There are broadly 3 working capital management strategies/ approaches to choosing the mix of long and short-term funds for financing the net working capital of a firm, viz. Conservative, Aggressive, Hedging (Or Maturity Matching) approach. These strategies are different because of their different trade-off between risk and profitability. Another remarkable difference is the extent or proportion of long- and short-term funds applied to finance the working capital.
People often use the terms ‘methods of working capital management’ and ‘strategies and approaches to working capital financing‘ interchangeably in general parlance. But, ultimately, the concept and achievement of the objective of working capital management are important. We need to understand the following relationship in-depth to understand the concept in its true sense.
Short Term vs. Long Term Financing vis-a-vis Risk & Profitability Tradeoff
Profitability Standpoint
In general, short-term interest rates are cheaper than long-term interest rates because of the term premium. That means short-term has lower interest cost and higher profitability, whereas long-term has higher interest cost and lower profitability. Especially when the long-term funds are in use for financing the working capital, unnecessary interest payment takes place for the periods when the funds are not in use. In essence, short-term financing wins the race if profitability is the concern. Let’s now look at the risk concern.
Risk Standpoint
There are two risks in short-term financing, viz. refinancing risk and risk of interest rate fluctuations with refinancing. Refinancing is very uncertain, and if the lender denies it for any reason, the options left to the borrower for making the payment are either to sell off the assets and pay off or file for liquidation if they failed to realize the assets. The risk of adverse change in interest rate while refinancing may increase the cost of financing, leading to low profitability. On the contrary, long-term financing neither has to refinance risk nor the risk of change of interest rate frequently. Here, the long-term financing wins the race.

Types of Working Capital Strategies/Approaches
The three working capital strategies have the best explanation with the help of the following graph and equations. First, we need to understand the graph correctly. The red horizontal lines represent the lines of 3 strategies. The simple line is Conservative strategy, below that line with spaces is hedging strategy, and below that dotted line is an aggressive strategy. These lines indicate the extent of utilization of long-term sources. The higher the line, the more significant is the investment through the long-term source of finance.
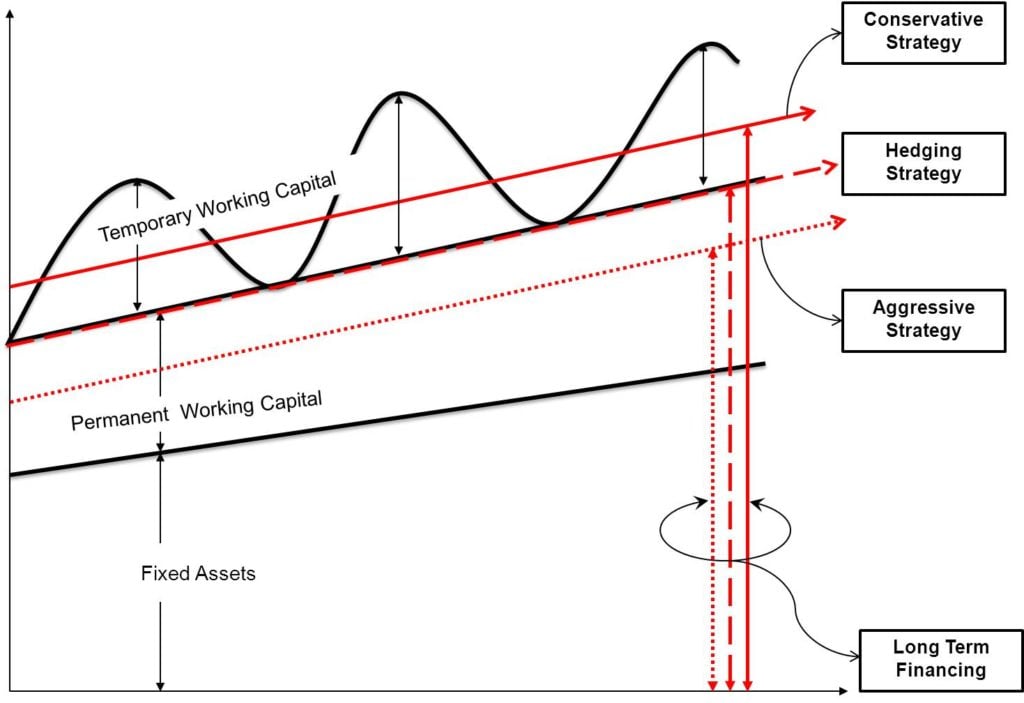
For equations, we will use the following abbreviations:
FA = Fixed Assets
PWC = Permanent Working Capital
TWC = Temporary Working Capital
Hedging (Maturity Matching) Strategy
This is a meticulous strategy of financing the working capital with moderate risk and profitability. Each asset would be financed by a debt instrument of almost the same maturity in this strategy. It means if the asset matures after 30 days, the payment of the debt that has financed it will also have its due date of payment after almost 30 days. Maturity matching or hedging strategy works on the cardinal principle of financing, i.e., utilizing long-term sources for financing long-term assets, i.e., fixed assets and a part of permanent working capital and temporary working capital are financed by short-term sources of finance. Here, funds are applied as below and can be seen in the above diagram.
Long Term Funds will Finance >> FA + PWC
Short Term Funds will Finance >> TWC
Conservative Strategy
As the name suggests, it is a conservative strategy of financing the working capital with low risk and low profitability. In this strategy, apart from the fixed assets and permanent current assets, long-term financing sources are also financing a part of temporary working capital. It has the lowest liquidity risk at the cost of a higher interest outlay. Here, funds are applied as below and can be seen in the above diagram.
Long Term Funds will Finance >> FA + PWC + Part of TWC
Short Term Funds will Finance >> Remaining Part of TWC
Aggressive Strategy
This strategy is the most aggressive strategy out of the three. The complete focus of the strategy is on profitability. It is a high-risk, high-profitability strategy. In this strategy, the dearer funds, i.e., the utilization of long-term funds are only to finance fixed assets and a part of the permanent working capital. The short-term funds finance the complete temporary working capital and also a part of permanent working capital.
It saves the interest cost at the cost of high risk. Here, funds are applied as below and can be seen in the above diagram.
Long Term Funds will Finance >> FA + Part of PWC
Short Term Funds will Finance >> Remaining Part of PWC + TWC
Conclusion
These three strategies are plotted on a number line with one side as ‘risk’ and the other as ‘profitability’ Conservative strategy is on the side of lower profitability and lower risk. On the contrary, an aggressive strategy is on the side of higher profitability and higher risk.
The hedging strategy is somewhere between the two. Executing the hedging strategy in its true sense is not practically possible. The management’s attitude towards risk and other factors would decide their place on this number line.
Continue reading – Working Capital Policy – Relaxed, Restricted, and Moderate
And, A Comparison between 3 Strategies of Working Capital Financing.


This is very helpful article for understanding Working capital management Approachees.
Very much useful Mr. Sanjay. Appreciate your participatio.
Thanks and very useful !
Keep working ,terrific job!
Beautiful work bro,,,