Innovation Matrix is a model or visualization that depicts different aspects of innovation. We can say that it is a strategic option that helps companies visualize innovative dimensions to come up with a new product or service. Basically, this matrix helps a firm to identify what category they fall into and what changes they need to incorporate to be ready for innovation. This matrix facilitates, guides, and leads a company to find the right innovation strategy.
Primarily, an Innovation Matrix helps a company with the following aspects in relation to an innovation:
- To help in finding the source of innovation.
- To find out its strategic relevance.
- And to find the type of governance system to use.
This matrix can include many variables to help companies make decisions, but the two most used variables are Competence and Commitment. A point to note is that different types of Innovation Matrix can include different forms of these two variables. For instance, one popular Innovation Matrix uses these two variables: Defining the problem and Defining the Domain and skills. Defining the problem is similar to Commitment, and Defining the Domain and skills is similar to Competence.
There are many kinds of Innovation Matrix. However, here we would like to focus on and discuss the two most popular kinds of innovation matrix. The first is the ‘4 types of Innovation,’ and the other is the ‘Competence and Commitment.’
Innovation Matrix: 4 Types of Innovation
This matrix helps a company to choose the right type of innovation strategy on the basis of their understanding of the problem at hand and the resources they need to address it.
Also Read: Strategic Options
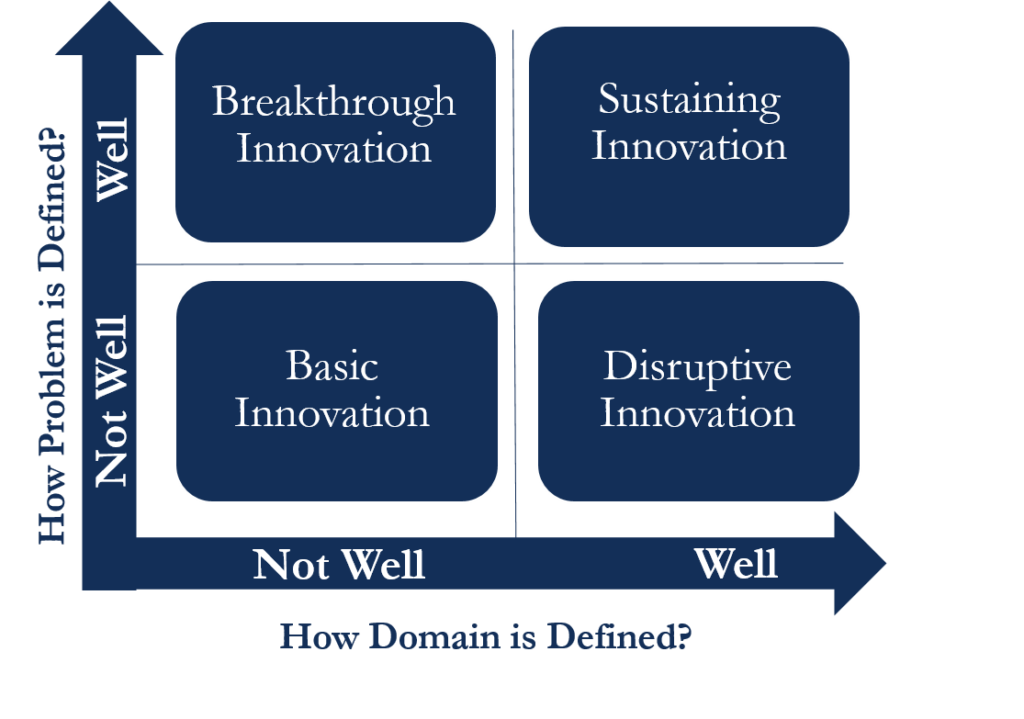
This Innovation Matrix primarily talks about four types of innovations. These four innovations are – Breakthrough Innovation, Disruptive Innovation, Basic Research, and Sustaining Innovation.
This matrix evaluates these four innovations in two aspects. First is how well a company is able to define the problem for which they need a particular type of innovation. This aspect comes on the vertical axis.
And the second crucial aspect that helps in choosing the right innovation strategy is defining the domain and skills that are necessary to address the issue. This aspect comes on the horizontal axis.
Types of Innovation
As said above, this Innovation Matrix usually talks about four types of innovation. These are:
Breakthrough Innovation
Other names for this innovation are radical innovation or revolutionary innovation. Such types of innovation create a paradigm shift—for example, the invention of a computer chip and the discovery of the structure of DNA.
Disruptive Innovation
Such innovation helps to make available expensive or highly sophisticated products or services that were previously available to high-end users to a broader population. So, such an innovation proves disruptive for the already established players in the industry. This could be in terms of ease of use, easy availability with less costs, etc.
Basic Research
Groundbreaking innovations do not just happen; instead, there is usually a major discovery preceding it. So, the basic research here means that companies invest in R&D with the hope to use that research to come up with an innovation in the future.
Sustaining Innovation
Such an innovation leads to further improvement and expansion of current product/service possibilities. In this, the utility of the product, usage possibility of product, or operational ease will further improve. Or, we can say that a company can easily manage such an innovation using its current governance and accountancy models. Another name for this type of innovation is incremental innovation.
Innovation Matrix: Competence and Dedication
This Innovation Matrix helps to identify what kind of innovator a company is. Or how serious a company is towards innovating. Moreover, it also tells companies what they need to do to reach a desired level of innovativeness.
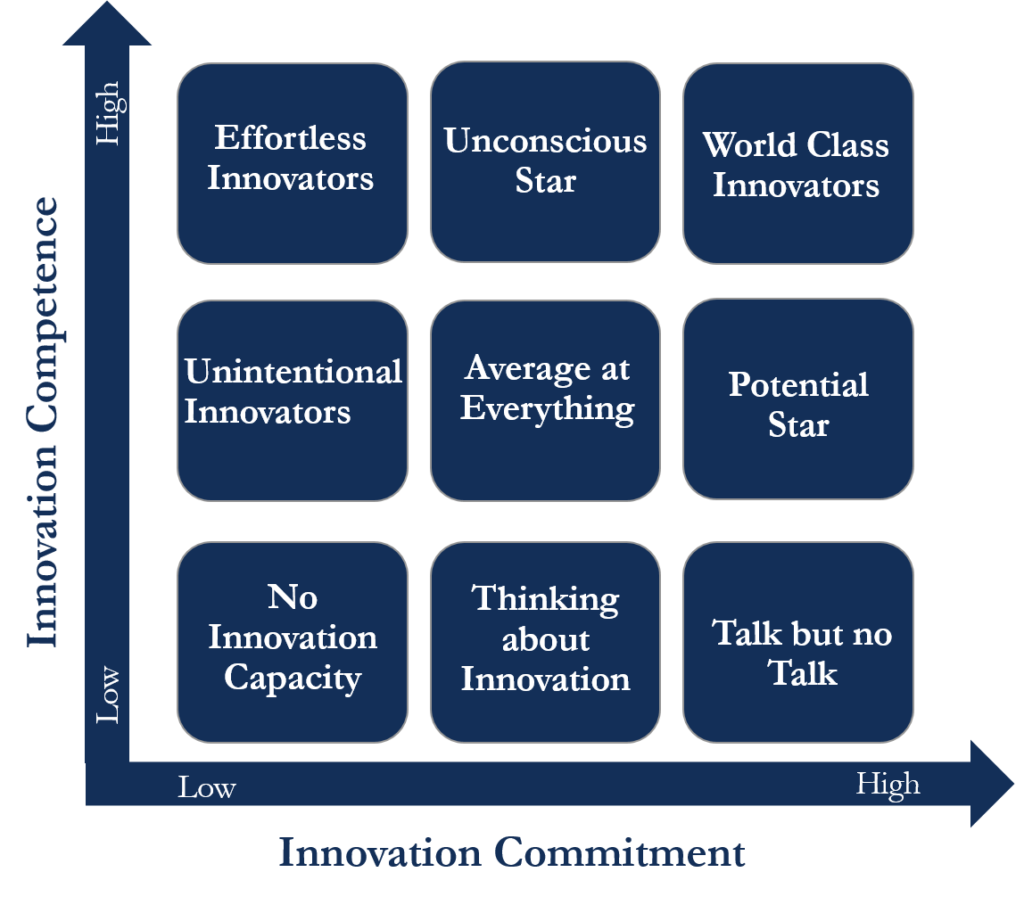
To identify this, the matrix takes into consideration two aspects or two dimensions:
The vertical line represents the degree of innovation competency, or the ability of a firm to come up as well as execute new ideas.
And the horizontal axis represents the dedication or commitment of a company towards innovation. Or, we can say how vital innovation to a company is or how many resources a company is willing to invest in coming up with an innovation.
Competence and Dedication: Classifications
The above two dimensions – competency and dedication, resulting in nine different classifications. These are:
No Innovation Capacity
This category represents companies that do not have the commitment as well as competence to innovate. Such a thing is not always negative. Some firms may not innovate, but they still work to add value to their product or service. Also, there are firms that do not innovate because they hold a strong position in an industry where other players are still struggling. So being in a comforting and commanding zone, they do not want to get distracted. And thereby do not want to divert their focus and resources.
Thinking about Innovation
This category includes companies that show moderate commitment to innovation. Or, we can say this category includes firms that are now starting to take innovation seriously. Looking at the possibilities and advantages, they may start thinking/exploring innovation as part of their mission statement.
Talk but no Action
Such companies do understand the importance and criticality of innovation. However, still, they are not focused on it and lack either the capacity or the commitment. And they do not pursue the course further.
Unintentional Innovation
Such companies do not demonstrate any commitment to innovation but still are able to come up with a new product or service. Or, we can say that such companies have the ability to innovate, but they lack the commitment. The innovation comes up as a secondary act. And by choice, also such companies do not internally consider that they can be or they are innovators.
Average at Everything
This category includes firms that show a moderate commitment and have a moderate capacity to create innovation. Such companies exhibit a good potential to become great innovators going ahead. If results in one of such innovations far exceed their expectations. Either vast publicity or a windfall gain changes their perspective towards innovation.
Potential Stars
This category includes firms that show a great deal of commitment and possess the capability to innovate. Such companies set aside a great deal of resources for innovation. Also, they have the talent to develop a novel idea and convert it into a reality. So such companies, over a period, achieve adulthood in innovation though they are at the starting stage today.
Effortless Innovators
This category includes firms that are great at creating innovations. Such firms may not exhibit a robust commitment to innovate, but that is only because they already have proper functioning systems in place. Here the innovation remains a part of their operational philosophy, and the systems are so well placed that the innovation becomes a routine. Or comes up in an auto mode.
Unconscious Stars
This category comprises companies that possess a great deal of capacity to innovate but exhibit only moderate commitment. Since they show moderate commitment, they do not set aside a large portion of their capital towards innovation. Such an atmosphere only inspires employees to better their products or service rather than revolutionize them.
World-Class Innovators
Such a category represents companies that show a high commitment and have all the capacity to come up with the best and unique product and service.

