Material Non-public Information is an important aspect of corporate governance. It is now a big part of the security risk that companies face with regards to their important aspects of functioning.
Confidential Information, if gone public, might affect the goodwill, spot value, or trading of the security. The information is quite confidential, neither published nor known to the public. It is also designated as Insider Information or Trading. Non-public Information can influence the decision-making power of the investor. Material Non-public Information is manipulative and can gain an unfair advantage in the marketplace. Furthermore, the information is“material” if its disclosure would affect security.
The opposite of using MNPI is Mosaic Theory which most analysts and retail investors like to utilize.
What is Material Non-Public Information
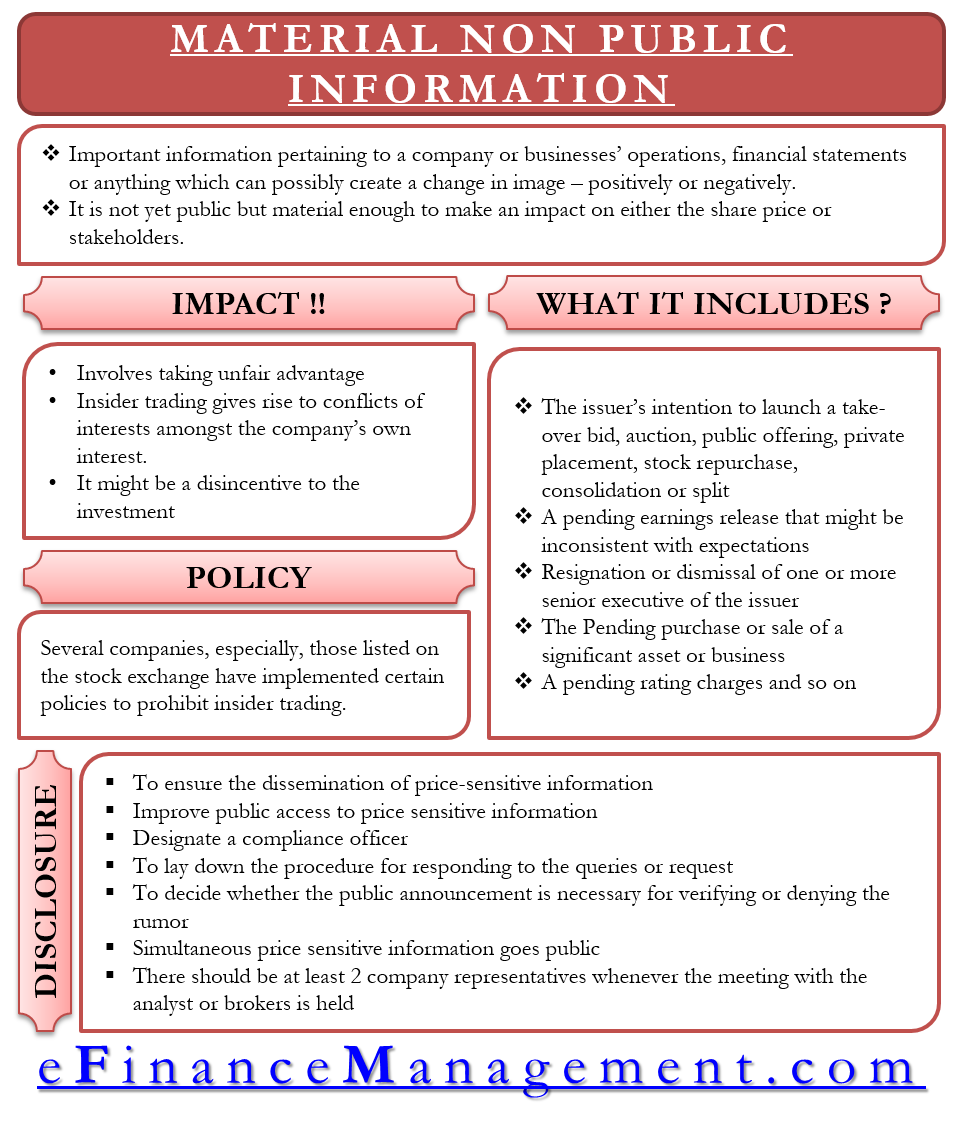
It is the important information pertaining to a company or businesses’ operations, financial statements, or anything which can possibly create an image change – positively or negatively. As the name suggests, it is not yet public but material enough to impact either the share price or stakeholders.
Impact of Material Non-Public Information
- It involves taking unfair advantage of the company’s information
- Insider trading gives rise to conflicts of interest amongst the company’s own interests and the insider’s interest
- Material Non-Public Information might be a disincentive to the investment
The US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) states the following comments regarding insider trading or non-public information. “Illegal trading generally refers to buying or selling a security, in breach of a fiduciary duty or other relationship of trust and confidence, while in possession of material nonpublic information about the security.”
Example of Material Non-Public Information
Suppose you are the owner of the Accor chain of hotels that has its branches all over the world and includes great services and value holiday packages. People like your hotels because of their service and cost-benefit value.
The confidential meeting held quotes that the hotel business was going through a heavy loss; a few Accor hotels might be sold to recover it. As soon as this news goes public, people may not revisit the hotel, thinking of its depriving state.
Suppose one of your relatives owns about 20% shares of the Accor hotel, and you tell him to sell the shares immediately. You are doing this based on insider trader or material non-public information. After you review the share, your relative decides to sell it off before bearing any loss.
Therefore, the above scenario causes unlawful insider trading, which is an imprisonable offense.
Policy for Material Non-Public Information
Several companies, especially those listed on the stock exchange, have implemented certain policies to prohibit insider trading.
‘Moody’s’ explains on its website how insider trading laws and regulations the world over do not allow buying or selling a company’s securities while in possession of Material Non-Public Information about that company. Disclosing such Material Non-Public Information is in itself a violation of these laws. This is especially true of the party you have disclosed this uses this information to make a financial decision regarding the company’s securities. Even if you personally do not gain or lose, you become a party to this violation.
Famous Case Study
One of the most famous case studies is the disclosure of material non-public information by consulting firm McKinsey’s CEO – Rajat Gupta, to hedge fund manager Raj Rajaratnam. Both were convicts under securities fraud in 2012, with Gupta as part of the hedge fund manager’s insider trading ring. The case clearly defines the strictness that dealt with the material non-public information in the U.S.
Material Non-Public Information Includes
- The issuer’s intention is to launch a takeover bid, auction, public offering, private placement, stock repurchase, consolidation, or split.
- A pending earnings release that might be inconsistent with expectations.
- Resignation or dismissal of one or more senior executives of the issuer.
- The pending purchase or sale of a significant asset or business.
- A pending rating charges and so on.
Disclosure Practice to Prevent Insider Trading
As per SEBI regulation, all listed companies need to follow a prescribed code for disclosure practice. However, the code prescribed by the company in this regard should have the following norms that might follow in the practice:
- To ensure the dissemination of price-sensitive information to the stock exchange continuously and immediately.
- Improve public access to price-sensitive information by the announcement in media.
- Designate a compliance officer who oversees corporate disclosures of price-sensitive information to an analyst, shareholders, and public.
- To lay down the procedure for responding to the queries or request for verification of market rumors by the stock exchange.
- To decide whether the public announcement is necessary for verifying or denying the rumor
- Simultaneous price sensitive information goes public.
- There should be at least 2 company representatives whenever the meeting with the analyst or brokers is held.
- Highlight the information on the website after the meeting with analysts and institutional advisor.
- Companies background information and other details are available on the website, enabling investors to get direct information.
- The stock exchange may disseminate information by listed companies through website or exchange network.
New Measures by Companies
To prevent the passing of sensitive information outside the organization, companies have now started employing strict and complex firewalls that block information with specific words in emails and attachments. It requires special permission for sending the documents and information to external ID. Traders and sales personnel are required to fulfill certain criteria to ensure that delicate information is not exposed. With secure attachments and the external drives for the purpose of emailing and posting procedures, their client communications are also recorded. Employees get periodic training on these policies and practices for self-updating.
Research wings of companies come under special scrutiny as many analysts are privy of a number of sensitive and private information through their interaction with fund managers and company people.
Punishment for insider trading ranges from dismissal and bad track record to civil injunctions, imprisonment, penalties and returning of profits.
Read a related term – adverse election. It is a situation where either buyer or seller has some material information on the product which the other party does not have.
