Elaboration of the need to calculate Diluted EPS arises from the factor needed to value a company so as to obtain financial figures to assure investors of the market performance. However, it is important to recap some basic concepts.
The portion of a company’s profit allocated to each individual outstanding share is Earnings Per Share or EPS. The measurement of Earnings Per Share without making any adjustments is Basic EPS. On the other hand, Diluted EPS is the measurement of the quality of Earnings Per Share after accounting for exercised convertible securities.
Since our focus is on calculating Diluted EPS, let us understand its concept primarily. In simple terms, EPS is the company’s income minus preferred dividends, divisible by the total number of shares outstanding.
Since companies also issue additional shares, existing shareholders are often ‘diluted.’ Therefore, Diluted EPS measures the EPS after a modified number of shares, thus accounting for the additional units.
Also Read: Diluted EPS Calculator
Diluted EPS: Calculation
In a normal scenario where details of all adjustments are available, we would use the following formula:
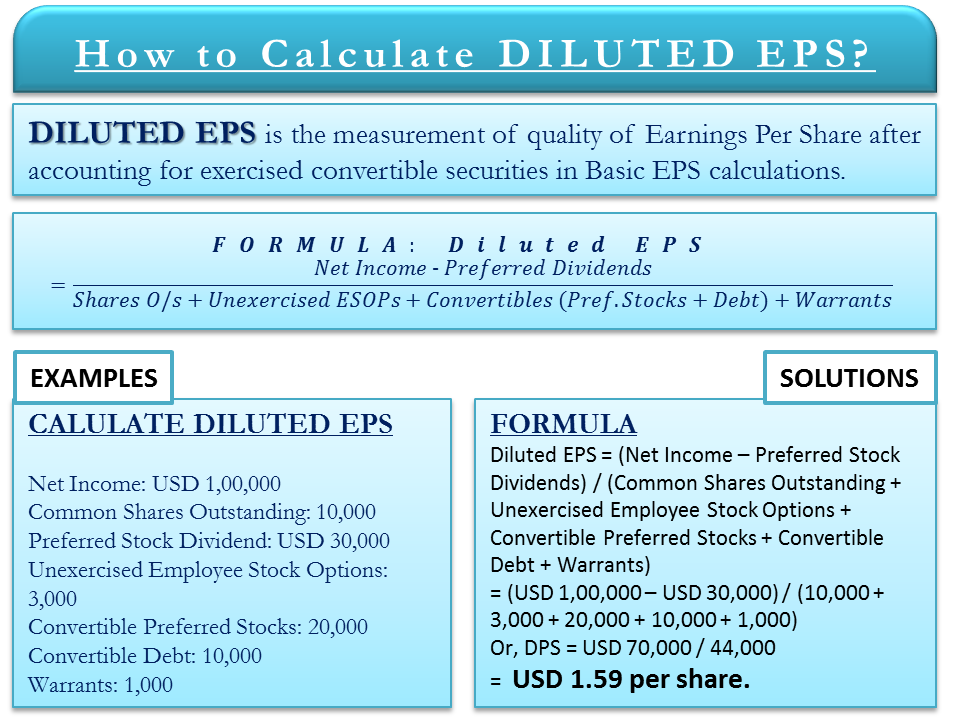
Diluted Earnings Per Share = (Net Income – Preferred Dividends) / (Shares Outstanding + Unexercised Employee Stock Options + Convertible Preferred Stocks + Convertible Debt + Warrants)
OR
When considering the effect that stock options have on issued shares, we would consider the following set of formulas:
Diluted Earnings Per Share = (Net Income – Preferred Dividends) / (Shares Outstanding + Diluted Shares)
Where Diluted Shares = Stock Options Issued – Value of Stock Options in Current Shares
We would also need to find out the value of the payment made to exercise options:
Amount Paid = (Options Issued) x (Exercise Price Per Share)
Followed by determining the value of options in stocks:
Value of Options in Current Shares = Amount Paid to Exercise Options / Current Share Price
Diluted Earnings Per Share Examples
Example 1
Following is the information from the reports of Fizzy Ltd.:
Net Income: USD 1,00,000
Common Shares Outstanding: 10,000
Preferred Stock Dividend: USD 30,000
Unexercised Employee Stock Options: 3,000
Convertible Preferred Stocks: 20,000
Convertible Debt: 10,000
Warrants: 1,000
From the provided figures, we calculate Diluted EPS as follows:
Diluted Earnings per Share Formula = (Net Income – Preferred Stock Dividends) / (Common Shares Outstanding + Unexercised Employee Stock Options + Convertible Preferred Stocks + Convertible Debt + Warrants)
= (USD 1,00,000 – USD 30,000) / (10,000 + 3,000 + 20,000 + 10,000 + 1,000)
Or, DPS = USD 70,000 / 44,000
= USD 1.59 per share.
Example 2
Company Bubbly Inc. provides the following figures from its statements:
Net Income: USD 10,00,000
Common Shares Outstanding: 1,00,00,000
Current Share Price: USD 10
Options Issued: 10,00,000
Exercise Price: USD 20
From the above numerical figures, we would first obtain the value paid:
Amount Paid = (Options Issued) x (Exercise Price Per Share)
= 10,00,000 x USD 20
= 20,000,000
Then, find out the current value of shares:
Value of Options in Current Shares = Amount Paid to Exercise Options / Current Share Price
= USD 20,000,000 / USD 10
= USD 2000,000
Thereby, Diluted Earnings Per Share can be finally obtained:
Diluted Earnings Per Share = (Net Income – Preferred Dividends) / (Shares Outstanding + Diluted Shares)
= USD 10,00,000 / (10,000,000 + 2,000,000)
= USD 0.0833
You can also use our Diluted EPS Calculator.
Importance of Calculating Diluted EPS
Investors and analysts assume that Basic Earnings Per Share overstates the actual Earnings Per Share2. Thus this also over calculates that a common shareholder is entitled to more shares.
The objective of calculating Diluted Earnings Per Share is to determine and present earnings per share, improving the comparison of performance among different business concerns for the reporting period and between
Also Read: Basic vs Diluted EPS – All You Need To Know
different accounting periods for the same business. The calculation focuses on the denominator of the earnings per share calculation. Which even though earnings per share data has limitations because of different accounting
policies used for determining ‘earnings,’ a consistently determined denominator enhances the quality of financial reporting.
Options and warrants are often outstanding in companies. This increases the total number of outstanding shares upon conversion. Considering this, the growth in the count of shares dilutes the conversion. This dilution can be accounted for only by calculating Diluted EPS, especially where options are pending conversion.
The importance of calculating Diluted EPS is validated by its means to account for shares a company might issue.
Practical Aspects of Calculating Diluted EPS
In calculating Diluted Earnings Per Share, we consider including convertible shares in the formula. Convertible shares are converted into the company’s shares. Diluted Earnings Per Share hence accounts for lower Earnings Per Share as the denominator value is higher. This is in comparison to the calculation of Basic Earnings Per Share.
Note: As a comparison, let us compare Basic EPS with Diluted EPS to obtain differentiation from Example 1 above by using the formula:
Basic EPS = Net Income / Common Shares Outstanding
= USD 1,00,000 / 10,000 = USD 10 per share.
Therefore, it can be seen that Basic EPS is USD 10 per share, whereas Diluted EPS obtains USD 1.59 per share.

