Hedging and Speculation are the terms you would normally hear with futures trading. People, including traders, often use the term to convey the same thing or when talking about the price movement. In reality, the two terms refer to different things. The basic difference between the two is that hedging refers to reducing risk, while the objective of speculation is to make a profit. To clearly understand the two concepts and their usage, it is crucial that we know the differences between Hedging vs Speculation.
Hedging
Hedging is a strategy to minimize price risk in case of adverse movement. Or, we can say that it helps investors to reduce or even eliminate the chances of loss because of a significant movement in the underlying asset’s price. A trader needs to take opposite positions in two separate markets to execute hedging. In this way, a loss in one market could be offset by the gain in the other market.
Speculation
Speculation is basically buying and selling of assets with expectations of making a profit from the change in the price. Thus, speculators/traders here enter into trading by identifying opportunities in the market to gain monetary benefit from the fluctuations in the price of the underlying asset. The underlying asset could be stock, bonds, derivatives, currencies, etc.
Speculators use their expertise and various methodologies (fundamental and technical analysis) to make calculated guesses or estimates on the price movement of the underlying asset. For instance, if a trader believes the share is overpriced, then he may short it now.
Also Read: Hedging
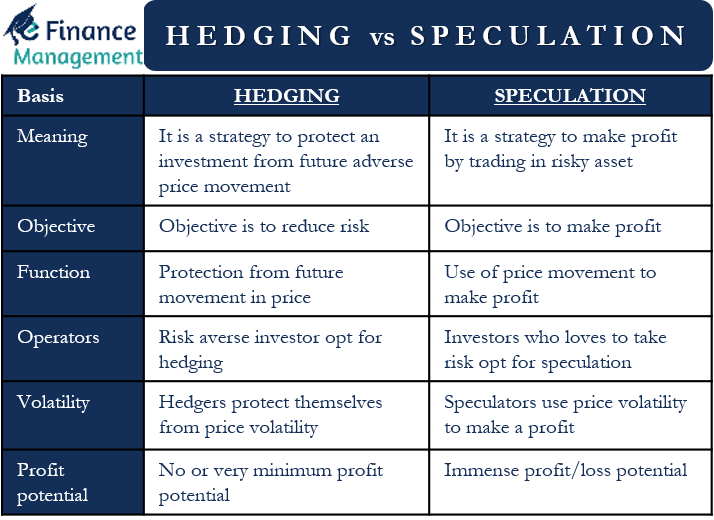
Hedging vs Speculation – Differences
Following are the differences between Hedging vs Speculation:
Meaning
Hedging is a strategy to protect an investment from future adverse price movement. Speculation, in contrast, is a strategy to make a profit by trading in a risky asset.
Objective
In hedging, the objective is to reduce or do away with the risk. The sole objective of speculation is to earn a profit by taking some amount of risk.
Involves
Hedging involves protection from the future movement in price. The speculation involves using price movements to make a profit.
Operators
Usually, a risk-averse investor goes for hedging. On the other hand, investors who love taking a risk to earn a profit goes for speculation.
Businesses also go for hedging to protect themselves from the rise in the cost of materials. Speculators, in contrast, are usually day traders.
Risk Management
Hedgers use hedging to manage their risk. On the other hand, Speculators use other techniques to manage risks, such as stop-loss and limit orders.
Volatility
Speculators use price volatility to make a profit. Hedgers, on the other hand, try to protect themselves from price volatility.
Profit Potential
In hedging, there is no or very minimum profit potential as the objective is to reduce risk. There is immense profit potential in speculation, which pushes investors to take a risk. Similarly, loss potential is also immense in speculation.
Hedging vs Speculation -Example
First, let’s take the example of hedging. Suppose a food-processing company contracts with a farmer to grow wheat, which is a key ingredient for the company. The company is worried about the rise in wheat prices and thus, purchases a futures contract.
Now, if the wheat prices go up, the contract would allow the company to offset the higher prices of wheat. And, if the prices go down or remain the same, the company won’t use the contract. The loss, in this case, will only be the cost of the futures contract or the premium paid for that contract.
Similarly, the farmer can also go for hedging as they would lose if the price goes down. Thus, the farmer would sell futures on wheat. If the wheat prices drop, the futures contract will help offset the drop. And, if the prices go up, then the farmer will lose only the cost of the futures contract.
Now let’s take an example of speculation. Suppose trader A believes the price of the company’s ABC stock would go up in some time. To benefit, the trader will buy the shares of ABC now and sell them once the price moves up.
The price movement, however, could be either way. Suppose the current market price of ABC stock is $50. Now, if, after one month, the price moves up to $70, investor A would gain $20, but if the price drops to $30, the trader will lose $20.
Hedging vs Speculation – Which is Better?
We can say that hedging is a type of insurance. One doesn’t buy it to make a profit instead of as protection from unforeseen losses. Though a hedger pays the cost of the contract, in the long run, it helps stabilize the profit margin.
Initially, hedging was limited to farming, but almost every industry uses it now. For example, airlines use hedging to protect themselves from the volatility in oil prices. The trucking and shipping sectors also use hedging for oil prices.
Speculation may appear to be a sort of gambling, but in the long-term, it eventually helps to improve the markets. This is because the trading from speculators helps to bring clarity to the price of the underlying asset.
Suppose the market only includes farmers, agribusinesses, and consumers. In the absence of speculators, it becomes easy for an organization to manipulate prices. But, speculators help to avoid such situations by betting on the price movement on the basis of macro and micro factors. We can say that speculators, in a way, help with price discovery.
Final Words
Both hedging and speculation are the most popular and common practices of the financial market and businesses across the world. One helps to protect an investment, while the other helps to make a profit. Hedging is popular not just with traders but with businesses as well. Speculation, in contrast, is popular among traders. An investor, however, must make use of both the strategies so as to protect their portfolio as well as to earn profit by taking a calculated risk.

