The acid test ratio is the ratio that measures the liquidity of a company and its ability to take care of its short-term liabilities. This ratio is an improvised version of the current ratio. And it tries to do away with the limitations of the current ratio. The Acid test ratio is also called a Quick ratio. The article discusses the advantages and disadvantages of the acid test ratio/quick ratio.
Advantages of Acid Test Ratio
Removal of Inventory in Calculation
The acid test ratio removes the inventory from the formula of the current ratio. The inventory may not always be considered liquid. Thereby, it gives a more appropriate picture of the company’s liquidity position.
Removal of Bank Overdraft and Cash Credit
Bank overdraft and cash credit are removed from current liabilities because inventory is not included in current assets. Bank OD and CC are usually secured by inventory. The removal makes the ratio more meaningful in arriving at the company’s liquidity position.
No Complication due to Inventory Valuation
Inventory valuation can be tricky, and it may not always be at marketable value. Thus, the acid test ratio is not handicapped as there is no need for the valuation of the inventory.
Avoid Seasonal Impact
Inventory can be very seasonal in nature and may vary in quantity over a yearly period. If considered, it may deflate or inflate the liquidity position. By avoiding inventory from the calculation, the acid test ratio does away with this problem.
Reliable Payment Capability
In a dying industry, which usually may have a very high inventory level, this ratio will provide a more reliable repayment ability of the company against the current ratio, which includes inventory.
Appropriate Short-term Financial Strength
Due to the large inventory base, a company’s short-term financial strength may be overstated if the current ratio is used. By using the acid test ratio, this situation can be handled. It will limit companies from getting an additional loan, the servicing of which may not be as easy as stated by the current ratio.
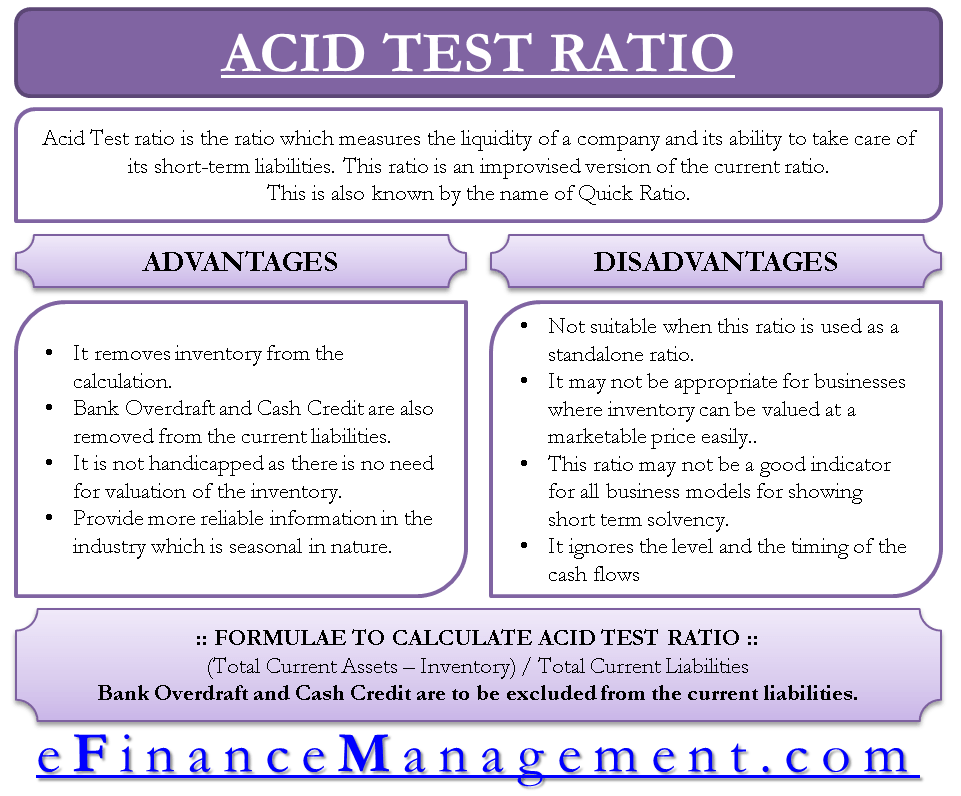
Disadvantages of Acid Test Ratio
Not Suitable as a Standalone Ratio
Using this ratio on a standalone basis may not be sufficient to analyze the company’s liquidity position. A comparative analysis with peers and industry standards may be required for effective analysis. This ratio, when looked at along with its parent ratio, i.e. current ratio, gives better insights.
Exclusion of Inventory
This ratio removes inventory from the calculation, which may not be appropriate for businesses where inventory can easily be valued at a marketable price. It should instead be included than excluded to arrive at the company’s liquidity position.
Inappropriate for Inventory Intensive Businesses
This ratio may not be a good indicator for all business models for showing short-term solvency because if companies with usually higher inventory, like supermarkets, exclude inventory to arrive at a liquidity position, it may not be essentially correct to do so.
Ignores the Timing of Cash Flow
The acid test ratio ignores the level and the timing of the cash flows. Which actually would be a major parameter determining the company’s ability to pay liabilities when they become due.
Includes Accounts Receivable
The ratio considers accounts receivables as ‘liquid’. And can be easily converted to cash which may not always be the case in reality.
Ignores Working Capital Requirement
The formula for a quick ratio assumes that a company liquidates all its current assets to pay the current liabilities. That is not still the case as the company will need some working capital for the operations.


I have been absent for a while, but now I remember why I used to love this web site. Thank you, I will try and check back more often. How frequently you update your web site?
Thanks for the sensible critique. Me and my neighbor were just preparing to do some research on this. We got a grab a book from our area library but I think I learned more from this post. I’m very glad to see such great info being shared freely out there.