What is Cost Leadership?
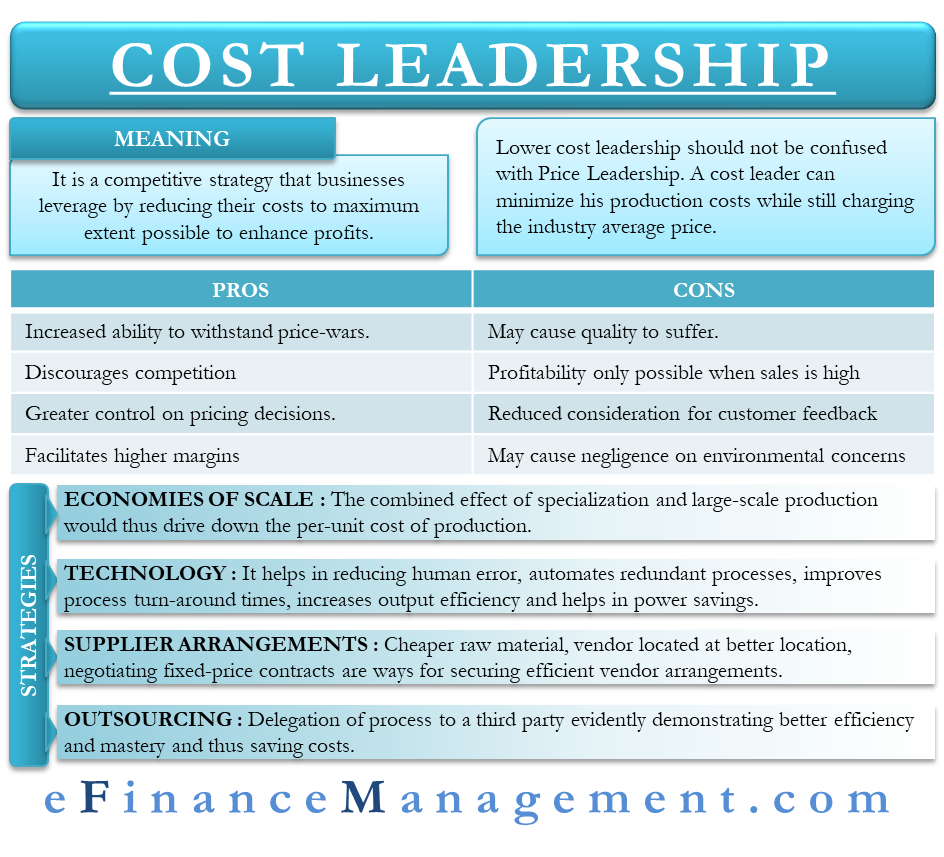
Cost leadership is a competitive strategy that businesses leverage by reducing their costs to the maximum extent possible to enhance profits. It is a strategic option. In this era of globalization and free trade economy, the competition is cutting edge. Businesses wanting to make a profit have no choice but to up their game and gain an advantage over their competitors at any cost. Securing a cost leadership is a sure-shot way of getting a head start over your competition. There is a direct impact on expense reduction and thereby increased profitability. Such low costs demonstrations also have an indirect benefit of discouraging new competition from entering into the market.
However, please do not confuse lower-cost leadership with price leadership. A cost leader can minimize production costs while still charging the industry average price. Therefore, attempts at market expansion may still be undercut by another player willing to undercut your prices.
Strategies of Cost Leadership
Economies of Scale
Adam Smith identified division of labor and specialization as the two key means of achieving greater returns on production. The theory asserted that as the production grew in scale, the workers would be more skilled at their specific tasks and perform with greater efficiency. The combined effect of specialization and large-scale production would thus drive down the per-unit cost of production and will result in economies of scale.
Technology
The importance of technology in today’s fast-paced competitive environment cannot be overemphasized. When all else fails, technological benefits can prove to be the key distinguishing factor placing a business in a position of vantage over its rivals. From the reduction of human error, automation of redundant processes, improving process turn-around times, and increased output efficiency to significant power savings, the application of technology to cost savings is endless and ever-evolving.
Supplier Arrangements
As is true for any business, raw material costs constitute the bulk of production costs. Therefore, a wrong deal could cause a blow to the entire budget and profitability forecasts. It may, therefore, be worthwhile for businesses to double-check the rates at which they purchase supplies and regroup their buying arrangements. Purchasing alternate cheaper raw materials, purchasing from vendors better located to save on logistics, negotiating fixed-price contracts are some of the ways to secure efficient vendor arrangements.
Outsourcing & Cutting Slacks
An able cost leader will not shy away from doing away with processes no longer serving the larger purpose. Instead, it would delegate a process to a third party, evidently demonstrating better efficiency and mastery and thus saving costs. Seeking consultancy and professional advice to identify lags in the production line may be a worthwhile investment, often leading to windfall cost savings in perpetuity.
Examples of Cost Leaders
McDonald’s
Often on the run to quell the fries and shake craving, you may have come across the noisy kitchen of a McDonald’s outlet. A well-coordinated line of employees with the almost robot-like efficiency of an assembly line prepares your order in perfect sync. This is no coincidence but a consciously employed practice of division and specialization of labor. With a highly-skilled kitchen staff, this outlet is, therefore, able to seamlessly carry out its operations with minimum managerial personnel. Thus, saving huge on remuneration expenses and driving down overall costs.
Walmart
When it comes to retail shopping, Walmart is inevitably the first to come to mind. Walmart’s primary assertion of “Everyday Low Prices” is one not made lightly. Consistently promising such low prices would not be possible without securing a cost leadership vantage. The mammoth scale of operations gives almost a monopoly-like position to Walmart. Thus, allowing it to negotiate on its own terms with the suppliers. Additionally, the low prices have attracted a wide customer base, thus reinforcing a vicious cycle of large volumes leading to lower prices and so on.
Southwest Airlines
This is perhaps the most direct example of applying Porter’s fundamental principles of cost savings or Porter’s Generic Strategies. The company has implemented several cost reduction initiatives such as high-density seating, lesser flight times, and operating from smaller airports to avoid increased ground time and congestion. All these factors directly contribute to lower costs, thus enabling it to charge aggressively low fares. The airline also remains abreast of technological advancements. It has been quick to switch to newer and better models of aircraft for better fuel efficiency and reduced maintenance costs, among other advantages, all consequently aimed at cutting costs.
Pros & Cons of Cost Leadership
Advantages of Cost Leadership
- Increased ability to withstand price wars.
- Discourages competition from setting up shop by demonstrating unbeatable margins.
- Flexibility to fix selling prices as per demand-supply forces currently in force, therefore, rendering greater control on pricing decisions.
- Facilitates higher margins, thus leading to increased capital available for plow back and expansion.
Disadvantage of Cost Leadership
- Hyper-focus on cost reduction may cause quality to suffer.
- Profitability can be seen only when sales volumes are high.
- Reduced consideration for customer feedback jeopardizes a loyal customer base.
- Pressure to keep costs to a minimum may cause businesses to neglect environmental concerns and best practices.

