Corporates making losses for a considerably longer period and facing severe financial distress adopt reconstruction as a method of reviving. Certainly, there are two primary methods of reconstruction. They are internal and external reconstruction. In this article, we will discuss the differences between internal and external reconstruction in detail.
Difference between Internal and External Reconstruction
Meaning
What is Internal Reconstruction?
A reconstruction that is undertaken by any entity under which significant changes are done in the company’s capital structure without exercising the option of liquidation of the company is called internal reconstruction. Therefore, the main purpose of internal reconstruction is that the management wants to build a good reputation to raise more funds for the expansion of the company.
What is External Reconstruction?
A reconstruction under which the company’s financial statements are wound up and a new company is formed while the existing assets and liabilities are taken over by the new entity after the reorganization of the financial position.
Methods Used
Internal Reconstruction
- Revaluation of assets
- Removing the fictitious assets
- Revise the share capital
- Negotiate with third parties such as banks and creditors
External Reconstruction
Certainly, there are two ways through which external reconstruction takes place:
- Amalgamation– “A” and “B” will lose their own existence to become a part of a new company
- Absorption- “A” will lose its existence and become a part of a completely new entity, “Q”
Example
Internal Reconstruction
The company ABC ltd. is incurring losses for the past 3 years. The directors of the company plan the internal reconstruction of the company. See the exhibit below:
| Liabilities | Pre ($) | Post ($) | Change | Remarks |
| Share Capital | 3,00,000 | 2,50,000 | -50,000 | |
| Preference Shares | 200,000 | 180,000 | 20,000 | Paid in cash |
| General Reserve | 150,000 | 30,000 | -120,000 | Loss on the asset side is set off |
| 16% Bank Loan | 250,000 | 250,000 | – | |
| 18% Debentures | 400,000 | 400,000 | – | |
| Creditors | 200,000 | 150,000 | -50,000 | 20,000 rebate and 30,000 paid |
| Bills Payable | 250,000 | 250,000 | – | |
| Total | 1,750,000 | 1,510,000 | -240,000 | |
| Assets | Pre ($) | Post ($) | Change | Remarks |
| Machinery | 200,000 | 170,000 | -30,000 | Revalued |
| Building | 700,000 | 730,000 | 30,000 | Revalued |
| Furniture | 200,000 | 180,000 | -20,000 | Revalued |
| Debtors | 120,000 | 120,000 | – | |
| Cash | 80,000 | 30,000 | -50,000 | 20,000 to preference shareholders & 30,000 to creditors |
| Goodwill | 250,000 | 200,000 | -50,000 | Subject to impairment |
| Profit & Loss | 120,000 | – | -120,000 | Set off using general reserve |
| Discount on Share | 80,000 | 80,000 | – | |
| Total | 1,750,000 | 1,510,000 | -240,000 |
The company ABC Ltd. conducted the internal reconstruction as follows:
- Reduced the share capital and preference share capital
- Reduced the general reserve to set off the loss of $ 120,000
- Negotiated with the debenture holders to reduce the interest rate
- Requested the creditors for a rebate and brought down the balance by $50,000
- Revalued the assets such as machinery, building, furniture, and goodwill
External Reconstruction
XYZ Ltd. has been incurring losses for the last 7 years. The company’s management has tried to revive the company through internal reconstruction but the company incurred severe failures even after internal reconstruction Hence, the management decided to go for external reconstruction by selling off XYZ Ltd to PQR Ltd.
| Liabilities | Amt ($) | Assets | Amt ($) |
| Share Capital (10000@100) | 1,000,000 | Fixed Assets | 800,000 |
| Capital Reserve | 200,000 | Current Assets | 400,000 |
| Bank Loan | 200,000 | Cash at Bank | 200,000 |
| Creditors | 300,000 | P&L A/C | 300,000 |
| 1,700,000 | Total | 1,700,000 |
PQR Ltd took the fixed assets and 60% of the current assets at a value of $900,000. They agreed to pay $740,000 in equity at $10 per share and the balance in cash. The creditors and bank loan were paid off in full settlement by PQR Ltd.
Let’s see the key differences between internal and external reconstruction in more depth.
Treatment of Losses
In the case of internal reconstruction, the losses incurred are settled against future profits. However, in the case of external reconstruction, the previous losses could not be balanced out by the future profits of the new company. This is because the old company gets completely dissolved and the losses are settled at the time of liquidation.
Who Undertakes?
Internal reconstruction is undertaken mainly by solvent companies or companies which have the potential to become profitable again. On the contrary, external reconstruction is undertaken by companies without the potential to bounce back, this implies that the management has tried to revise the financial structure but it continues to make losses over time. Therefore, external reconstruction seems to be the only way out.
Also Read: Recapitalization
Capital Treatment
Internal reconstruction follows a course of action that includes a reduction in capital and external liabilities while there is no reduction in the capital in the case of external reconstruction.
Assets and Liabilities
In the case of internal reconstruction, the assets and liabilities are not transferred while in the case of external reconstruction the liabilities and assets are taken over by the new entity at the time of liquidation.
Process Duration
The process of internal reconstruction is tedious and slow as it needs thorough discussions over various components of the balance sheet. however, on a contrary, external reconstruction is a quick process as the entire company is dissolved.
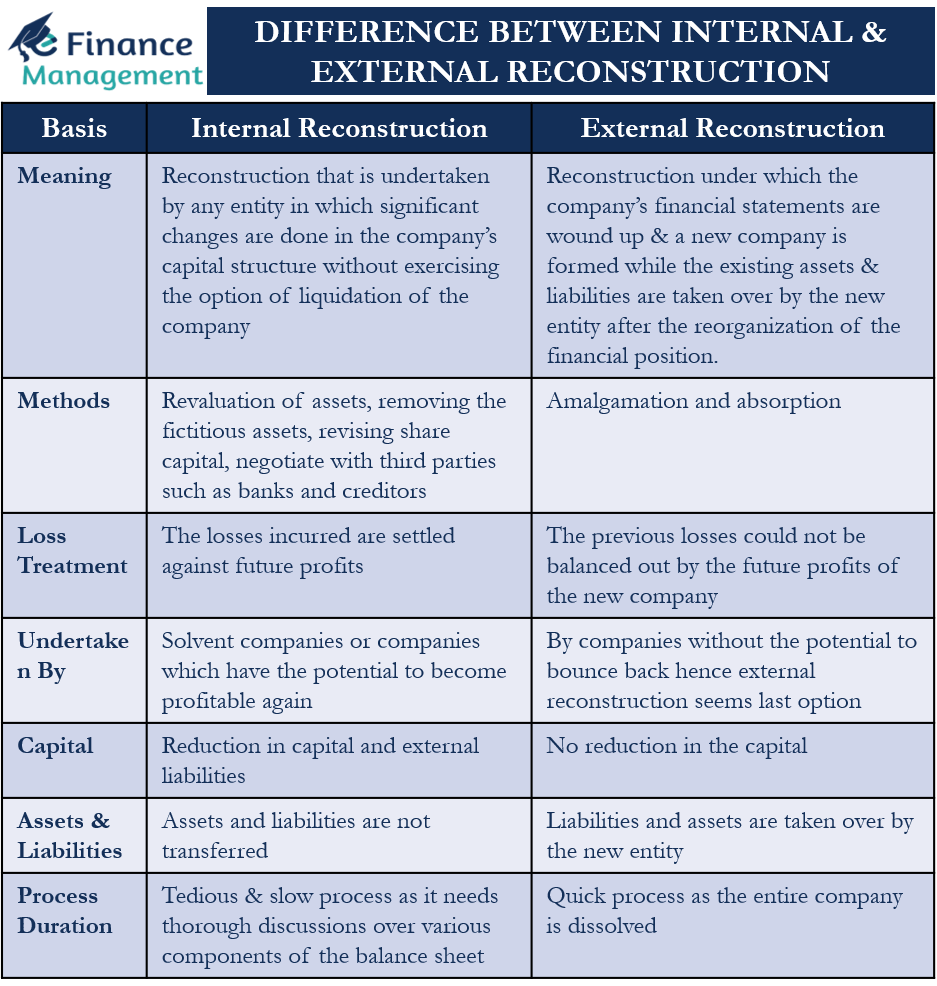
Table of Differences
| Basis | Internal Reconstruction | External Reconstruction |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Reconstruction that is undertaken by any entity in which significant changes are done in the company’s capital structure without exercising the option of liquidation of the company | Reconstruction under which the company’s financial statements are wound up & a new company is formed while the existing assets & liabilities are taken over by the new entity after the reorganization of the financial position. |
| Methods | Revaluation of assets, removing the fictitious assets, revising share capital, negotiate with third parties such as banks and creditors | Amalgamation and absorption |
| Loss Treatment | The losses incurred are settled against future profits | The previous losses could not be balanced out by the future profits of the new company |
| Undertaken By | Solvent companies or companies which have the potential to become profitable again | By companies without the potential to bounce back hence external reconstruction seems last option |
| Capital | Reduction in capital and external liabilities | No reduction in the capital |
| Assets & Liabilities | Assets and liabilities are not transferred | Liabilities and assets are taken over by the new entity |
| Process Duration | Tedious & slow process as it needs thorough discussions over various components of the balance sheet | Quick process as the entire company is dissolved |
Conclusion
Any company considering some revision or appraisal in its financial structure can consider any options between internal and external reconstruction. However, these methods are more difficult and complex than they seem to be. Therefore, it is important to have a proper understanding of the company to understand which treatment would be best suitable for the revival of the business.

