Equity vs Fixed Income has been a battle for the ages. Investors and companies alike have had to make decisions between the two for various purposes.
The market has a basket of financial products offering various characteristics to meet the needs of the investors. They are in the form of Equity, Fixed Deposits, Bonds, etc. Here we are going to discuss Equity and Fixed Income investment instruments.
Meaning of Equity and Fixed Income
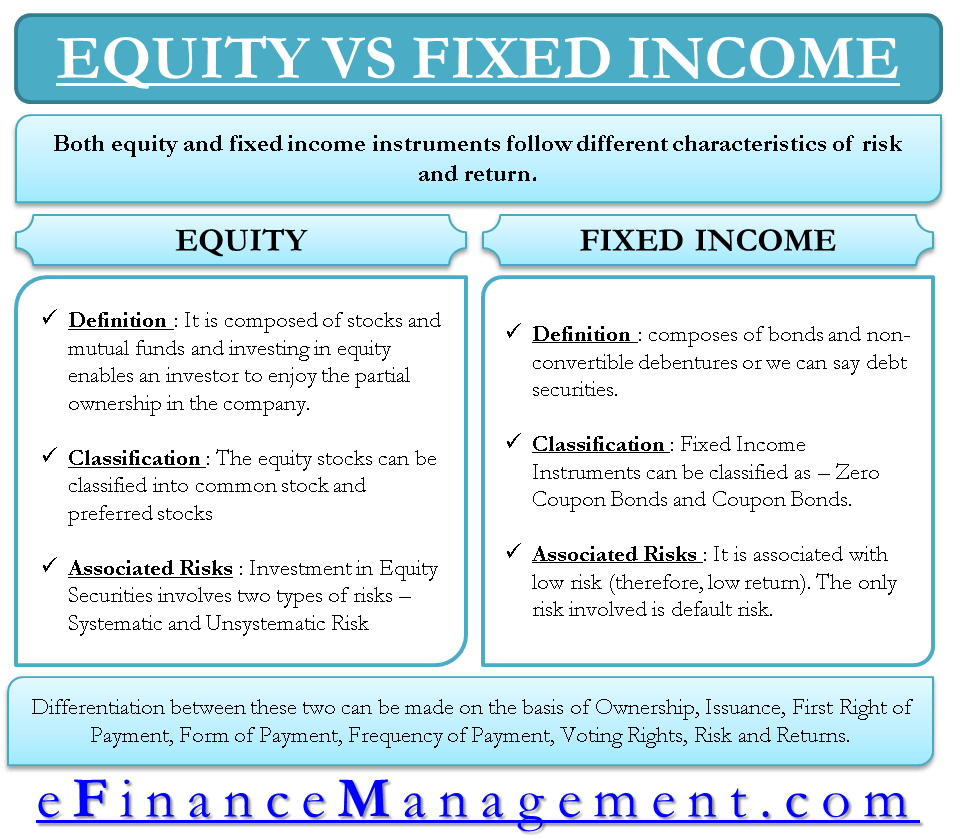
Both equity and fixed income instruments follow different characteristics of risk and return. Equities are considered one of the risky investments as they are driven by the market sentiment along with various economic parameters.
Equity
Equity mainly comprises of stocks and mutual funds. Investing in equity enables an investor to enjoy partial ownership in the company. Equity market trading requires buying and selling (trading) on a regular basis, and since these are quite volatile, the investment is exposed to market risks and market sentiments.
Exposure to equity involves undertaking risk with the belief to earn a reward for it. However, this risk can be managed by ongoing fundamental and technical analysis for predicting the desired returns.
Fixed Income
Coming to Fixed income instruments, bonds provide moderate returns in the predetermined period. Based on risk appetite, the investor then decides the instrument for investment; he can go with both of them or either. Most portfolios consist of investments across both instruments. Let us take both the investment options in detail:
Classification of Equity Stocks
The equity stocks can be classified into common stock and preferred stocks:
Common Stock
They trade often, and the investors have the part right in the ownership of the company and are liable for receiving dividends and hold the voting right in shareholder’s meeting.
Preferred Stock
These stocks grant the same rights to their shareholders as stated in common stock, except for voting right.
Dividends are the profit of the company distributed among its shareholders. In the case of preferred stock, shareholders have a right to receive dividends even before common shareholders. Further, both the shareholders receive dividends only after payment to all the creditors.
Also Read: Various Avenues and Investments Alternative
Type of Risks Associated with Equity
Investment in equity involves two types of risk:
Systematic Risk
Market risk is another name for systematic risk, and it is unavoidable. This depends on economic sentiments and volatility. Examples of systematic risk are Interest rate risk, Inflation risk, and so on.
Unsystematic Risk
Another name for it is a diversifiable risk. It entails from companies’ operations and is avoidable. Examples of unsystematic risk are weather conditions, depreciation of machinery, and so on. Companies hedge these risks using futures and options.
Risk and return of the company use two variables, such as expected return and standard deviation.
Fixed Income Securities
A fixed income instrument composes of bonds, non-convertible debentures, and other debt securities. Fixed income instruments provide guaranteed returns irrespective of market sentiments. Fixed income instruments do not yield high returns but are stable in their returns. The instrument has a specific time period of maturity, unlike equity shares.
Classification of Types of Bonds (Fixed Income Instruments)
Zero-coupon Bond
Zero-coupon bond doesn’t pay interest and trades at a deep discount. The repayment of face value is at maturity, and the calculation of return is the difference between the purchase price and the face value of the bond.
Coupon Bond
A normal bond promises to pay interest to the bondholder during the tenure of the bond. Calculation of coupon rate is the ratio of the coupon to the face value.
The coupon payment for US bonds is semi-annually and annually for European bonds.
Risks Associated with Fixed Income Securities
A fixed income instrument provides low assured returns as it is associated with low risk. The only risk that a fixed income instrument carries is default risk, wherein the issuer is unable to meet the cash obligations. Further, government treasury securities do not involve any default risk as well. Fixed income securities include treasury bills, notes, and long-term bonds.
Basic Differences between Equity and Fixed Income
Ownership
Equity holders are the part owners of the company that allows them to claim profits. On the other hand, debt instrument holders are creditors of the company and only lay a claim on the amount of the loan.
Issuance
The issuance of stocks is mainly done by corporate & startups. Fixed income instruments are usually by government institutions. However, financial institutions or corporate debentures are also quite popular.
First Right of Payment
In the case of liquidity, fixed income holders have the first priority to claim assets when compared with equity holders. Returns on Fixed income instruments are low in addition to being guaranteed. In contrast, equity provides high returns to compensate for the high risk.
Form of Payment
Equity shares pay dividends, whereas fixed income securities pay interest income.
Frequency of Payments
Interest payments on fixed income securities are paid periodically. Cash positions of the company decide the share dividends payout of the company. It may or may not pay out a dividend. Above all, non-payment of interest is an alarming sign for any company. It determines the creditworthiness and credit rating of a company.
Voting Rights
Equity holders have a right to cast their vote; fixed-income holders have no right to cast a vote or interfere in company matters.
Risk & Return
The basis of returns, risk carried, and method of trade are major differences between equity and fixed income securities. Equity depends on market sentiments for returns. Fixed income securities remain unaffected by such sentiments. Cash flow status and the ability to pay are the factors that affect the fixed income interest payments of a company.
RELATED POSTS
- Public Securities – Types and Accounting Treatment
- Income Stock: Meaning, Characteristics, Advantages, Criticisms, and More
- Preferred Stock Vs Bond: Meaning, Differences and More
- Advantages and Disadvantages of the Certainty Equivalent Method
- Financial Risk – Meaning, Types, Management And More
- Financial Securities


I am from Ethiopia, East Africa. I really appreciate your efforts. You are doing good go a head.