Overdraft Definition
An overdraft occurs when an account balance goes below zero after a transaction and can be viewed as a short-term loan from a financial institution. The most common example is when a company writes a check for more than the amount available in the checking account. For example, if a company has a balance of USD 200 in its bank account and has issued a check for USD 400, the account will be overdrawn by USD 200 after the check is cleared. This situation implies that the company had an agreement with the bank for an overdraft and that the overdraft limit was higher than USD 200. Otherwise, the check would not have been cleared.
What is Bank Overdraft?
A bank overdraft facility means an additional source of liquidity available to businesses and a helpful tool to manage short-term cash flow problems. Generally, an overdraft account will be an integral part of a company’s cash management, typically including an offsetting arrangement against the other company’s accounts.
Overdraft facilities are customized to the needs and financial situation of the borrower. The specific terms and conditions will be set forth in a credit agreement, typically including the following provisions.
Use of Bank Overdraft
Overdrafts are made available for general corporate purposes. They are used to ease pressure on working capital and as a backup for unexpected expenditures. Overdraft facilities are provided on a revolving basis meaning that funds can be reimbursed and re-used at any time.
Also Read: Overdraft Vs. Loan
Also, refer to – Advantages and Disadvantages of Bank Overdraft
Amount of Bank Overdraft
An overdraft limit is determined based on a borrower’s creditworthiness and the availability of collateral or a guarantee.
Pricing of Bank Overdraft
Interest on the overdraft will accrue from day to day only on the amount outstanding. The interest rate will usually be a fixed margin over the appropriate base rate. A margin between 4% and 9% over the base rate is usual. Banks will typically charge an overdraft fee and a set-up fee as well.
Security of Bank Overdraft
Some lenders will require borrowers to provide collateral in the form of deposits or fixed assets to secure their position if something goes wrong. A secured overdraft could also benefit from more favorable pricing than an unsecured overdraft. In case the borrower defaults, a bank could seize and liquidate the collateral up to the amount owed to the lender. In some cases, the bank will also require the borrower to maintain a certain amount of fixed deposit with the bank.
One should also learn about How does an Overdraft Facility Works?
Term of Overdraft
Overdraft facilities are usually approved for a short period of time, ranging from a few months to a year, and companies should not use them as a source of long-term financing. It should be noted that overdraft facilities are often structured as demand loans giving the lender the right to call, or cancel, the overdraft at any time without further explanation.
Also, refer to Temporary Overdraft
Guarantee for Overdraft
In large groups, it is common for a subsidiary parent company with a strong balance sheet to provide a guarantee for the overdraft account of a weaker sister company.
Financial Reporting
In the general ledger, the cash account will have a credit balance when there is a negative balance in the bank account. The negative balance will not appear as a negative asset, but it will instead show as a short-term liability as an overdraft is considered a short-term loan. The overdraft will also be included in the cash section as an asset on the Balance Sheet. Like any other loan, the overdraft will also appear in the Cash Flow Statement as an increase in cash flow from financing activities. Conversely, the repayment of the overdraft will decrease the short-term liability and appear as a decrease in cash flow from financing activities.
The interests and fees charged by the bank will be recorded as an expense on the P&L and reduce net income and shareholder equity through the retained earnings section on the Balance Sheet,
Finally, when a guarantee is provided to a bank on the overdraft facility of another company, the guarantor will typically report as a contingent liability section in the footnotes of its financial statements.
Continue reading – Overdraft Vs. Loan
Example of Bank Overdraft
A company has a cash account balance of USD 200 and has issued a check of USD 400 to pay raw materials to its suppliers. The company has an overdraft limit of USD 1,000, and the bank charges an interest rate of Prime Rate (3%) + 2% plus an overdraft fee of USD 50. The company has covered its overdraft position after one month.
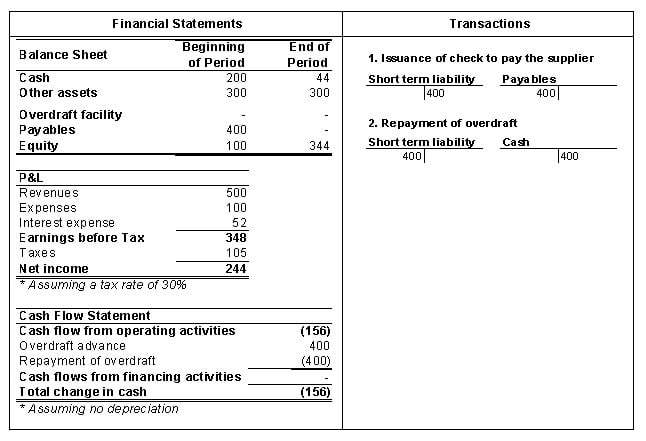
Cash flow from operating activities is arrived at as follows:
244 (Net Income) – 400 (Payment for Raw Material Suppliers) = (156)
For better understanding, refer to the Difference between Overdraft and Cash Credit.


You have made the topic a smooth sailing! Well written.
this comment or writeup is very useful,thanx