue earned by the company and the corresponding expenses. As the name suggests, the Cash Flow statement is simply the cash record of the company. Cash flow becomes important because both the income statement and balance sheet reveal the financial health of the company on an accrual basis and, therefore, do not talk about the real financial position.
Let’s understand each of the GAAP financial statements in detail.
GAAP Financial Statements
Balance Sheet
The balance sheet primarily consists of Assets and Liabilities. Assets include both current and non-current assets, and so are the liabilities. All the assets that a company can easily convert into cash are known as current assets. On the other hand, the assets that can’t be converted into cash easily are non-current assets. Current Assets include items such as cash, account receivables, inventory, prepaid expenses, and so on. Non-current assets (or mainly fixed assets) include land and building, equipment, prepaid insurance, etc.
Also Read: Types of Cash Flow
On the other hand, Liabilities are the portion of the firm’s assets that a company owes to the creditors. Depending on the duration, one can categorize liabilities into both long and short term. Some examples of current liabilities are accounts payable, taxes payable, wages payable, etc. The long-term liabilities are bonds, payable mortgages payable, and more.
Statement of Owner’s Equity
This statement shows the changes in the equity (in the balance sheet) during an accounting period. Or, we can say it reports the events that lead to an increase or decrease in the owner’s equity over a given period. Stockholders’ Equity statement in a corporation consists of:
Common Stock (recorded at par value)
Add: Preferred Stock (recorded at par value)
Add: Premium on Common Stock (issue price – par value)
And also, Add: Premium on Preferred Stock (issue price – par value)
Add: Retained Earnings
The ending result is Stockholder’s Equity
Income Statement
The income statement is the representation of the company’s operation during the period of time. A simple equation to describe the Net Income would be Revenue Less Expenses. Here revenue represents the funds received from the sale of the end product or the service offered to the customers.
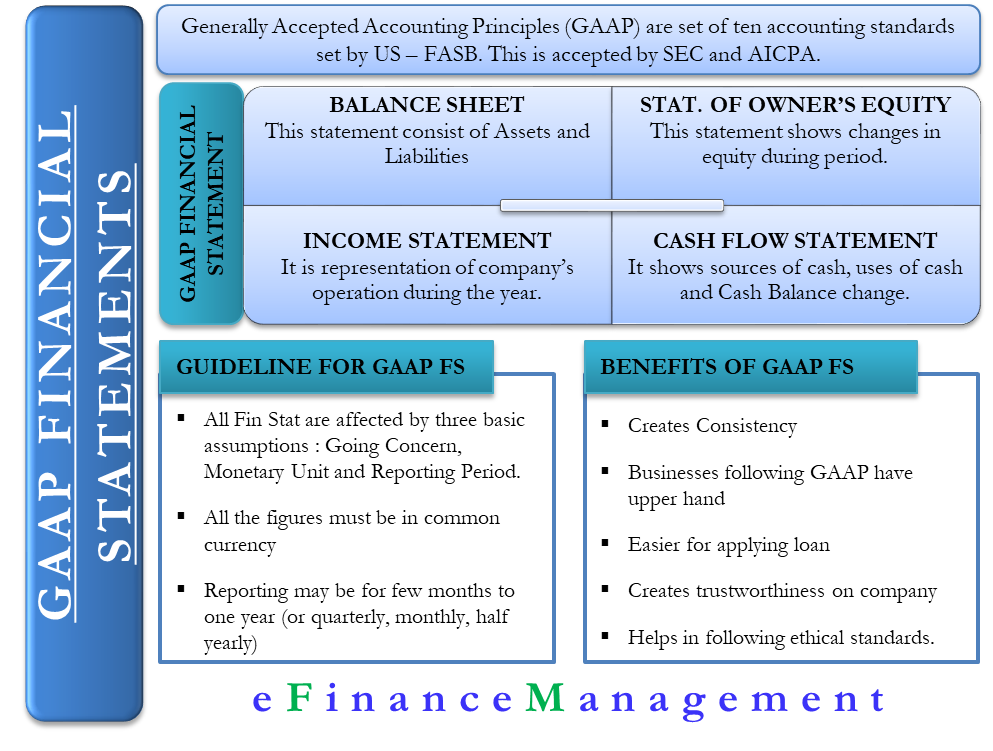
Cash Flow Statement
The underlying premise of the accrual basis of accounting is that the company might be earning a profit but may be short of cash. Cash is essential to keep the business running and meet the day-to-day expenses of the company. Therefore, understanding the sources of cash in a company becomes very crucial. For a given period, the cash flow statement should include the following information:
Also Read: Cash Flows from Financing Activities
- Source of Cash
- Uses of Cash
- Change in Cash Balance
Further, the cash flow statement does not only include cash transactions from operations but from other activities as well. For instance, businesses make investments, buy assets, sell assets, raise cash, etc. All these activities can be categorized into three heads;
- Operating activities
- Investing activities
- Financing activities
Guidelines for GAAP Financial Statements
All financial statements under GAAP are affected by three basic assumptions. These are the monetary unit for financial reporting, “going concern” assumption, and reporting period options.
All the financial statements must display data in a common currency, such as the US dollar. If, for any reason, a transaction does not have a monetary unit, an accountant must not include it in the financial statements.
The reporting period for a business could be from a few months to one year. Also, businesses can choose to report the financial statements either quarterly or semi-annually, or both. For a given reporting period, the financial statement should include a heading describing the time period, such as “the three months ended September 30, 2013.”
The going concern assumption implies that the business is not in the process or considering liquidation. This assumption makes it possible for the business to defer certain expenses to a future date.
Read Types of Financial Statements in detail to learn more.
Benefits of Using GAAP Financial Statements
GAAP helps create consistency because all financial statements follow the same set of principles. Businesses that follow and maintain their financial statements as per GAAP have the upper hand as they offer the best information to run a business.
Also, since all the organizations, financial institutions, banks, and authorities accept GAAP principles, it becomes easier for the companies to apply for loans and other financial aid. Banks and other financial institutions trust companies that maintain their financial statements as per the GAAP rules.
All stakeholders know that the GAAP financial statements are based on facts and not speculation. Be it a loan provider, investor, promoter, or anyone else, they trust the financial statements made as per GAAP and base their decisions on the same.
Moreover, it is important for companies to have ethical standards and follow them religiously. GAAP financial statements are such that they help the organizations in following the ethical standards and establish trust among all the parties.

