Cost Plus Contract: Meaning
An agreement between two parties whereby one party promises to reimburse the other party for the costs incurred and any additional profit after the completion of the project is called a cost-plus contract. Moreover, the profit amount is usually a predefined rate. It is usually 10% -20% of the project’s total cost. This type of incentive contract is mainly seen in the construction sector, where the buyer of the property promises to pay the total cost and profit to the contractor after the completion of the construction of the property. In this case, the contractor must provide proof of all expenses incurred during the duration of the project. As part of the cost-plus contract, the contractor will be reimbursed for both fixed and variable costs.
The term “cost-plus” refers to the payment/reimbursement of the total costs together with a pre-determined profit. However, some expenses are not considered at times. This is due to an error or negligence on the part of the contractor. Furthermore, in some cases, both parties set the upper limit for the total costs of the project at the time of entering into the contract. The most important element of the cost-plus contract is that the client has to trust the contractor for the smooth execution of the project. Many central and state governments often use cost-plus contracts for quality infrastructure services with the help of qualified contractors.
The other name of Cost Plus Contract is Cost Reimbursement Contract or Cost Plus Fixed Fee Contract.
Types of Cost Plus Contract
There are only a few types of cost-plus contracts. And each of these types of contracts has a special characteristic that serves a specific purpose. They are as follows:-
Cost Plus Award Fee Contract
As part of the Cost Plus Award Fee Contract, the contractor receives a performance-based award upon completion of the project. In addition, the client and the contractor determine the price and amount in advance and write these into the contract. Depending on the quality of the service, this reward can be positive or negative.
Cost Plus Fixed Fee Contract
In the Cost Plus Fixed Fee Contract, the Contractor receives a fixed fee in addition to the reimbursement of the total costs. The client decides on this fee in advance and releases it after completing the project. In this context, the Contractor does not receive an appreciation bonus for good quality, cost reduction measures taken by him, or for the timely or early completion of the contract.
Cost Plus Incentive Fee Contract
Under the Cost Plus Incentive Fee Contract, the Contractor receives an incentive if it has met or exceeded expectations. Clients give incentives for such outstanding performance. This contract provides the Contractor with the opportunity to achieve higher profits. These incentives are under the contractual provisions of the Contract. In such contracts, the final payout is the total cost plus the pre-decided profit share plus the incentive under the slab or agreed terms.
Cost Plus Percentage of Cost Contract
As part of the cost-plus percentage of the cost contract, the contractor receives a predetermined percentage of the project cost as his profit. Profit would increase with an increase in the actual project cost, which is included in the copy of the contract. Most buyers or clients do not prefer this type of contract.
These types are not exhaustive; there could be other varieties as well.
Advantages
- In a Cost Reimbursement Contract, the contractor has sufficient flexibility in the design or any other aspect of the project.
- According to the Cost Reimbursement Contract, the risk of the contractor is minimal.
- This contract works best if the actual cost of the project is assumed to be below the projected cost.
- This type of contract focuses more on the quality of the project than on the overall cost of the project.
- If the budget for construction is low, this contract will fit. Simply put, it is a budget-friendly contract.
- Cost Reimbursement contracts are useful when outsourcing research and development activities, as it is difficult to estimate the cost of such projects.
- Regardless of the extent to which a particular project is unclear, construction can begin. Cost Plus Contract gives this liberty to the contractor and the client.
- In almost all cases, the actual total cost of the project is less than the cost estimated in the reimbursement contract.
- Such contacts are also useful when new experiments in terms of design, building material, process, or timeline are required, and the outcome and costs are uncertain.
These advantages are not exhaustive.
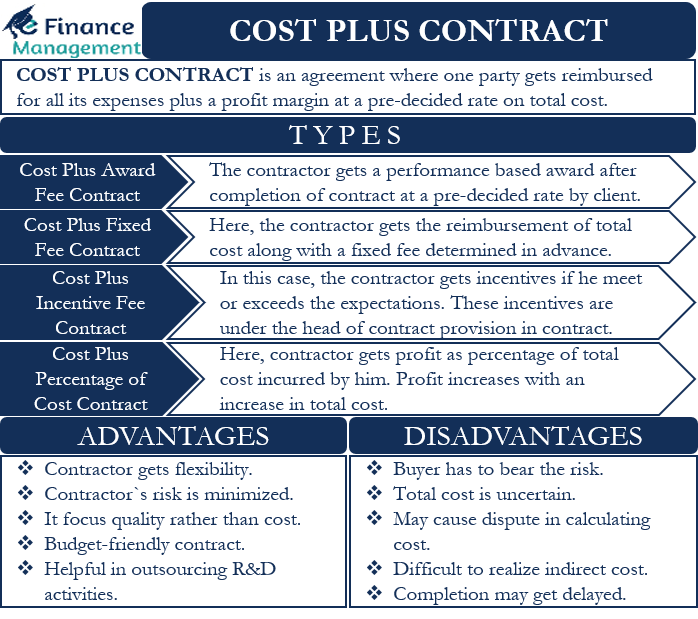
Disadvantages
- In a cost-reimbursement contract, the buyer of the contract bears the risk of the project.
- The total cost of the project is uncertain until the completion of the project. This might create pressure on the buyer of the project.
- Cost-plus contracts can take longer to conclude than other types of contracts.
- When calculating the total cost of the project, there is a high probability of disputes between the contractor and the buyer of the project.
- Sometimes the documentation work, which represents all costs, becomes a bone of contention for the contractor at the time of settlement.
- Sometimes it becomes difficult for the contractor to realize, estimate and include the indirect costs of the project.
- Since the reimbursement takes place after the project is completed, the contractor must manage the outflow of funds. Sometimes, it becomes a difficult task for the contractor to raise and manage funds until the reimbursement is made. However, the contacts may include clauses relating to advance payments and phased payments to take this aspect into account.
These drawbacks are not exhaustive.
Example of Cost Plus Contract
Let us understand the Cost Reimbursement Contract with a hypothetical example.
Contractual Terms
PQR is the contractor and has received a contract from STU Company- the client, to construct a building with an estimated total cost of 5 million USD. STU will reimburse all costs incurred by PQR. POR would make a profit of 15% on the actual total cost of the project. If PQR completes the project within 60 days of the legalization of the contract, PQR will receive an incentive of $0.2 Million.
Payment and Incentive Status on Completion of the Contract
PQR successfully completed the qualitative project within 55 days at a total cost of $4 million. Thus, the total payout to PQR would be $4.8 million. Calculation of the disbursement is described as follows:
Project cost of Rs. $4 million + $0.6 Million (15% profit on the total cost) + $0.2 million incentive for early completion of the project = total $4.8 million.
Conclusion
Despite some drawbacks of the Cost Plus contract, it is one of the most promising types of contract in the construction industry. It is extremely useful in the construction sector, and the contractor and the client usually prefer it. Especially if the design and flow chart is not finished or the scope is confusing, this contract works best in such a situation. It focuses on quality by showing all expenses with valid proof. Thus Cost Reimbursement Contract is one of the very popular and simple types of contract.

