Definition of Cost Volume Profit Analysis
Cost Volume Profit Analysis explains the behavior of profits in response to a change in cost and volume. In other words, it is an analysis presenting the impact of cost and volume on profits. Commonly called CVP Analysis, a manager can find out the level of sales where the company will be in a no-profit-no-loss situation with this analysis. This situation is called the break-even point. Similarly, CVP analysis can also explain the no. of units of sales required to achieve a particular targeted operating income.
Example with Formula
Cost Volume Profit analysis thinks like a number line wherein it starts with negatives, then comes 0, and then positives. Similarly, with the increasing level of sales, first will see a phase of losses, second a break-even, and third where we make profits. The first priority of any businessman is to safeguard his investment and therefore try to save the capital shrinkage. This is possible if a business achieves the break-even point. The question is:
How much volume of sales/activity can achieve a break-even point for a business?
Let’s try to understand with the help of following assumptions:
Sales Price = $15
Variable Cost = $10
Total Fixed Cost = $50,000 / year
Contribution Margin
We will first introduce another term here, i.e., Contribution Margin. It is the difference between the sales price per unit and its variable cost per unit. The formula for Contribution Margin is as follows:
Contribution Margin = Price Per Unit – Variable Cost Per Unit = $15 – $10 = $5
Breakeven Point
Next, the formula for calculating breakeven point is as follows:
Breakeven point (in Units) = Total Fixed Costs / Contribution Margin = $50,000 / $5 = 10,000 Units.
So, if this business is able to sell 10,000 units in a year, it will neither make profits nor losses. So, this is the point from where it will start making profits in multiples of its contribution margin.
Units 10001 = Profit $5
Units 10002 = Profit $10
And, Units 10003 = Profit $15
Why is the profit increase in the multiples of contribution margin? It is because the contribution margin was first utilized to cover the fixed costs of the year. Once they are covered, the whole of this margin contributes towards profit. This makes the breakeven point all the more significant because this is the grey line between making losses and earning profits.
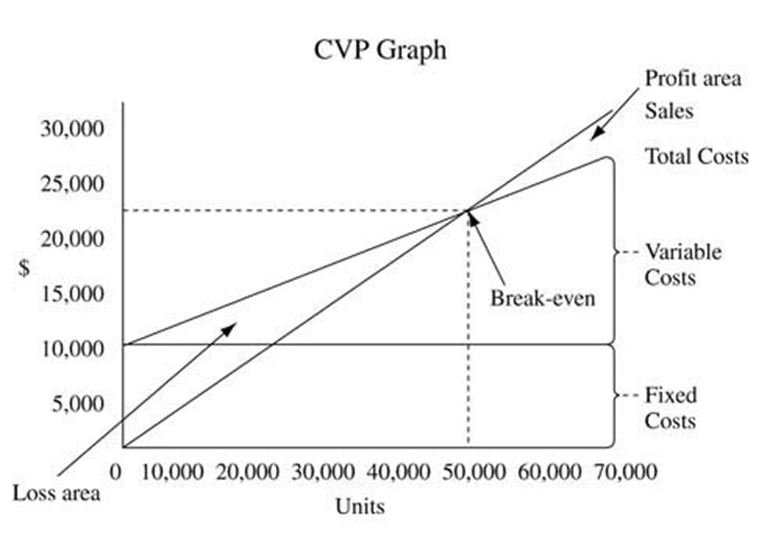
Margin of Safety
The margin of safety is the sales that a company makes over its breakeven point.
The formula for calculating the margin of safety is:
| Margin of Safety = Total Revenue – Breakeven Point |
Use Marginal Costing Ratios Calculator for a quick calculation
Assumptions
Following are the assumptions of CVP Analysis:
No. of Units – Only Driver for Costs and Revenues
It assumes that the total variable costs and revenues would increase or decrease only due to a change in the number of units. There are no factors that will affect it.
Costs – Either Variable or Fixed
This assumption says that all the costs are either variable or fixed. In other words, it says that there are no semi-variable or semi-fixed costs.
No Change in Price, Variable Cost, and Fixed Costs
CVP analysis assumes that there are no changes in the price and variable cost per unit irrespective of changes in the time period and relevant range. If we see it closely, it neglects the chances of changes in prices due to inflation, economic conditions, etc. Also, neglecting the bulk order discounts and small order premiums.
Also Read: Break Even Point

Importance
If you are offered a business idea wherein you sell chairs. The first thing few things that will strike your mind is
- Required initial investment
- Amount of sales required to break-even
- Assess whether you are capable of achieving that sale
This analysis is important because it answers the second most important question. This is not a one-time question as well. This is a regular assessment. A businessman must keep checking whether he is reaching the milestones set as per cost volume profit analysis. This will guide his decision-making process relating to increases in fixed costs, the speed of business operations, etc.
Advantages
- It helps managers find out a break-even point, target operating income, etc.
- Cost Volume Profit technique is used to evaluate investment proposals
- Sets the base for planning the marketing efforts of a business
- Helps in setting up the basis for budgeting activity
Disadvantages
- In a current dynamic business environment, the costs and prices can’t remain constant throughout the year. A manager is forced to react and make necessary changes in prices and costs due to changes in economic conditions, customer bargaining powers, competitors, etc.
- All costs cannot be classified as fixed or variable. There is a significant list of costs that are neither fixed nor variable but are semi-variable or semi-fixed. For example, a utility or electricity invoice contains rent as a component that remains constant irrespective of the change in usage of no. of electricity units.
- No. of units cannot be the only driver of total costs and revenues. There are other factors also that impact the prices as well as costs. The raw material price reduction can reduce the variable cost, and therefore the customers with knowledge of this change will demand a reduction in prices as well. Similarly, the entrance of a new big player in the market forces all the firms in the market to reduce their cost or compromise or bear the loss of customers.


Nice?
topics r define vry clearly
Really helpful
Thnq u
hello!,I really like your writing so so much! percentage we keep up a correspondence extra about your post on AOL? I need a specialist in this space to resolve my problem. Maybe that’s you! Looking ahead to look you.
Brief and to the point… Helpful..