Meaning and Definition
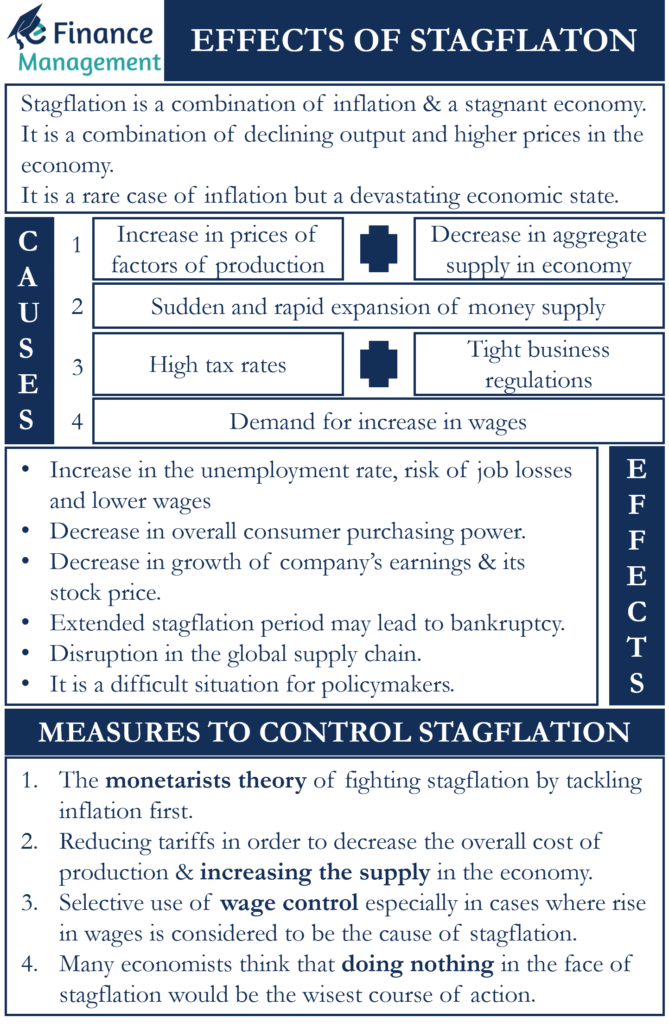
Stagflation is an economic situation where an economy faces a combination of inflation and a stagnant economy. Inflation refers to an increase in the prices of goods and services and a stagnant economy refers to a declining economy where the demand for goods and services decreases leading to high unemployment. Therefore, it is a combination of declining output and higher prices in the economy. It is a rare case of inflation but a devastating economic state.
During such times, the economy operates in crisis mode. The prices of goods and services increase while economic growth declines and the unemployment rate rises in the economy. It is very difficult to control stagflation and the economy may go through an extended period of recession or depression before recovery.
Causes of Stagflation
The following are the reasons which can cause a state of stagflation in the economy:
- A decrease of aggregate supply in the economy because of an increase in the prices of factors of production. For example, raw materials or energy required for production.
- A combination of high tax rates and tight business regulations imposed by the government in the economy.
- Monetarists’ theory believes that the reason for stagflation is the sudden and rapid expansion of the money supply in the economy.
- The demand for an increase in wages in the economy.
Any of the above-mentioned reasons or a combination of them may lead to a situation of stagflation in the economy.
Stagflation Example in the USA
Stagflation is believed to have first occurred in America. During the economic crisis of the 1970s USA experienced inflation while going through a recession. The main cause behind this state of the economy was considered to be the increase of money supply in the economy along with the strategy of wage and price control.
The inflation rate breached double digits and the unemployment rate more than doubled in the economy. It had a very adverse effect on the supply chain in all major sectors of the economy. A fall was witnessed in aggregate demand and supply of the economy which meant a lower growth rate along with a higher price level. Thus, resulting in stagflation.
Also Read: Inflation
Effect on Economy and Business
The following are the various effects of stagflation and the numerous ways in which it can negatively impact the economy:
- Stagflation can lead to an increase in the unemployment rate in the economy. This increases the risk of job losses and lower wages. Hence, decreasing the overall consumer purchasing power in the economy.
- Investors are also adversely affected because of the decrease in the growth of the company’s earnings. This impacts the share price of the company on the stock exchange. An extended period of stagflation may lead to businesses going bankrupt which can lead to massive financial losses for the investors.
- It also impacts international trade further disrupting the global supply chain as a result of the rise in prices of all commodities in the economy, including food and crude oil. The possibility of a rise in inflation increases in such cases.
- Stagflation impacts businesses greatly, especially small businesses. Businesses often face labor disruptions because of the demand for higher wage rates by the workers due to an increase in the price level, which employers cannot afford because of a fall in overall demand and sales in the economy. It causes many businesses to shut down which leads to a further increase in the unemployment rate in the economy.
- It is also a difficult situation for policymakers because actions to increase aggregate demand to restore full employment will also increase the price level even more. Conversely, a decision by policymakers to fight inflation by decreasing aggregate demand will decrease GDP even further.
Measures to Control Stagflation
The following are the ways on deciding how to respond to stagflation.
Monetarists Theory
The monetarists’ theory of fighting stagflation is to tackle inflation first. The first step is to use monetary policy to control inflation. Even if that leads to a rise in the unemployment rate and a decrease in economic growth in the short run.
Supply-Side
Fiscal and monetary policies can be used for reducing tariffs in order to decrease the overall cost of production in the economy. This helps in increasing business efficiency and overall supply in the economy.
Wage Control
Wage control is used selectively, especially in cases where the rise in wage prices is considered to be the cause of stagflation. This helps in reducing the overall cost of production and helps in controlling inflation.
Waiting
Many economists think that doing nothing in the face of stagflation would be the wisest course of action. The problem can occasionally go away with time, but attempts to do so may trigger recessions with sharp drops in GDP.

