The gross profit margin is the first benchmark of a business model. Businesses failing to achieve the maximization of gross profit margin fails to move further as the business model itself is not economically viable. How to analyze the gross profit margin is a common question that every entrepreneur and business person asks.
Gross profit margin (GP Margin) measures the initial sales margin before deducting operating expenses such as selling and distribution, administrative, financing, taxes, etc. A business is meant to earn profits. To avoid losses and make sufficient profits, there is a need to earn desirable profit margins to cover all the other operating expenses and still leave a margin for the owners of the capital.
It is essential to achieve good gross margins as high as possible. Achieving and sustaining those margins requires a careful analysis of the margins to find out internal reasons, even when the margins are high.
How to Analyze GP Margin?
To improve the gross margins, first, we need to analyze them for the cause.

Reasons for Higher Gross Profit Margin (GPM)
Efficient Management
Efficient and effective management of the processes may genuinely lead to higher GPM. The gross profit margin is very dynamic and may change every year. In such a situation, with a good gross profit margin in a particular year, management cannot sit and wait for gross margins to decline. It should keep a close watch to sustain such margins for the future.
Also Read: Gross Profit Margin and its Interpretation
Low Cost of Production
If, due to the introduction of new and improved techniques, the production cost reduces, the gross margin may improve, which is a good sign of profit maximization, future sustainability, and growth. Maintaining the new and improved techniques is also very important. In the absence of proper maintenance, the gross profit margins in future years may decline.
Increase in Sales Price
An increase in the product’s price would directly impact the gross margin. It is a sound performance of management only if the management has achieved higher prices because of the introduction of new features and improved product quality. If the prices are driven by the economy, there is no management role, and the economy may move in the other direction also in the future. Therefore, the management should be ready for the downside economy.
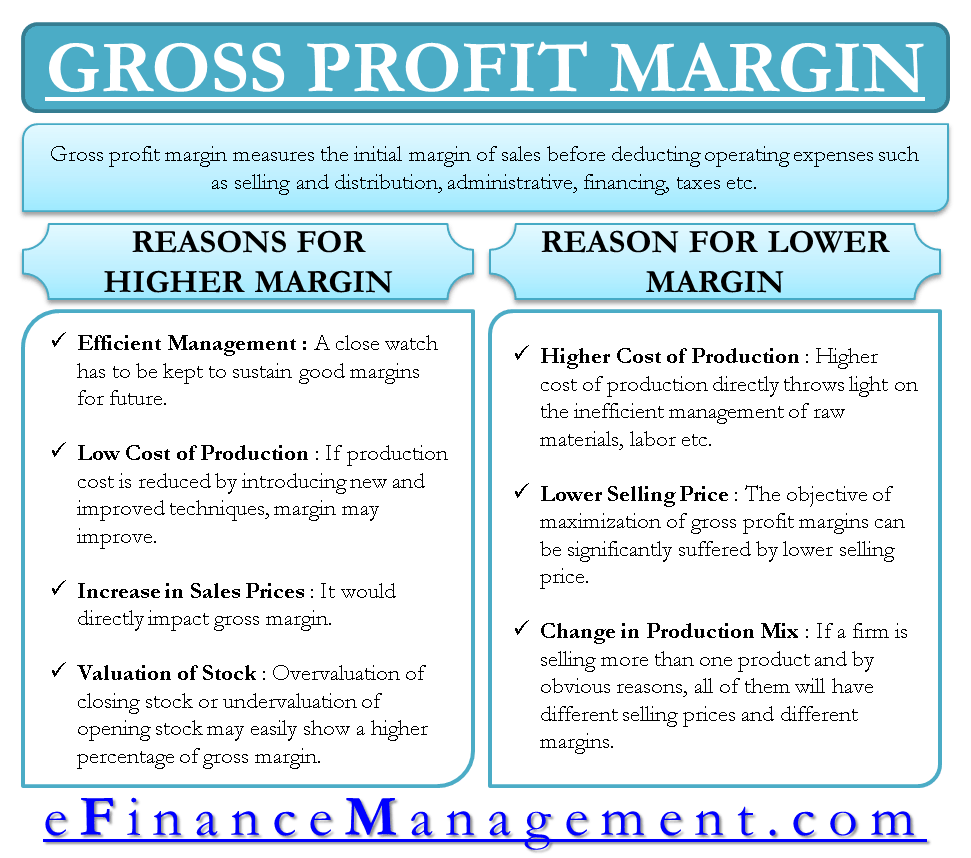
Valuation of Stocks
This is a very sensitive point. Overvaluation of closing stock or undervaluation of opening stock may easily show a higher gross margin percentage. This is not a real business tactic to maximize gross margin but a misrepresentation of facts. Owners and investors should always focus here on discouraging such practices.
Reasons for Lower Gross Profit Margin (GPM)
A lower gross profit margin is a bad sign for any business, and it calls for a very extensive and careful analysis. Various reasons for lower GPM maybe
Also Read: How to Increase Gross Margin?
Higher Cost of Production
The higher cost of production directly throws light on the inefficient management of raw materials, labor, etc. The problem may also lie in the utilization of current and fixed assets simultaneously. The hurdle has to be figured out first. If the hurdle is the higher labor cost, the management may think of shifting the plant to a different location, provided it is economically feasible. Similarly, other factors need careful examination.
Lower Selling Price
The objective of maximization of gross profit margins can suffer significantly by lower selling prices. Now, lower selling prices may be a reason for the low quality of products. The quality needs to be focused on and improved to regain the gross profit margins. The other uncontrollable reasons may be severe competition and lack of demand. These situations call for innovation in terms of new products and innovative selling techniques or better services.
Change in Product Mix
If a firm sells more than one product for obvious reasons, it will have different selling prices and margins. If the sales of a product with a lower margin are more, it will affect the overall gross profit margin. At times, it requires focusing on the mix of selling the products on managing the levels of gross profit margin.
The gross profit margin maximization may be attained with new techniques such as six sigma, total quality management, and just-in-time. However, implementing such techniques requires a lot of research on the current business model. They bring about a paradigm shift in the way of conducting business. Generally, consultants are hired to do the feasibility test about the implementation.
To learn more about GP Margin, refer to GROSS PROFIT PERCENTAGE.


I liked your furture accountant information which is helpful to clarify the basics of accounting terms