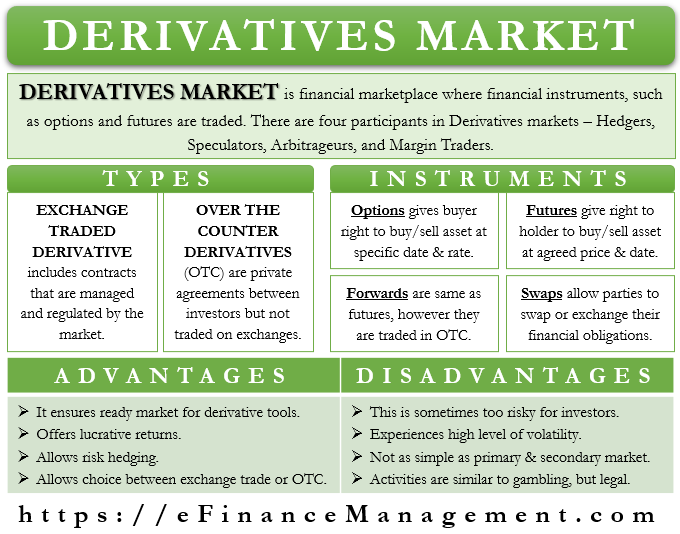
A Derivatives Market is a financial marketplace where financial instruments, such as options and futures, and other derivative instruments are traded. Different types of investors take part in this market with varying objectives. For instance, some want to earn a profit, some speculate, while some enter the market to hedge their risk.
Types of Derivatives Market
We can primarily divide this market into two parts:
Exchange-Traded Derivatives
This includes the contracts that are managed and regulated by the market. Such contracts are standardized futures or options contracts, thus trading on a recognized exchange. These contracts have less risk (default) for the investor. The parties need to deposit an initial payment at the time of entering the contract.
Over the Counter (OTC)
There are private agreements between investors. The provisions of the agreement remain private. Such contracts do not trade on any exchange, nor do they have any intermediaries. These are not standardized contracts. And therefore, parties can easily modify and customize the terms of the contract.
Derivatives Market Instruments
Following are the instruments that investors or traders use in the derivative market:
Options
It gives the buyer the right (not an obligation) to buy or sell the underlying asset at a specific price and at a specific date. On the basis of when the buyer executes the contract, an option could either be American, European, or Bermudan. Options involve buying put or call options.
Futures
Like options, futures are the standard agreements between the parties. And these contracts give a right to the holder to buy or sell the underlying asset at an agreed price and at a future date. However, unlike options, a futures contract is both a right and an obligation to execute the agreement on or before the specified date, as per the provisions. Since these are standard agreements, they trade on the exchange market.
Forwards
These are the same as the futures contract, with the only difference being they are over-the-counter products. This means they are not standardized contracts and are not regulated, nor do they trade on any exchange. The parties are free to customize the contracts as per their requirements.
Swaps
These contracts allow parties to swap or exchange their financial obligations. Such contracts are also OTC and do not trade on any exchange market. These swaps are available for currency, interest rate, commodity, etc. However, the most popular and widely used swaps are interest rate swaps.
Advantages of Derivative Market
Following are the advantages of a Derivative Market:
- They ensure a ready market for the derivative financial tools.
- They offer investors lucrative returns. In fact, in the derivative market, one can trade with limited capital, and profit potential is huge as compared to the investments in the primary securities. However, these investments in the derivatives market also carry higher risk in case of adverse movement than the normal stock market investments. But, the higher returns that this market offers to lure the investors towards it.
- It allows investors to hedge their risk and save themselves and their capital from unchartered or high swings.
- An investor can choose to invest in OTC or exchange-traded derivate depending on their risk profile and need.
Features of Derivative Market
Following are the distinguishing features of this market:
- It is a massive market with traders all around the globe. Its volume and traded value are almost greater than 3 to 15 times the routine market volumes and values.
- The OTC trades are more popular, with a total market value of about $600 trillion.
- The derivative market attracts many speculators and hedgers, as they can earn higher profits with lesser capital investments.
- Trading in a derivative market requires the participant to know the market and the economy well.
Participants in the Derivatives Market
Primarily there are four types of participants in a derivative market:
Hedgers
These are the investors who enter the derivative market to reduce their risk or hedge their risk. In fact, hedging is the biggest motive that drives investors to the derivative market. The option route is preferred by the hedgers to reduce their risks.
Also Read: Types of Derivatives Traders
Speculators
It is the most common market activity in any financial market. This basically involves betting against the future price movement and taking positions accordingly. It is a risky activity involving buying the underlying asset and then betting on its price. Earning a big profit is the driving force for speculative activities.
For example, an investor expects the price of a share to drop going ahead. Thus, to profit from this, the investor will short sell the share now and buy later when the price drops.
Arbitrageurs
Arbitrage is also a profit-making activity by taking advantage of the price volatility in the different financial markets. Arbitrageurs earn a profit using the price difference resulting in investment between the two markets. Or, we can say they buy an asset at less price in one market and sell it in another at a higher price. For example, buying a share for $100 in the cash market and selling it at $102 in the future market.
Margin traders
Another derivative market participant is margin traders. The margin is the initial deposit that an investor makes at the time of entering into a contract.
Read about Types of Derivative Traders in detail.
Drawbacks
Following are the drawbacks of a derivative market:
- Over the years, many have criticized the market for being too risky for investors. Those who criticize this market cite the role of CDS, a derivative tool, in triggering the 2008 financial meltdown.
- The derivative market also sees a high level of volatility, enough to erase the full investment of an investor. Also, the financial instruments in the derivatives market are extremely sensitive to even small changes in the interest rate, maturity, any political, medical, or economy-related issues, and more.
- Financial instruments in the derivatives market are not as simple as the ones you will see in the primary and secondary markets. Because of this, new and occasional investors avoid this market. They, however, have an option to take the services of brokers and trading agents to invest in the derivatives market.
- Another criticism against the market is that their activities are similar to gambling but legal. This is because the activities in the derivative markets are similar in nature to gambling.
Differences – Cash vs. Derivative Market
The key differences between the cash and derivative markets are as follows:
- In the cash market, investors can buy in any quantity, while in a derivative market, the buying and selling are in pre-fixed lots.
- Only tangible assets trade in the cash market. In the derivative market, both tangible and intangible assets trade.
- Investors use the cash market to invest, while traders use the derivative market for hedging, arbitrage, or speculation.
- The investor needs to have a trading and Demat account to trade in a cash market. For investing in futures, an investor needs only a future trading account.
- In the cash market, all funds are invested upfront. However, only the margin money is paid in advance in the futures market. Balance money instead the difference money is paid on exiting or expiry, only if the trade goes negative. Otherwise, no more money needs to be paid if it is favorable.
- When an investor buys a share in the cash market, they own a part of that firm. However, as derivatives are based on some underlying asset, the investor or holder of the derivative instrument has no ownership. Need to note that even the right or obligation or option bought or sold has a maturity/expiry. Therefore, it is a very short-term trading contract only and does not give ownership rights even on expiry or maturity.
- In the cash market, the investor may get dividends, but there are no such things as a dividend in the derivative market.
Final Words
Even though the Derivatives Market is an important part of the financial ecosystem, they have come under attack lately for its role in the 2008 financial crisis. Credit Default Swaps (CDS), the main culprit of the 2008 financial crisis, trade OTC in the derivative market. Following the crisis, financial authorities have come up with stricter norms, focusing on risk management and accountability of the financial companies in the derivative market.
RELATED POSTS
- Secondary Market – Features, Types, Importance And More
- Put and Call Options
- Options on Futures – Meaning, How it Works, Importance, and More
- Futures Contracts – Meaning, Features, Pros, Cons, and More
- What are Options in Trading – Types, Pros, Cons, and More
- Financial Markets – Functions, Importance And Types


Thank you very much for this beautiful article. This is really great & informative. I read it & learn about many things. I appreciate your thoughts. Great.
Thanks for the positive feedback. Pl do keep visiting the site for more such interesting and informative articles.