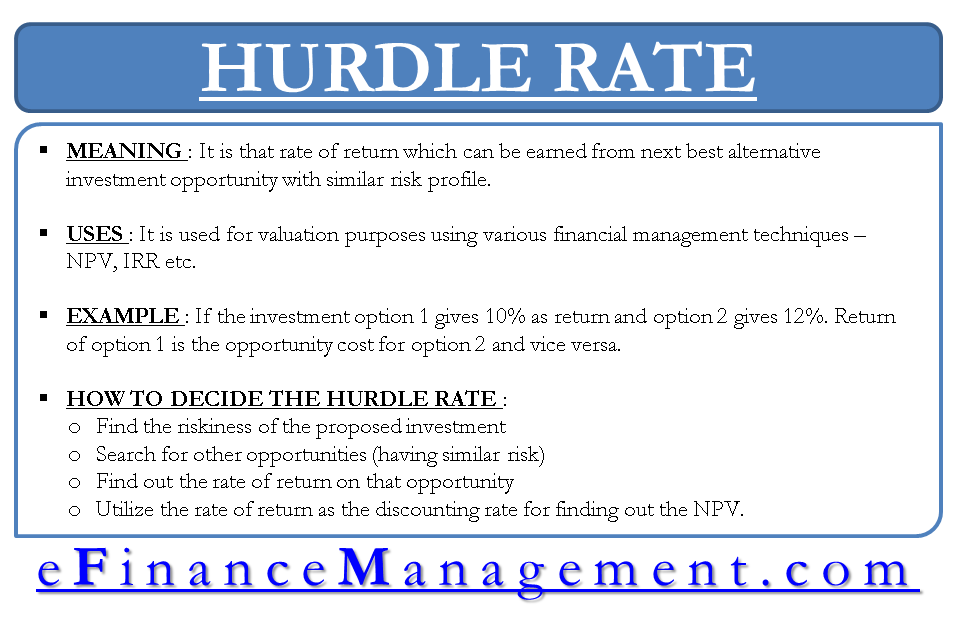
What is Hurdle Rate?
Hurdle rate, the opportunity cost of capital, and discounting rate are all same. It is that rate of return that can be earned from the next best alternative investment opportunity with a similar risk profile. The hurdle rate concept is used widely for valuation purposes in prominent techniques such as net present value, internal rate of return, etc.
The term ‘opportunity cost’ is a general and straightforward term that can be used in any normal day-to-day situation. For example, if you have two options for your breakfast, a sandwich and burger. You can have only one of the two. How do you decide? Normally, you will try choosing the one which gives you more satisfaction. If you choose a sandwich, you will lose the satisfaction which you were about to get in having a burger and vice versa. So, the amount of satisfaction you realize in having a burger is your opportunity cost for having a sandwich and vice versa.

Calculating Hurdle Rate
In finance also, the meaning of opportunity cost does not change. Only the factors change. Opportunity cost is the benefit of one investment sacrificed for investing in another. If investment option 1 gives 10% as return and option 2 offers 12%. Return of option 1 is the opportunity cost for option 2 and vice versa.
Suppose a company is willing to invest 1 million dollars in a real estate firm. After one year in the best, normal, and worst scenarios, the firm’s value will be 1.3, 1.1, and 0.9 million dollars. All three scenarios have an equal chance of occurrence. Therefore, the expected value of the farm is 1.1 [(1.3+1.1+0.9)/3].
Also Read: NPV vs IRR vs PB vs PI vs ARR
For finding out the net present value of the underlying investment opportunity, we need to have the correct opportunity cost of capital. Assume there is a stock in the share market which sells at $100 and is forecasted to have a value of 115$ a year later. Also, this stock has the same risk profile. The rate of return on the stock is 15%. [(115-100)/100].
Since the investment in stock and real estate has the same risk, we will consider a 15% rate of return on the stock as the opportunity cost of capital for evaluating the investment in the real estate farm.
Net Present Value (NPV) = -1,000,000 + 1,100,000 / 1.15 = – 43,500
As per the NPV, the investment in real estate is not worth choosing because the NPV is negative. Instead of investing in real estate, if the company invests in the stock, it will get better returns. This is how the comparison with opportunity cost reveals whether you should enter into certain investment options or not.
How to decide the discounting rate of return/hurdle rate/opportunity cost of capital for NPV calculation?
- Find the riskiness of the proposed investment. (Real Estate Farm)
- Search for other opportunities for investment having similar risks. (Stock)
- Find out the rate of return on that opportunity. (15% on Stock)
- Utilize the rate of return as the discounting rate for finding out the NPV.
RELATED POSTS
- Capitalization Rate – Meaning, Formula, Examples and Drawback
- How to Evaluate Investments and their Attributes?
- Net Present Value (NPV)
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Profitability Index
- Opportunity Cost of Capital – Concept, Example, and Consideration
- Crossover Rate – Meaning, Formula, Example, and More

