What is Chapter 7 Bankruptcy?
Bankruptcy under Chapter 7 is like Liquidation Bankruptcy. Filing bankruptcy under this is most suitable when there is a lag in paying bills and there are no other means to honor the monthly commitments and expenses. It is the last remedy to help you reshape your finances. In the process, you may have to liquidate some of your assets and further affecting your creditworthiness.
Upon filing under this Chapter, the Court grants a temporary stay on current debts. It stops creditors from recovering their dues, foreclosing on your home, etc. Then, the Court appoints a bankruptcy trustee who takes charge of the assets and, most importantly, liquidates the “non-exempt” assets to settle the overdue creditors. The trustee’s job is to review the asset-liability position and meanwhile also arrange for the creditor’s meeting. He further categorizes the debts into different classes based on their priorities and arranges for their payments.
The unsecured priority debts get their due first, which is followed by secured debts. Lastly, the non-priority unsecured debts get their money from the balance funds available. In case of insufficient funds, the remaining debts get a pro-rata disbursement for their dues.
Prerequisites for Filing under this Chapter
Before filing under this Chapter, the debtor needs to comply with specific conditions:
- Completion of credit counseling course from an approved agency at least six months before filing.
- The debtor’s current monthly income for the last six months has to be below the median standard of income for a similar household in your state. Alternatively, passing a mean test to determine that the disposable revenue is sufficient to meet the partial payments towards unsecured creditors.
- There should not be any filing of Chapter 7 bankruptcy in the last eight years.
- There was no filing of Chapter 13 bankruptcy in the last six years.
- If your case was earlier has undergone dismissal under Chapter 7 or Chapter 13, reapplication is not permissible before six months.
- The Court may dismiss your case if the intention is to defraud the creditors. For instance, taking a loan with the intent to declare bankruptcy to avoid paying the debt.
Steps for Filing under Chapter 7
Counseling & Filing of Forms
The applicant must first undergo credit counseling from an approved agency within 180 days before filling. If no approved agencies exist in the state, this step can be avoided. Grant of other relaxations happens on a case-to-case basis. The applicant must complete the filing of several forms entailing details like personal information, debtor’s finances, creditors, properties, incomes, and expenses. A petition also has to be filed in the Court, based on which grant of an automatic stay takes place that prevents the creditors from collecting the debts.
Also Read: Bankruptcy – Chapter 13
Appointment of Trustee and Creditor’s meeting
The Court engages a Trustee who takes the hoard of all the assets and categorizes those that can be liquidated to settle the creditors. Post this, the creditors’ meetings happen to confirm the validity of the petition and the claims. It further allows them to meet the debtor as well as the trustee and ask questions.
Classification of Assets and Repayment of Debt
The assets of the debtor are classified under the Exempt and Non-Exempt categories by the trustee. It is required to sustain the basic standard of living of the debtor. The exemptions vary from state to state, and in many cases, they are allowed to continue ownership of their primary homes, car, and personal belongings. The Non Exempt assets are seized, liquidated, and settled against the creditors.
Discharges of balance Debt
Most of the obligations get their due under this process, which releases the debtor from personal liability. Post this; the creditor may no longer avail of future recourse. There are certain debts as per the US Bankruptcy Code that cannot be discharged under this Chapter. The list, as per the Code, consists of 19 categories. Some of them are Alimony, Child Support, Income tax, federal student loans, etc., which are not allowed to be released during the process of bankruptcy.
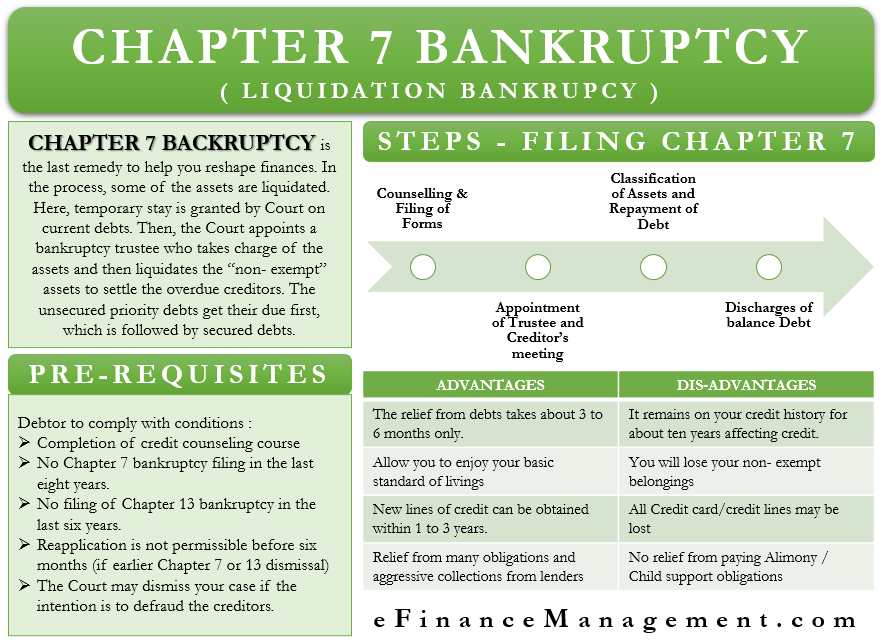
Settlement of Debts
The below table gives a glimpse of the debts that can be discharged under this Chapter, along with their discharge rates:
| Debts discharged under Chapter 7 | Debts not discharged/challenging to be discharged under Chapter 7 |
| Credit card outstanding, medical bills, personal loan without collateral | Child Support, Alimony, Student loans, tax debts, Court fees and penalties, Homeowners association fees, and Personal injury debts caused by accident under intoxication. |
Recent studies indicate up to 99% of discharges in credit cards and medical bills. Of the same, more than 90 % are fully discharged. Taxes and student loans follow it at 61 % and 15 %, respectively.
Also Read: Bankruptcy
Also, read Absolute Priority to learn more about the process or rule of settling debt.
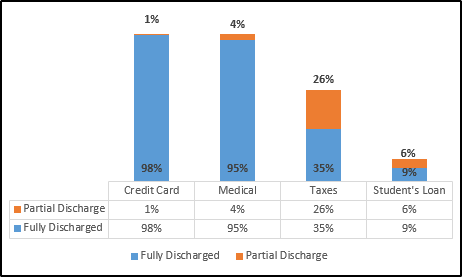
Emerging from Chapter 7
Unlike Chapters 11 and 13 bankruptcy, which usually takes a long time to discharge the debts with low success rates, the turnaround time in Chapter 7 is much better and affordable. About 90 % of the applicants who filed for Chapter 7 had their debts settled in six months or less. About 85 % of them got further relief, such as no phone calls for recovery because the Court issues an automatic stay.
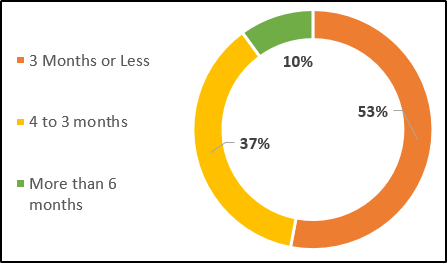
Advantages & Disadvantages of Chapter 7
Although it is much simpler to file bankruptcy under this Chapter, It is equally important to know the pros and cons associated with it to decide the best options for your needs. The below table features some of them:
| Points | Disadvantages | Advantages |
Credit Score | Chapter 7 bankruptcy remains on your credit history for about ten years, which may affect your credit score. | Though bankruptcy stays for some years in your credit history, the relief from debts takes about 3 to 6 months only. If you miss Chapter 7 when it may be right for you, it may be more challenging to explain the future lender other than bankruptcy. |
Liquidation of Assets | You will lose your non-exempt belongings in the process of settling the debts. | Many State exemptions allow you to enjoy your basic standard of livings to continue with your primary house, car, salary, or wages that you earn, etc. |
Credit Lines | All Credit card/credit lines may be lost. | New lines of credit can be obtained at higher interest rates within 1 to 3 years. |
Relief from Debts | It will not relieve you from paying Alimony / Child support obligations or Student loans. | It will relieve you from many other obligations and prevent you from aggressive collections from lenders. But only a Family Court can suspend Alimony / Child support dues. |
Time for refining under Chapter 7 | No Filing under this Chapter can be done within six years of filing bankruptcy under Chapter 7 or 13 earlier. | The limitation of 6 years does not apply if at least 70 % of unsecured debts are paid under Chapter 13 in good faith. |
Earlier Dismissal under Chapter 7 of 13 | Refilling under this Chapter cannot be done within 180 days if the case was dismissed under Chapter 7 or 13 due to a) Violation of Court order or b) The dismissal was requested after a creditor asked for relief from the automatic stay. | These limitations last only for six months. It can be avoided when the Court orders are respected and not having the case is dismissed. |
Continue reading about other What is Bankruptcy & its Types.

