The working capital policy of a company refers to the level of investment in current assets for attaining their targeted sales. It can be of three types: restricted, relaxed, and moderate. The relaxed policy has higher and restricted has lower levels of current assets, whereas moderate places itself between relaxed and restricted. Commonly, these policies are also named aggressive, conservative, and hedging policies.
Important Decisions in Working Capital Management – Level of Current Asset and their Means of Financing.
Working capital management has two main decisions at two consecutive stages. They are as follows:
1. The level of Current Assets – How much to invest in Current Assets to achieve the Targeted Revenue?
2. Means of Financing Current Assets – How should the above Current Asset Investment be financed, i.e., the mix of long and short-term finance?
Difference between Working Capital Policies and Working Capital Financing Strategies
Commonly, policies of working capital and strategies (approaches) of working capital financing are interchangeably used and which is not correct. There is a thin line of difference between the two. Working capital management policy deals with the first decision, and working capital management strategies or approaches deal with the second decision. Working capital policies are restricted, relaxed, and moderate, whereas the working capital strategies are aggressive, conservative, and hedging (Maturity Matching).
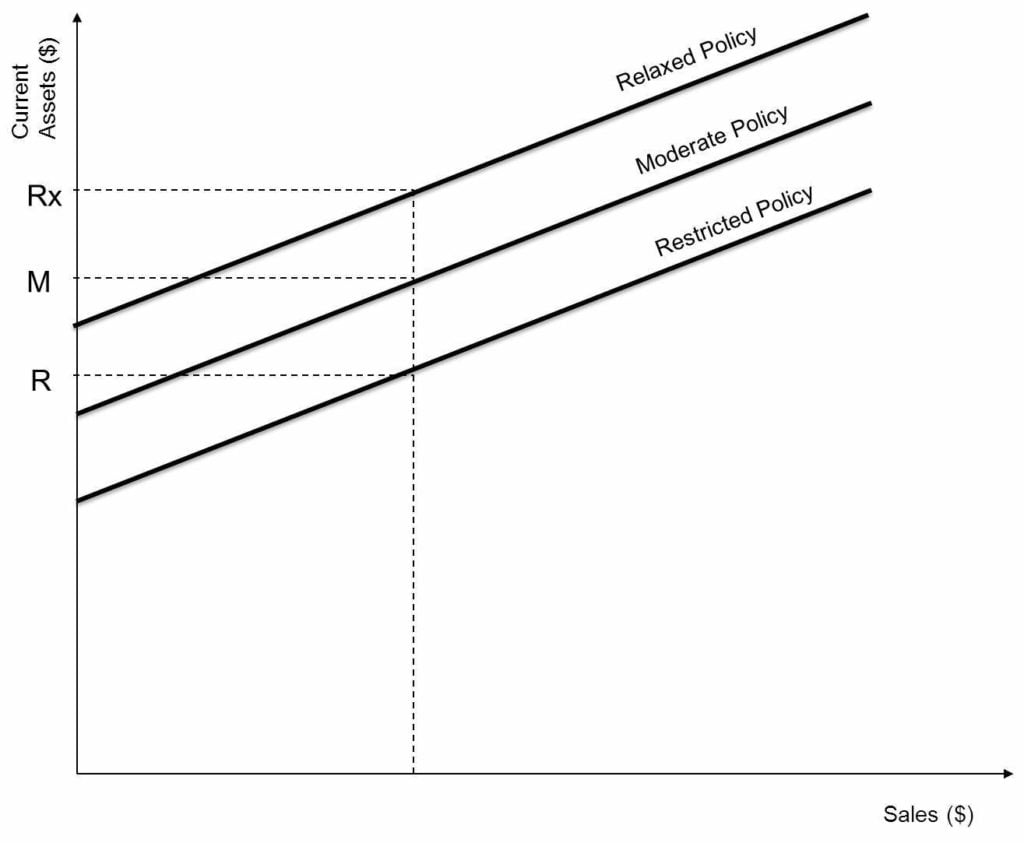
Three Types of Working Capital Policies
Based on the attitude of the finance manager towards risk, profitability, and liquidity, the working capital policies can be divided into the following three types.
Restricted Policy
In restricted policy, the estimation of current assets for achieving targeted revenue is done very aggressively without considering any contingencies and provisions for any unforeseen event. After deciding, these policies are forcefully implemented in the organization without tolerating any deviations. In the diagram, point R represents the restricted policy that attains the same revenues level with the lowest current assets.
Also Read: Working Capital Management
Adopting this policy would benefit the lower working capital requirement due to the lower level of current assets. This saves the interest cost to the company, which produces higher profitability, i.e., higher return on investment (ROI). On the other hand, there is a disadvantage in the form of high risk due to a very aggressive policy. That is why; it is also called an aggressive working capital policy.

Relaxed Policy
The relaxed policy is just the opposite of a restricted policy. In this policy, the estimation of current assets for achieving the targeted revenue is prepared after carefully considering uncertain events such as seasonal fluctuations, a sudden change in the level of activities or sales, etc. After the reasonable estimates, a cushion to avoid unforeseen circumstances is left to prevent the maximum possible risk. The diagram represents the point Rx which uses the highest level of current assets for achieving the same level of sales.
Companies with relaxed working capital policies assume the advantage of almost no risk or low risk. This policy guarantees the entrepreneur of the smooth functioning of the operating cycle. We know that earnings are more important than higher earnings. On the other hand, there is a disadvantage of lower return on investment because higher investment in the current assets attracts higher interest costs, reducing profitability. Because of its conservative nature, this policy is also called a conservative working capital policy.
Moderate Policy
The moderate policy balances the two policies, i.e., restricted and relaxed. It assumes the characteristics of both policies. To strike a balance, moderate policy assumes the risk to be lower than restricted and higher than conservative. In the profitability front also, it lies between the two.
The biggest benefit of this policy is that it has reasonable assurance of smooth operation of working operating capital cycle with moderate profitability.
Working capital policies can be further framed for each component of networking capital, i.e., cash, accounts receivable, inventory, and accounts payable. Cash policies can be to maintain an appropriate level of cash. When the level is high, it should be invested in liquid investments for the short term and vice versa. Accounts receivable policy may state payment terms, credit period, credit limit, etc. Inventory policy may speak of minimizing inventory levels to the point it poses any risk to the satisfaction of customer demands. Accounts payable policies include policies of payment terms, quality terms, return policies, etc.
Also read – A Comparison between 3 Strategies of Working Capital Financing
Quiz on Working Capital Policy
This quiz will help you to take a quick test of what you have read here.
RELATED POSTS
- Aggressive Approach to Working Capital Financing
- Conservative Approach to Working Capital Financing
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Working Capital Management
- Techniques for Finding Optimal Level of Working Capital
- Types of Working Capital – Gross and Net, Temporary and Permanent
- Objectives of Working Capital Management


“Thanks for sharing the three types of working capital policies. This will definitely help me to understand working capital and be able to handle it well.Thanks for sharing this.
“
is this the same with the guideline for the choice of working capital policy
Thank u so much for sharing this information