Market efficiency is concerned with the extent to which market prices of assets incorporate the available information. An informationally efficient capital market is one in which the current price of a security fully, quickly, and rationally reflects all available information about that security. The subject of market efficiency is of great interest to investors. In this article, we will learn about weak-form vs semi-strong form efficient markets
Weak Form Vs Semi-Strong Efficient Markets
The efficient market hypothesis can lead to different details in each kind of market. Weak form and semi-strong form markets have some major differences and an investor needs to understand the precise nature of each market to act accordingly. The following are the differences between weak and semi-strong form markets:
Availability of Information
In weak-form markets, only historical data and trading volume are present in the market. Whereas, in a semi-strong form market, current information is available publicly. Therefore, the price of assets adjusts to the new information rapidly and more efficiently in case of a semi-strong efficient market.
Arbitrage Opportunities
Arbitrage is buying an asset in one market and simultaneously selling it at a higher price in another market. The chances of mispricing an asset are more in a weak-form efficient market because the price of assets takes a long time to adjust to the new information coming to the market. Hence, arbitrage opportunities are more in the weak-form efficient markets when compared to semi-strong-form efficient markets.
Also Read: Semi- Strong Form of Market Efficiency
Market Analysis
There are various methods to analyze the efficiency of a market. In the case of a weak-form efficient market, it is the technical analysis that we use to analyze the hypothesis. If an investor can earn above-average profit using technical analysis, it leads to the rejection of the weak-form hypothesis. In the case of a semi-strong form efficient market, fundamental analysis is used to analyze the hypothesis.
Portfolio Management
There are two strategies available to manage a portfolio of financial assets. And these are active or passive strategies. The efficiency of a market directly influences the way in which investor and managers maintain their portfolios. Researchers have observed that in a weak-form efficient market, active management of a portfolio can yield above-average profits. Whereas, in the case of a semi-strong form efficient market, passive management of a portfolio is recommended to earn a maximum risk-adjusted return.
Table of Difference
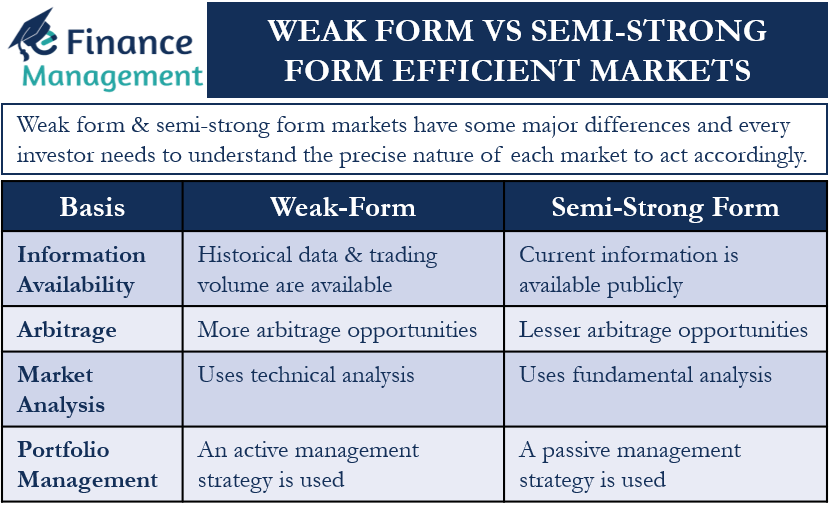
To summarise the whole article, weak-form vs semi-strong form efficient markets, let us look at this table of differences.
| Basis | Weak Form | Semi-Strong Form |
|---|---|---|
| Information Availability | Historical data & trading volume are available | Current information is available publicly |
| Arbitrage | Arbitrage opportunities are more | Lesser arbitrage opportunities |
| Market Analysis | Uses technical analysis | Uses fundamental analysis |
| Portfolio Management | An active management strategy is used | A passive management strategy is used |

